In chemistry, a monomer is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
In polymer chemistry, polymerization, or polymerisation, is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many forms of polymerization and different systems exist to categorize them.

Polyvinyl chloride (alternatively: poly(vinyl chloride), colloquial: polyvinyl, or simply vinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic polymer of plastic (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of PVC are produced each year.

Tacticity is the relative stereochemistry of adjacent chiral centers within a macromolecule. The practical significance of tacticity rests on the effects on the physical properties of the polymer. The regularity of the macromolecular structure influences the degree to which it has rigid, crystalline long range order or flexible, amorphous long range disorder. Precise knowledge of tacticity of a polymer also helps understanding at what temperature a polymer melts, how soluble it is in a solvent and its mechanical properties.
A Ziegler–Natta catalyst, named after Karl Ziegler and Giulio Natta, is a catalyst used in the synthesis of polymers of 1-alkenes (alpha-olefins). Two broad classes of Ziegler–Natta catalysts are employed, distinguished by their solubility:

Petrochemicals are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable sources such as maize, palm fruit or sugar cane.

Polyethylene or polythene (abbreviated PE; IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most commonly produced plastic. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging (plastic bags, plastic films, geomembranes and containers including bottles, etc.). As of 2017, over 100 million tonnes of polyethylene resins are being produced annually, accounting for 34% of the total plastics market.

A thermoplastic, or thermosoftening plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling.

Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene.

Vinyl chloride is an organochloride with the formula H2C=CHCl. It is also called vinyl chloride monomer (VCM) or chloroethene. This colorless compound is an important industrial chemical chiefly used to produce the polymer, poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC). Vinyl chloride monomer is among the top twenty largest petrochemicals (petroleum-derived chemicals) in world production. The United States remains the largest vinyl chloride manufacturing region because of its low-production-cost position in chlorine and ethylene raw materials. China is also a large manufacturer and one of the largest consumers of vinyl chloride. Vinyl chloride is a flammable gas that has a sweet odor and is carcinogenic. It can be formed in the environment when soil organisms break down chlorinated solvents. Vinyl chloride that is released by industries or formed by the breakdown of other chlorinated chemicals can enter the air and drinking water supplies. Vinyl chloride is a common contaminant found near landfills. Before the 1970s, vinyl chloride was used as an aerosol propellant and refrigerant.
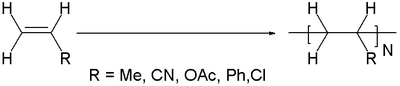
In polymer chemistry, an addition polymer is a polymer that forms by simple linking of monomers without the co-generation of other products. Addition polymerization differs from condensation polymerization, which does co-generate a product, usually water. Addition polymers can be formed by chain polymerization, when the polymer is formed by the sequential addition of monomer units to an active site in a chain reaction, or by polyaddition, when the polymer is formed by addition reactions between species of all degrees of polymerization. Addition polymers are formed by the addition of some simple monomer units repeatedly. Generally polymers are unsaturated compounds like alkenes, alkalines etc. The addition polymerization mainly takes place in free radical mechanism. The free radical mechanism of addition polymerization completed by three steps i.e. Initiation of free radical, Chain propagation, Termination of chain.

Chain-growth polymerization (AE) or chain-growth polymerisation (BE) is a polymerization technique where unsaturated monomer molecules add onto the active site on a growing polymer chain one at a time. There are a limited number of these active sites at any moment during the polymerization which gives this method its key characteristics.
Coordination polymerisation is a form of polymerization that is catalyzed by transition metal salts and complexes.
A polyolefin is a type of polymer with the general formula (CH2CHR)n where R is an alkyl group. They are usually derived from a small set of simple olefins (alkenes). Dominant in a commercial sense are polyethylene and polypropylene. More specialized polyolefins include polyisobutylene and polymethylpentene. They are all colorless or white oils or solids. Many copolymers are known, such as polybutene, which derives from a mixture of different butene isomers. The name of each polyolefin indicates the olefin from which it is prepared; for example, polyethylene is derived from ethylene, and polymethylpentene is derived from 4-methyl-1-pentene. Polyolefins are not olefins themselves because the double bond of each olefin monomer is opened in order to form the polymer. Monomers having more than one double bond such as butadiene and isoprene yield polymers that contain double bonds (polybutadiene and polyisoprene) and are usually not considered polyolefins. Polyolefins are the foundations of many chemical industries.
In polymer chemistry, a repeat unit or repeating unit is a part of a polymer whose repetition would produce the complete polymer chain by linking the repeat units together successively along the chain, like the beads of a necklace.

Commodity plastics or commodity polymers are plastics produced in high volumes for applications where exceptional material properties are not needed. In contrast to engineering plastics, commodity plastics tend to be inexpensive to produce and exhibit relatively weak mechanical properties. Some examples of commodity plastics are polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, polyvinyl chloride, and poly(methyl methacrylate) .Globally, the most widely used thermoplastics include both polypropylene and polyethylene. Products made from commodity plastics include disposable plates, disposable cups, photographic and magnetic tape, clothing, reusable bags, medical trays, and seeding trays.

In polymer chemistry photo-oxidation is the degradation of a polymer surface due to the combined action of light and oxygen. It is the most significant factor in the weathering of plastics. Photo-oxidation causes the polymer chains to break, resulting in the material becoming increasingly brittle. This leads to mechanical failure and, at an advanced stage, the formation of microplastics. In textiles the process is called phototendering.

A polymeric foam is a special foam, in liquid or solidified form, formed from polymers.
Living cationic polymerization is a living polymerization technique involving cationic propagating species. It enables the synthesis of very well defined polymers and of polymers with unusual architecture such as star polymers and block copolymers and living cationic polymerization is therefore as such of commercial and academic interest.