Related Research Articles
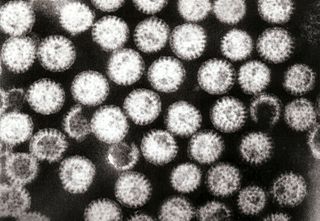
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin with loss of the normal stretchiness of the skin and irritable behaviour. This can progress to decreased urination, loss of skin color, a fast heart rate, and a decrease in responsiveness as it becomes more severe. Loose but non-watery stools in babies who are exclusively breastfed, however, are normal.
Classical swine fever (CSF) or hog cholera is a highly contagious disease of swine. It has been mentioned as a potential bioweapon.
Porcine circoviral disease (PCVD) and porcine circovirus associated disease (PCVAD), is a disease seen in domestic pigs. This disease causes illness in piglets, with clinical signs including progressive loss of body condition, visibly enlarged lymph nodes, difficulty in breathing, and sometimes diarrhea, pale skin, and jaundice. PCVD is very damaging to the pig-producing industry and has been reported worldwide. PCVD is caused by Porcine circovirus 2 (PCV-2).
Porcine parvovirus (PPV), a virus in the species Ungulate protoparvovirus 1 of genus Protoparvovirus in the virus family Parvoviridae, causes reproductive failure of swine characterized by embryonic and fetal infection and death, usually in the absence of outward maternal clinical signs. The disease develops mainly when seronegative dams are exposed oronasally to the virus anytime during about the first half of gestation, and conceptuses are subsequently infected transplacentally before they become immunocompetent. There is no definitive evidence that infection of swine other than during gestation is of any clinical or economic significance. The virus is ubiquitous among swine throughout the world and is enzootic in most herds that have been tested. Diagnostic surveys have indicated that PPV is the major infectious cause of embryonic and fetal death. In addition to its direct causal role in reproductive failure, PPV can potentiate the effects of porcine circovirus type II (PCV2) infection in the clinical course of postweaning multisystemic wasting syndrome (PMWS).
Pale, soft, exudative meat, or PSE meat, describes a carcass quality condition known to occur in pork, beef, and poultry. It is characterized by an abnormal color, consistency, and water holding capacity, making the meat dry and unattractive to consumers. The condition is believed to be caused by abnormal muscle metabolism following slaughter, due to an altered rate of glycolysis and a low pH within the muscle fibers. A mutation point in the ryanodine receptor gene (RYR1) in pork, associated to stress levels prior to slaughter are known to increase the incidence of PSE meat. Although the term "soft" may look positive, it refers to raw meat. When cooked, there is higher cook loss and the final product is hard, not juicy.
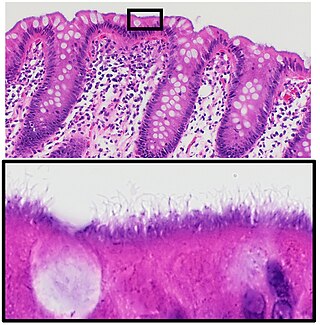
Human intestinal spirochetosis, often called just intestinal spirochetosis when the human context is implicit, is an infection of the colonic-type mucosa with certain species of spirochetal bacteria. Similar infections sometimes occur in pigs, dogs, and birds; porcine intestinal spirochaetosis is an economically important disease of livestock.
Bovine Adenovirus, also known as BAdV, is a member of the Adenoviridae family that causes disease in cattle. There are 10 serotypes recognised and the virus had a worldwide distribution—being particularly common in Africa and Central America.
Brachyspira pilosicoli is a gram-negative, anaerobic, host-associated spirochete that colonizes the intestinal tract of animals and humans. It appears as a characteristic "false brush border" due to its end-on attachment to enterocytes of the colon where it interferes with intestinal absorption. B. pilosicoli is unique from other Brachyspira species because it colonizes a variety of domestic animals including pigs, chickens, dogs, wild birds, rodents, and humans. It is the causative agent of intestinal spirochetosis in pigs, chickens and humans. In particular, B. pilosicoli has been described as an important colonic pathogen of pigs and chickens, causing colitis and diarrhea resulting in depressed rates of growth and impaired production on farms where infections with B. pilosicoli may be endemic. Bacterial attachment disrupts the colonic enterocytes and associated villi, causing the symptoms characteristic of intestinal spirochetosis. Additionally, B. pilosicoli is associated with clinical disease in human infections where it has implications for public health.

Cardiovirus A is a member of the Picornaviridae family. Infection with the virus causes encephalomyocarditis and reproductive disease in pigs. Although a variety of mammals may host the virus, pigs are classed as the domestic host as they are most easily infected. It is thought to be spread by rodents.
Inclusion body rhinitis (IBR), or cytomegalic inclusion disease, is a pig disease caused by Suid betaherpesvirus 2 (SuHV-2), which is a member of the herpesvirus family. It is a notifiable disease that is found worldwide. It is spread both vertically and horizontally and prevalence is high.
Mycoplasma hyorhinis is a species of bacteria in the Mycoplasmataceae family. It is often found as a commensal in the respiratory tract of pigs, and rarely in the skin of humans. M. hyorhinis is thought to facilitate and exacerbate the development of diseases such as porcine enzootic pneumonia and porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS). Rarely, it may cause mycoplasma arthritis, mycoplasmal polyserositis or mycoplasma septicaemia in piglets without the involvement of other bacteria. This presents as polyarthritis or polyserositis.
Porcine adenovirus is a virus in the family Adenoviridae. It causes mild gastrointestinal diseases in pigs and is thought to contribute to multifactorial porcine respiratory diseases complexes. Several strains of the virus can be found worldwide, and transmission occurs horizontally by the fecal-oral route.
Blue eye disease is caused by La Piedad Michoacán Mexico virus (LPMV), the only member virus of the species Porcine orthorubulavirus in the Paramyxoviridae family. Synonyms for the disease include "Blue Eye Syndrome" and "Porcine Paramyxovirus Blue Eye Disease", and "La Piedad Michoacán Paramyxovirus Infection".
Porcine enzootic pneumonia, also known as mycoplasmal pneumonia, is a chronic respiratory disease of pigs caused by Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae.
Porcine epidemic diarrhea is a condition caused by the porcine epidemic diarrhea virus that leads to severe gastrointestinal disease in pigs.
Brachyspira is a genus of bacteria classified within the phylum Spirochaetota.

Gastrodiscoides is genus of zoonotic trematode under the class Trematoda. It has only one species, Gastrodiscoides hominis. It is a parasite of a variety of vertebrates, including humans. The first definitive specimen was described from a human subject in 1876. It is prevalent in Bangladesh, India, Burma, China, Kazakhstan, Philippines, Thailand, Vietnam, and the Volga Delta of Russia, with isolated cases from Africa, such as Nigeria. It is especially notable in the Assam, Bengal, Bihar, Madhya Pradesh, Orissa and Uttar Pradesh regions of India.
Amphistomiasis is a parasitic disease of livestock animals, more commonly of cattle and sheep, and humans caused by immature helminthic flatworms belonging to the order Echinostomida. The term amphistomiasis is used for broader connotation implying the disease inflicted by members of Echinostomida including the family Paramphistomidae/Gastrodiscidae ; whereas paramphistomiasis is restricted to that of the members of the family Paramphistomatidae only. G. discoides and Watsonius watsoni are responsible for the disease in humans, while most paramphistomes are responsible in livestock animals, and some wild mammals. In livestock industry the disease causes heavy economic backlashes due to poor production of milk, meat and wool.
Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, respiratory pathogen found in pigs. It was first reported in 1957, and was formally declared to be the causative agent of porcine pleuropneumonia in 1964. It was reclassified in 1983 after DNA studies showed it was more closely related to A. lignieresii.
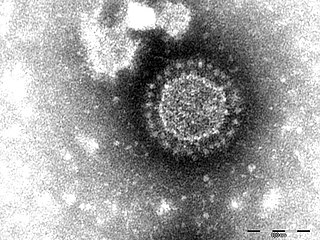
Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus is a coronavirus that infects the cells lining the small intestine of a pig, causing porcine epidemic diarrhoea, a condition of severe diarrhea and dehydration. Older hogs mostly get sick and lose weight after being infected, whereas newborn piglets usually die within five days of contracting the virus. PEDV cannot be transmitted to humans, nor contaminate the human food supply.
References
- Porcine Intestinal Spirochaetosis, reviewed and published by WikiVet at http://en.wikivet.net/Porcine_Intestinal_Spirochaetosis, accessed 19/09/2011.