| Polyvinyl esters: General formula |
|---|
 (R = CH3; CH2Cl; C2H5 etc.) |
Polyvinyl esters are a group of thermoplastic vinyl polymers. The most important examples of this group are polyvinyl acetate (PVAC) and polyvinyl propionate. [1]
| Polyvinyl esters: General formula |
|---|
 (R = CH3; CH2Cl; C2H5 etc.) |
Polyvinyl esters are a group of thermoplastic vinyl polymers. The most important examples of this group are polyvinyl acetate (PVAC) and polyvinyl propionate. [1]
The radical polymerization of vinyl ester 1 (e.g. in case of vinyl acetate; R = CH3) yields polyvinyl ester 2:

The transparent polymers are used for the production of lacquers and as adhesives. [1] The hydrolytic cleavage of the ester bonds of vinyl acetate is of industrial significance. [2]

In chemistry, an ester is a chemical compound derived from an acid in which at least one –OH (hydroxyl) group is replaced by an –O–alkyl (alkoxy) group. Usually, esters are derived from substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides, which are fatty acid esters of glycerol, are important esters in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids, and making up the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils. Esters with low molecular weight are commonly used as fragrances and found in essential oils and pheromones. Phosphoesters form the backbone of DNA molecules. Nitrate esters, such as nitroglycerin, are known for their explosive properties, while polyesters are important plastics, with monomers linked by ester moieties. Esters usually have a sweet smell and are considered high-quality solvents for a broad array of plastics, plasticizers, resins, and lacquers. They are also one of the largest classes of synthetic lubricants on the commercial market.

Petrochemicals are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable sources such as maize, palm fruit or sugar cane.

An acetate is a salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with a base. "Acetate" also describes the conjugate base or ion typically found in aqueous solution and written with the chemical formula C
2H
3O−
2. The neutral molecules formed by the combination of the acetate ion and a positive ion are also commonly called "acetates". The simplest of these is hydrogen acetate with corresponding salts, esters, and the polyatomic anion CH
3CO−
2, or CH
3COO−
.
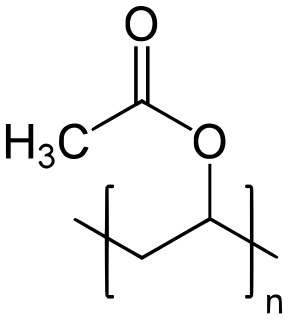
Polyvinyl acetate (PVA, PVAc, poly(ethenyl ethanoate): best known as wood glue, white glue, carpenter's glue, school glue, Elmer's glue in the US, or PVA glue) is an aliphatic rubbery synthetic polymer with the formula (C4H6O2)n. It belongs to the polyvinyl ester family, with the general formula -[RCOOCHCH2]-. It is a type of thermoplastic.

Polyvinyl fluoride (PVF) or –(CH2CHF)n– is a polymer material mainly used in the flammability-lowering coatings of airplane interiors and photovoltaic module backsheets. It is also used in raincoats and metal sheeting. Polyvinyl fluoride is a thermoplastic fluoropolymer with the repeating vinyl fluoride unit:

Poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVOH, PVA, or PVAl) is a water-soluble synthetic polymer. It has the idealized formula [CH2CH(OH)]n. It is used in papermaking, textile warp sizing, as a thickener and emulsion stabilizer in PVAc adhesive formulations and a variety of coatings. It is colourless (white) and odorless. It is commonly supplied as beads or as solutions in water.
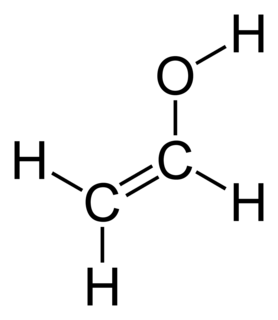
Vinyl alcohol, also called ethenol (IUPAC name), is the simplest enol. With the formula CH2CHOH, it is a labile compound that converts to acetaldehyde. It is not a precursor to polyvinyl alcohol.

Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), also known as poly (PEVA), is the copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate. The weight percent of vinyl acetate usually varies from 10 to 40%, with the remainder being ethylene. There are three different types of EVA copolymer, which differ in the vinyl acetate (VA) content and the way the materials are used.

Hair spray is a common cosmetic hairstyling product that is sprayed onto hair to protect against humidity and wind. Hair sprays typically consist of several components for the hair as well as a propellant.

Vinyl acetate is an organic compound with the formula CH3CO2CH=CH2. This colorless liquid is the precursor to polyvinyl acetate, an important industrial polymer.
Vinyl polymers are a group of polymers derived from vinyl monomers of the type CH2=CHR. Their backbone is an extended alkane chain ...-CH2-CHR-CH2-CHR-..). In popular usage, "vinyl" refers only to polyvinyl chloride (PVC).

In organic chemistry an enol ether is an alkene with an alkoxy substituent. The general structure is R2C=CR-OR where R = H, alkyl or aryl. A common subfamily of enol ethers are vinyl ethers, with the formula ROCH=CH2. Important enol ethers include the reagent 3,4-dihydropyran and the monomers methyl vinyl ether and ethyl vinyl ether.
Polyvinyl is a group of polymers derived from vinyl monomers.
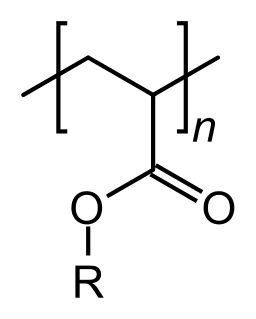
Acrylate polymers are a group of polymers prepared from acrylate monomers. These plastics are noted for their transparency, resistance to breakage, and elasticity. They are also commonly known as acrylics or polyacrylates. Acrylate polymer is commonly used in cosmetics, such as nail polish, as an adhesive.
Polyvinyl nitrate (PVN) is a polymeric explosive material, an ester of nitric acid and polyvinyl alcohol. It has the idealized formula [CH2CHNO2 ]n. It is prepared by nitration of polyvinyl alcohol or transesterification of polyvinyl acetate. It is a thermoplastic substance with softening zone between 30-45 °C, depending on the molecular weight of the starting polyvinyl alcohol.

Flubber, Glorp, Glurch, or Slime are common names referring to a rubbery polymer formed by cross-linking of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) with a boron compound. Flubber can be made by combining polyvinyl-acetate-based adhesives such as Elmer's Glue with baking soda, borax, and (optionally) shaving cream as an elementary science education experiment.

A polymeric foam is a foam, in liquid or solidified form, formed from polymers.
Methyl vinyl ether is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3OCH=CH2. A colorless gas, it is the simplest enol ether. It is used as a synthetic building block, as is the related compound ethyl vinyl ether (a liquid at room temperature).
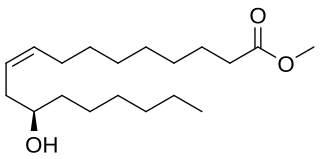
Methyl ricinoleate is a clear, viscous fluid that is used as a surfactant, cutting fluid additive, lubricant, and plasticizer. It is a plasticizer for cellulosic resins, polyvinyl acetate, and polystyrene. It is a type of fatty acid methyl ester synthesized from castor oil and methyl alcohol.
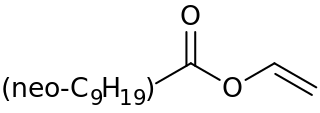
Vinyl neodecanoate is a vinylic monomer that is virtually always used in combination with other monomers to create lattices or emulsion polymers. The trade name is an acronym of Vinyl ester of Versatic Acid with the number 10 meaning 10 carbons in the molecule. It has a medium to low glass transition temperature of -3 °C. Chemically, it is a mixture of isomeric vinyl esters of neodecanoic acid.