
South West Africa, renamed to Namibia from 12 June 1968 was a territory under South African administration from 1915 to 1990, after which it became modern-day Namibia. It bordered Angola, Botswana, South Africa, and Zambia. During its administration, South Africa applied its own apartheid system in the territory of South West Africa.

Hardap is one of the fourteen regions of Namibia, its capital is Mariental. Hardap contains the municipality of Mariental, the towns Rehoboth and Aranos, and the self-governed villages Gibeon, Gochas, Kalkrand, Stampriet and Maltahöhe. It is home to the Hardap Dam.

The Basters are a Southern African ethnic group descended from Cape Coloureds and Nama of Khoisan origin. Since the second half of the 19th century, the Rehoboth Baster community has been concentrated in central Namibia, in and around the town of Rehoboth. Basters are closely related to Afrikaners, Cape Coloureds, and Griquas of South Africa and Namibia, with whom they share a language and culture. They are also related to the local Nama, with the Rehoboth Basters being considered a Nama clan by many, having a "Kaptein" just like many Nama settlements in Southern Namibia.

The Damara, plural Damaran are an ethnic group who make up 8.5% of Namibia's population. They speak the Khoekhoe language and the majority live in the northwestern regions of Namibia, however they are also found widely across the rest of the country.

Rehoboth is a town in central Namibia just north of the Tropic of Capricorn. Located 90 kilometres south of the Namibian capital Windhoek, Rehoboth lies on a high elevation plateau with several natural hot-water springs. It receives sparse mean annual rainfall of 240 millimetres (9.4 in), although in the 2010/2011 rainy season a record 731 millimetres (28.8 in) were measured. In 2005, it had a population of 21,378 later increased to 28,843 in 2011, according to the 2011 Namibian Population and Housing Census. In 2023, it had increased further to 40,788 people.

Rehoboth was a homeland in South West Africa intended by the apartheid-era government to be a self-governing homeland for the Baster people in the area around the town of Rehoboth.

Waterberg Plateau Park is a national park in central Namibia on the Waterberg Plateau, 68 kilometres (42 mi) south-east of Otjiwarongo. The plateau and the national park are named after the prominent table mountain that rises from the plateau, the Waterberg. The Waterberg Plateau is a particularly prominent landmark, elevating high above the plains of the Kalahari of Eastern Namibia. Waterberg Park and some 405 square kilometres (156 sq mi) of surrounding land were declared a Nature Reserve in 1972. As the plateau is largely inaccessible from beneath, several of Namibia's endangered animal species were relocated into the area during the early 1970s to protect them from predators and poaching to extinction. The programme was very successful and Waterberg now supplies other Namibian parks with rare animals. In 1989, the black rhinoceros was reintroduced to the area from Damaraland.

The Brandberg is Namibia's highest mountain.
Marotandrano Special Reserve is a wildlife reserve in Mandritsara, Sofia Region, Madagascar. It is 10 km from Marotandrano and 42 km from Mandritsara.
Hermanus Christoffel Beukes was a Coloured Namibian politician and activist. Beukes was a frequent petitioner of the United Nations because of Apartheid South Africa's actions while Namibia was held under its mandate.

The Gamsberg is a mountain in the Appenzell Alps, overlooking the region of Walenstadt in the canton of St. Gallen. Located in the Alvier group it is the culminating point of the range lying between Lake Walenstadt and Toggenburg.

Pioneers Park is a suburb in the south of Windhoek, Namibia, in the Windhoek West parliamentary constituency. It was developed in the second half of the 20th century as a white community, with the previous black residents being expelled to Katutura. The suburb is mainly residential, but also contains the main campus of the University of Namibia. Other local facilities include a cemetery and the Catholic Church of St. Boniface, built in 1928, which is now a national monument.
Naukluft Mountain Zebra Park is a protected reserve of Namibia. It is located south of Gamsberg Nature Reserve, northwest of Hardap Game Reserve and north of Namib-Naukluft National Park.

Rietoog is a settlement in the Hardap Region of Namibia. It is situated 112 kilometres (70 mi) southwest of Rehoboth and 130 kilometres (81 mi) north of Maltahöhe along the M47 gravel road and belongs to the Rehoboth Rural electoral constituency. The name Rietoog means Cane-eye in Afrikaans, named after a spring that looks like an eye, surrounded by canes, near the town.
Ghaamsberg is a mountain in South Africa. situated just east of Aggeneys, in the Namakwa District Municipality of the Northern Cape province, 33 km to the south of the border with Namibia. Its summit is 1148 metres above sea level.

The Swedish-ESO Submillimetre Telescope (SEST) is a 15-metre diameter radio telescope. It was originally located at the La Silla Observatory in Chile, and will be moved to Africa and repurposed as the Africa Millimetre Telescope.
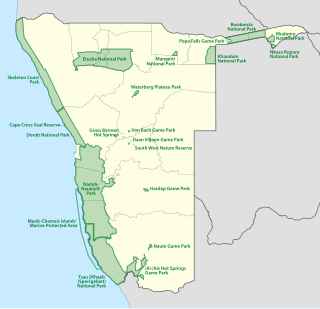
The protected areas of Namibia include its national parks and reserves. With the 2010 declaration of Dorob National Park, Namibia became the first and only country to have its entire coastline protected through a national parks network. Protected areas are subdivided into game reserves and/or nature reserves, such as special protected area, wilderness areas, natural areas, and development areas. There are also recreation reserves. Facilities in the national parks are operated by Namibia Wildlife Resorts. Over 19% of Namibia is protected, an area of some 130,000 square kilometres. However, the Ministry of Environment & Tourism auctions limited hunting rights within its protected areas. The Namibia Nature Foundation, an NGO, was established in 1987 to raise and administer funds for the conservation of wildlife and protected area management. Communal Wildlife Conservancies in Namibia help promote sustainable natural resource management by giving local communities rights to wildlife management and tourism.
The Hoarusib River is an ephemeral river in the Kunene Region of north-western Namibia. Its source is near the regional capital Opuwo, and the river flows through the Tonnesen and Giraffe Mountains into the Atlantic Ocean. The Hoarusib occasionally carries surface water during the rainy season from November to February/March. The catchment area of the Hoarusib is 15,237 square kilometres (5,883 sq mi).

The geology of Namibia encompasses rocks of Paleoproterozoic, Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic and Paleozoic to Cenozoic age. About 46% of the countryʼs surface are bedrock exposure, while the remainder is covered by the young overburden sediments of the Kalahari and Namib deserts.
















