
The Serengeti National Park is a large national park in northern Tanzania that stretches over 14,763 km2 (5,700 sq mi). It is located in eastern Mara Region and northeastern Simiyu Region and contains over 1.5 million ha of virgin savanna. The park was established in 1940.

The Zambezi is the fourth-longest river in Africa, the longest east-flowing river in Africa and the largest flowing into the Indian Ocean from Africa. Its drainage basin covers 1,390,000 km2 (540,000 sq mi), slightly less than half of the Nile's. The 2,574 km (1,599 mi) river rises in Zambia and flows through eastern Angola, along the north-eastern border of Namibia and the northern border of Botswana, then along the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe to Mozambique, where it crosses the country to empty into the Indian Ocean.

Etosha National Park is a national park in northwestern Namibia and one of the largest national parks in Africa. It was proclaimed a game reserve in March 1907 in Ordinance 88 by the Governor of German South West Africa, Friedrich von Lindequist. It was designated as Wildschutzgebiet in 1958, and was awarded the status of national park in 1967, by an act of parliament of the Republic of South Africa. It spans an area of 22,270 km2 (8,600 sq mi) and was named after the large Etosha pan which is almost entirely within the park. With an area of 4,760 km2 (1,840 sq mi), the Etosha pan covers 23% of the total area of the national park. The area is home to hundreds of species of mammals, birds and reptiles, including several threatened and endangered species such as the black rhinoceros. Sixty-one black rhinoceros were killed during poaching in Namibia during 2022, 46 of which were killed in Etosha.

The Zambezi Region is one of Namibia's fourteen regions, situated in the north-eastern part of the country along the Zambezi River. The region's capital is Katima Mulilo. The Katima Mulilo Airport is 18 kilometres south-west of the town, while the village of Bukalo is located 43 kilometres south-east of Katima Mulilo. Known as the Caprivi Region until 2013, it has eight electoral constituencies and a population of 142,373 according to the 2023 census.

The Okavango River, is a river in southwest Africa. It is known by this name in Botswana, and as Cubango in Angola, and Kavango in Namibia. It is the fourth-longest river system in southern Africa, running southeastward for 1,600 km (1,000 mi). It begins at an elevation of 1,300 metres (4,300 ft) in the sandy highlands of Angola. Farther south, it forms part of the border between Angola and Namibia, and then flows into Botswana. The Okavango does not have an outlet to the sea. Instead, it discharges into the Okavango Delta or Okavango Alluvial Fan, in an endorheic basin in the Kalahari Desert. The Cuito River is a major tributary.

The Okavango Delta in Botswana is a vast inland delta formed where the Okavango River reaches a tectonic trough at an altitude of 930–1,000 m in the central part of the endorheic basin of the Kalahari Desert.

Samburu National Reserve is a game reserve on the banks of the Ewaso Ng'iro river in Kenya. It is 165 km2 (64 sq mi) in size and is 350 km (220 mi) from Nairobi. It ranges in elevation from 800 to 1,230 m. Geographically and administratively, it is part of Samburu County.

Simlipal National Park is a national park and tiger reserve in the Mayurbhanj district in the Indian state of Odisha covering 2,750 km2 (1,060 sq mi). It is part of the Mayurbhanj Elephant Reserve, which includes three protected areas, Similipal Tiger Reserve, Hadgarh Wildlife Sanctuary with 191.06 km2 (73.77 sq mi) and Kuldiha Wildlife Sanctuary with 272.75 km2 (105.31 sq mi). Simlipal National Park derives its name from the abundance of red silk cotton trees growing in the area.

Epupa Falls is a series of large waterfalls formed by the Cunene River on the border of Angola and Namibia, in the Kaokoland area of the Kunene Region. The river is about 0.5 kilometres (1,600 ft) wide in this area and drops in a series of waterfalls across a length of 1.5 kilometres (0.93 mi), with the greatest single drop being 37 metres (121 ft). The settlement near the falls is also called Epupa.

The wildlife of Zimbabwe occurs foremost in remote or rugged terrain, in national parks and private wildlife ranches, in miombo woodlands and thorny acacia or kopje. The prominent wild fauna includes African buffalo, African bush elephant, black rhinoceros, southern giraffe, African leopard, lion, plains zebra, and several antelope species.

The wildlife of Ivory Coast consists of the flora and fauna of this nation in West Africa. The country has a long Atlantic coastline on the Gulf of Guinea and a range of habitat types. Once covered in tropical rainforest, much of this habitat has been cleared, the remaining terrain being gallery forests and savanna with scattered groups of trees, resulting in a decrease in biodiversity. As of 2016, 252 species of mammal had been recorded in Ivory Coast, 666 species of bird, 153 species of reptile, 80 species of amphibian, 671 species of fish and 3660 species of vascular plant.

The wildlife of South Africa consists of the flora and fauna of this country in Southern Africa. The country has a range of different habitat types and an ecologically rich and diverse wildlife, vascular plants being particularly abundant, many of them endemic to the country. There are few forested areas, much savanna grassland, semi-arid Karoo vegetation and the fynbos of the Cape Floristic Region. Famed for its national parks and big game, 297 species of mammal have been recorded in South Africa, as well as 849 species of bird and over 20,000 species of vascular plants.

The wildlife of Zambia refers to the natural flora and fauna of Zambia. This article provides an overview, and outline of the main wildlife areas or regions, and compact lists of animals focusing on prevalence and distribution in the country rather than on taxonomy. More specialized articles on particular groups are linked from here.

The wildlife of Pakistan comprises a diverse flora and fauna in a wide range of habitats from sea level to high elevation areas in the mountains, including 195 mammal, 668 bird species and more than 5000 species of Invertebrates. This diverse composition of the country's fauna is associated with its location in the transitional zone between two major zoogeographical regions, the Palearctic, and the Oriental. The northern regions of Pakistan, which include Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Gilgit Baltistan include portions of two biodiversity hotspot, Mountains of Central Asia and Himalayas.
Divundu is a village on the south-eastern banks of the Okavango River in the Kavango East Region of Namibia, 200 kilometres (120 mi) east of Rundu. Divundu has a population of around 5,430 inhabitants and is the homestead of the local Hambukushu kings.

Bwabwata National Park is a protected area in northeastern Namibia that was established in 2007 and covers 6,274 km2 (2,422 sq mi). It was created by merging Namibia's Caprivi Game Park and Mahango Game Park. It is situated in the Zambezi and Kavango East regions, extending along the Caprivi Strip. It is bounded by the Okavango River to the west and the Kwando River to the east. Angola lies to the north and Botswana to the south.

Mudumu is a National Park in Caprivi Region of north-eastern Namibia. Established in 1990, the park covers an area of 737 square kilometres (285 sq mi). The Kwando River forms the western border with Botswana. Various communal area conservancies and community forests surround Mudumu National Park.
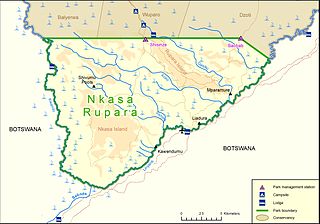
Nkasa Rupara National Park, also Nkasa Lupala National Park, formerly Mamili National Park, is a national park in Namibia. It is centered on the Nkasa and Rupara islands on the Kwando/Linyanti River in the south-western corner of East Caprivi. Botswana lies to the west, south and east, and Sangwali village to the north. It is Namibia's largest formally protected wetland area. It is one of Namibia’s protected areas that benefits local communities surrounding parks. The unfenced park forms a trans-boundary link for wildlife migration between Angola, Botswana, Namibia and Zambia. Nkasa Rupara is part of the Kavango Zambezi Transfrontier Conservation Area.
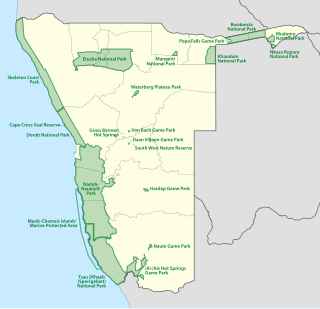
The protected areas of Namibia include its national parks and reserves. With the 2010 declaration of Dorob National Park, Namibia became the first and only country to have its entire coastline protected through a national parks network. Protected areas are subdivided into game reserves and/or nature reserves, such as special protected area, wilderness areas, natural areas, and development areas. There are also recreation reserves. Facilities in the national parks are operated by Namibia Wildlife Resorts. Over 19% of Namibia is protected, an area of some 130,000 square kilometres. However, the Ministry of Environment & Tourism auctions limited hunting rights within its protected areas. The Namibia Nature Foundation, an NGO, was established in 1987 to raise and administer funds for the conservation of wildlife and protected area management. Communal Wildlife Conservancies in Namibia help promote sustainable natural resource management by giving local communities rights to wildlife management and tourism.

The Mahango Game Park is a protected area in Namibia within Bwabwata National Park. It is situated at the country's eastern border with Botswana in the flood plains of the Okavango River basin, close to the Popa Falls on the river. The Caprivi Strip encloses the western part of the park. It was established in 1986 and covers an area of 24,462 hectares. With over 300 species of birds, it has been designated an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International. About two thirds of the bird species found in Namibia are located here as it includes both wetland and tropical terrestrial species of birds.



















