Related Research Articles

Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions that aspirin is used to treat include Kawasaki disease, pericarditis, and rheumatic fever.
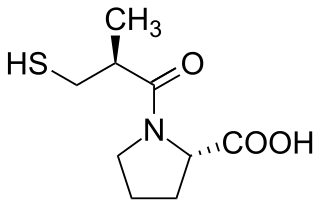
Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors are a class of medication used primarily for the treatment of high blood pressure and heart failure. This class of medicine works by causing relaxation of blood vessels as well as a decrease in blood volume, which leads to lower blood pressure and decreased oxygen demand from the heart.

Statins are a class of medications that reduce illness and mortality in people who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease.
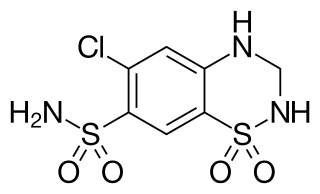
Hydrochlorothiazide, sold under the brand name Hydrodiuril among others, is a diuretic medication used to treat hypertension and swelling due to fluid build-up. Other uses include treating diabetes insipidus and renal tubular acidosis and to decrease the risk of kidney stones in those with a high calcium level in the urine. Hydrochlorothiazide is taken by mouth and may be combined with other blood pressure medications as a single pill to increase effectiveness. Hydrochlorothiazide is a thiazide medication which inhibits reabsorption of sodium and chloride ions from the distal convoluted tubules of the kidneys, causing a natriuresis. This initially increases urine volume and lowers blood volume. It is believed to reduce peripheral vascular resistance.
Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension. Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke, heart failure, kidney failure and myocardial infarction. Evidence suggests that reduction of the blood pressure by 5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34% and of ischaemic heart disease by 21%, and can reduce the likelihood of dementia, heart failure, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. There are many classes of antihypertensives, which lower blood pressure by different means. Among the most important and most widely used medications are thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEis), angiotensin II receptor blockers or antagonists (ARBs), and beta blockers.

Atorvastatin is a statin medication used to prevent cardiovascular disease in those at high risk and to treat abnormal lipid levels. For the prevention of cardiovascular disease, statins are a first-line treatment. It is taken by mouth.
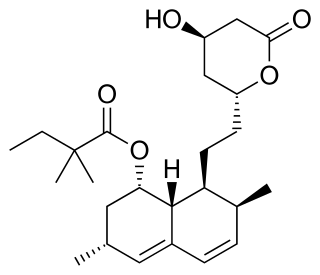
Simvastatin, sold under the brand name Zocor among others, is a statin, a type of lipid-lowering medication. It is used along with exercise, diet, and weight loss to decrease elevated lipid levels. It is also used to decrease the risk of heart problems in those at high risk. It is taken by mouth.

Fluvastatin is a member of the statin drug class, used to treat hypercholesterolemia and to prevent cardiovascular disease.
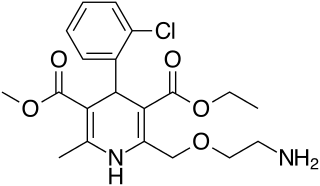
Amlodipine, sold under the brand name Norvasc among others, is a calcium channel blocker medication used to treat high blood pressure, coronary artery disease (CAD) and variant angina. It is taken orally.
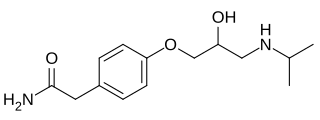
Atenolol is a beta blocker medication primarily used to treat high blood pressure and heart-associated chest pain. Although used to treat high blood pressure, it does not seem to improve mortality in those with the condition. Other uses include the prevention of migraines and treatment of certain irregular heart beats. It is taken orally or by intravenous injection. It can also be used with other blood pressure medications.

Chlortalidone, also known as chlorthalidone, is a thiazide-like diuretic drug used to treat high blood pressure, swelling, diabetes insipidus, and renal tubular acidosis. Because chlortalidone is effective in most patients with high blood pressure, it is considered a preferred initial treatment. It is also used to prevent calcium-based kidney stones. It is taken by mouth. Effects generally begin within three hours and last for up to three days. Long-term treatment with chlortalidone is more effective than hydrochlorothiazide for prevention of heart attack or stroke.
A polypill or single pill combination (SPC) is a type of drug combination consisting of a single drug product in pill form and thus combines multiple medications. The prefix "poly" means "multiple", referring to the multiplicity of distinct drugs in a given "pill". In precise usage, a pill is a polypill if it contains at least 4 drugs. An occasional synonym is combopill. A polypill commonly targets treatment or prevention of chronic conditions.
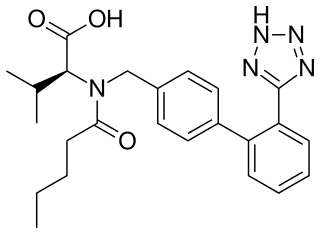
Valsartan, sold under the brand name Diovan among others, is a medication used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and diabetic kidney disease. It belongs to a class of medications referred to as angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). It is a reasonable initial treatment for high blood pressure. It is taken by mouth.

Perindopril is a medication used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, or stable coronary artery disease. As a long-acting ACE inhibitor, it works by relaxing blood vessels and decreasing blood volume. As a prodrug, perindopril is hydrolyzed in the liver to its active metabolite, perindoprilat. It was patented in 1980 and approved for medical use in 1988.

Nebivolol is a beta blocker used to treat high blood pressure and heart failure. As with other β-blockers, it is generally a less preferred treatment for high blood pressure. It may be used by itself or with other blood pressure medication. It is taken by mouth.

Vorapaxar is a thrombin receptor antagonist based on the natural product himbacine, discovered by Schering-Plough and developed by Merck & Co.

Laropiprant (INN) was a drug used in combination with niacin to reduce blood cholesterol that is no longer sold, due to increases in side-effects with no cardiovascular benefit. Laropiprant itself has no cholesterol lowering effect, but it reduces facial flushes induced by niacin.

Valsartan/hydrochlorothiazide, sold under the brand name Diovan HCT among others, is a medication used to treat high blood pressure when valsartan is not sufficient. It is a combination of valsartan, an angiotensin receptor blocker with hydrochlorothiazide, a diuretic. It is taken by mouth.
The PolyIran study is a pragmatic open-labeled randomized trial being conducted within Golestan cohort study (GCS) on 31000 subjects in 305 villages of Golestan Province, northeastern Iran. The pill used in this study namely "Polypill", has been successfully evaluated in a pilot study and consists of 4 components. It is estimated to decrease the death rate due to myocardial infarction and stroke by 30-53%. Participants were enrolled in the study during February 2011 and April 2013. The study will directly evaluate the effect of Polypill tablets on cardiovascular death and hospitalizations compared to lifestyle modification during 5 years of follow-up; unlike most of the studies that only investigate the impact of Polypill on indirect surrogate markers of cardiovascular diseases such as blood pressure or lipid profile. The study includes three arms. The first and largest arm are being just followed and receive no particular care other than care provided by the governmental health system in Iran. The second arm receive recommendations about a healthy lifestyle in face-to-face interviews and pamphlets, undergo blood pressure measurements in 6 months regular intervals, and are referred to secondary or tertiary medical centers for treatment upon necessity(minimal care arm). The third arm receive Polypill once daily in addition to the care provided to the minimal care arm. In case of a substantial decrease in mortality in Polypill arm at the end of the study, Polypill might be offered to all individuals above 50 years old as a cheap preventive alternative for cardiovascular diseases.
Bempedoic acid, sold under the brand name Nexletol among others, is a medication for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia.
References
- ↑ New England Journal of Medicine
- ↑ Yusuf, Salim; Joseph, Philip; Dans, Antonio; Gao, Peggy; Teo, Koon; Xavier, Denis; López-Jaramillo, Patricio; Yusoff, Khalid; Santoso, Anwar; Gamra, Habib; Talukder, Shamim (2020-11-13). "Polypill with or without Aspirin in Persons without Cardiovascular Disease". New England Journal of Medicine. 384 (3): 216–228. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2028220. ISSN 0028-4793. PMC 7116860 . PMID 33186492.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Marchione, Marilynn via Associated Press . "Study says one combo pill does work of five", The Record (Bergen County) , March 31, 2009. Accessed March 31, 2009.
- 1 2 "One Pill to Treat Them All: Polycap Strategy Sees Success in TIPS-3". TCTMD.com. Retrieved 2020-12-02.
- ↑ Yusuf, Salim & Pais, Prem & Sigamani, Alben & Xavier, Denis & Afzal, Rizwan & Gao, Peggy & Teo, Koon. (2012). Comparison of Risk Factor Reduction and Tolerability of a Full-Dose Polypill (With Potassium) Versus Low-Dose Polypill (Polycap) in Individuals at High Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases The Second Indian Polycap Study (TIPS-2) Investigators. Circulation. Cardiovascular quality and outcomes. 5. 463-71. 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.111.963637.
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT00443794 for "The Indian POLYCAP Study (TIPS)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ Xavier, Denis; Pais, Prem; Sigamani, Alben; Pogue, Janice; Afzal, Rizwan; Yusuf, Salim (2008). "The need to test the theories behind the Polypill: Rationale behind the Indian Polycap Study". Nature Clinical Practice Cardiovascular Medicine. 6 (2): 96–97. doi:10.1038/ncpcardio1438. PMID 19104516. S2CID 26305238.
- 1 2 3 Patel, Anil; Shah, Tarang; Shah, Gaurang; Jha, Vijay; Ghosh, Chinmoy; Desai, Jagruti; Khamar, Bakulesh; Chakraborty, Bhaswat S (2010). "Preservation of Bioavailability of Ingredients and Lack of Drug-Drug Interactions in a Novel Five-Ingredient Polypill (Polycap™)". American Journal of Cardiovascular Drugs. 10 (2): 95–103. doi:10.2165/11532170-000000000-00000. PMID 20334446. S2CID 31754902.