Related Research Articles

GnaeusMarcius Coriolanus was a Roman general who is said to have lived in the 5th century BC. He received his toponymic cognomen "Coriolanus" following his courageous actions during a Roman siege of the Volscian city of Corioli. He was subsequently exiled from Rome, and led troops of Rome's enemy the Volsci to besiege the city.
Ferentina was the patron goddess of the city Ferentinum, Latium. She was protector of the Latin commonwealth. She was also closely associated with the Roman Empire.
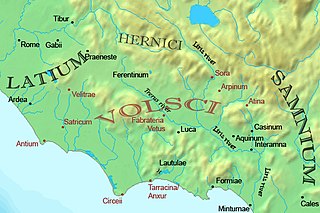
The Volsci were an Italic tribe, well known in the history of the first century of the Roman Republic. At the time they inhabited the partly hilly, partly marshy district of the south of Latium, bounded by the Aurunci and Samnites on the south, the Hernici on the east, and stretching roughly from Norba and Cora in the north to Antium in the south. Rivals of Rome for several hundred years, their territories were taken over by and assimilated into the growing republic by 300 BC. Rome's first emperor Augustus was of Volscian descent.

The Hernici were an Italic tribe of ancient Italy, whose territory was in Latium between the Fucine Lake and the Sacco River (Trerus), bounded by the Volsci on the south, and by the Aequi and the Marsi on the north.
Agrarian laws were laws among the Romans regulating the division of the public lands, or ager publicus. In its broader definition, it can also refer to the agricultural laws relating to peasants and husbandmen, or to the general farming class of people of any society.

Cori is a city and comune in the province of Latina, in the Lazio region of central Italy.
The Roman conquest of the Hernici, an ancient Italic people, took place during the 4th century BC. For most of the 5th century BC, the Roman Republic had been allied with the other Latin states and the Hernici to successfully fend off the Aequi and the Volsci. In the early 4th century BC, this alliance fell apart. A war fought between Rome and the Hernici in the years 366–358 BC ended in Roman victory and the submission of the Hernici. Rome also defeated a rebellion by some Hernician cities in 307–306 BC. The rebellious Hernici were incorporated directly into the Roman Republic, while those who had stayed loyal retained their autonomy and nominal independence. In the course of the following century, the Hernici became indistinguishable from their Latin and Roman neighbours and disappeared as a separate people.

Ecetra was a town of the ancient Volsci tribe of central Italy. Its location is no longer known.
The Roman–Sabine wars were a series of wars during the early expansion of ancient Rome in central Italy against their northern neighbours, the Sabines. It is commonly accepted that the events pre-dating the Roman Republic in 509 BC are semi-legendary in nature.
The Roman-Aequian wars were a series of wars during the early expansion of ancient Rome in central Italy against their eastern neighbours, the Aequi.
Manius Valerius Maximus was Roman dictator in 494 BC during the first secession of the plebs. His brothers were Publius Valerius Publicola and Marcus Valerius Volusus. They were said to be the sons of Volesus Valerius.
Longula was a town in ancient times in the territory of the Volsci in central Italy. It was located south of Rome, and just north of the Volscian capital Antium.
Lavici was an ancient town of Latium in central Italy, located near modern Colonna.
Pedum was an ancient town of Latium in central Italy, located between Tibur and Praeneste, near modern Gallicano nel Lazio. The town was a member of the Latin League.
Quintus Fabius Vibulanus was an aristocrat of the Early Roman republic. He was the first of three brothers to hold the consulate, in both 485 and 482 BC.
Lucius Aemilius Mamercus was a Roman statesman who served as consul three times: in 484, 478 and 473 BC.
Servius Sulpicius Camerinus Cornutus was a Roman politician in the 5th century BC, consul in 461 BC and decemvir in 451 BC.
Titus Veturius Geminus Cicurinus was a Roman politician of the 5th century BC, consul in 462 BC and maybe decemvir in 451 BC.
Lucius Lucretius Tricipitinus was a Roman senator in the fifth century BC, and was consul with Titus Veturius Geminus Cicurinus in 462 BC.
Marcus Valerius Poplicola was a politician of the Roman Republic who served as magister equitum under the dictator Gaius Sulpicius Peticus in 358 and as consul in 355 and 353 BC.
References
- ↑ Antonio Nibby (1837). Analisi storico-topografico-antiquaria della carta de'dintorni di Roma. pp. 748–.
- ↑ Livy, Ab urbe condita , 2.33
- ↑ Livy, Ab urbe condita , 2.39