
Stromatolites or stromatoliths are layered sedimentary formations (microbialite) that are created mainly by photosynthetic microorganisms such as cyanobacteria, sulfate-reducing bacteria, and Pseudomonadota. These microorganisms produce adhesive compounds that cement sand and other rocky materials to form mineral "microbial mats". In turn, these mats build up layer by layer, growing gradually over time.

Cyanobacteria, also called Cyanobacteriota or Cyanophyta, are a phylum of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via photosynthesis. The name 'cyanobacteria' refers to their color, which similarly forms the basis of cyanobacteria's common name, blue-green algae, although they are not scientifically classified as algae. They appear to have originated in a freshwater or terrestrial environment.

A reef is a ridge or shoal of rock, coral, or similar relatively stable material lying beneath the surface of a natural body of water. Many reefs result from natural, abiotic (non-living) processes such as deposition of sand or wave erosion planing down rock outcrops. However, reefs such as the coral reefs of tropical waters are formed by biotic (living) processes, dominated by corals and coralline algae. Artificial reefs, such as shipwrecks and other man-made underwater structures, may occur intentionally or as the result of an accident. These are sometimes designed to increase the physical complexity of featureless sand bottoms to attract a more diverse range of organisms. Reefs are often quite near to the surface, but not all definitions require this.

Coccoliths are individual plates or scales of calcium carbonate formed by coccolithophores and cover the cell surface arranged in the form of a spherical shell, called a coccosphere.

Stromatoporoidea is an extinct clade of sea sponges common in the fossil record from the Middle Ordovician to the Late Devonian. They can be characterized by their densely layered calcite skeletons lacking spicules. Stromatoporoids were among the most abundant and important reef-builders of their time, living close together in flat biostromes or elevated bioherms on soft tropical carbonate platforms.

Receptaculites is the name-bearing genus for an extinct group of conspicuous benthic marine genera, the receptaculitids, that lived from the Early Ordovician through the Permian period, peaking in the Middle Ordovician. The group's phylogenetic origin has long been obscure, with some arguing that they were calcareous algae, probably of the order Dasycladales. Receptaculitids lived in warm, shallow seas, but consensus disagreeing. They have been described from all continents except Antarctica. In some areas they were important reef-formers, and they also occur as isolated specimens.

Oncolites are sedimentary structures composed of oncoids, which are layered structures formed by cyanobacterial growth. Oncolites are very similar to stromatolites, but, instead of forming columns, they form approximately spherical structures. The oncoids often form around a central nucleus, such as a shell fragment, and a calcium carbonate structure is deposited by encrusting microbes. Oncolites are indicators of warm waters in the photic zone, but are also known in contemporary freshwater environments. These structures rarely exceed 10 cm in diameter.

Thrombolites are clotted accretionary structures formed in shallow water by the trapping, binding, and cementation of sedimentary grains by biofilms of microorganisms, especially cyanobacteria.
Girvanella is a fossil thought to represent the calcified sheath of a filamentous cyanobacterium known from the Burgess Shale and other Cambrian fossil deposits.
The extinct genus Hedstroemia was once thought to be a rivulariacean cyanobacterium. It forms oval blobs composed of sinuous tubes that have rounded outlines and occurs in conjunction with Solenopora.
Rothpletzella is a genus of calcimicrobe known from the Silurian of Gotland, the Devonian of France, as well as the Ordovician of China. It has been hypothesised to be a cyanobacterium, and shares morphological similarities with extant cyanobacteria. The genus is named in honor of August Rothpletz.
Wetheredella is a genus of calcimicrobes initially described from the Silurian of England, and subsequently reported from the Upper Ordovician to the end of the Carboniferous periods; its reefs are stated as being characteristic of the Ordovician-Silurian periods. Its taxonomic position is uncertain; it has been suggested to be a foraminiferan, a cyanobacterium or simply treated as a microproblematicum; Vachard & Cózar (2010) refer it to the Algospongia, a similarly controversial group that they assigned to the Protista but later, per Vachard, 2021, to Algae incertae sedis, in its own family and suborder (Wetheredellina) in the order Moravamminida. The genus is named in honor of the geologist Edward Wethered.

The Barberton Greenstone Belt of eastern South Africa contains some of the most widely accepted fossil evidence for Archean life. These cell-sized prokaryote fossils are seen in the Barberton fossil record in rocks as old as 3.5 billion years. The Barberton Greenstone Belt is an excellent place to study the Archean Earth due to exposed sedimentary and metasedimentary rocks.

The Laborcita Formation is a geologic formation in the Sacramento Mountains of New Mexico. It preserves fossils dating back to the late Pennsylvanian to early Permian.

Sphaerocodium is a fossil that represents the remains of bacteria in the phylum Cyanobacteria, often called blue-green algae.

Marine biogenic calcification is the production of calcium carbonate by organisms in the global ocean.
Proaulopora is a Cambrian–Ordovician fossil genus of calcareous algae. It has been variously thought to belong to the green algae, red algae or cyanobacteria. It was originally established by the Russian paleontologist Aleksandr Grigoryevich Vologdin in 1937, for species known from the Lower Cambrian of the western Altai Mountains.
"Spongiostromata" is an antiquated form taxon that refers primarily to fossil cyanobacteria. "Spongiostromate" is also used to describe stromatolites and oncolites that do not preserve clear tubules or other cellular microstructure.
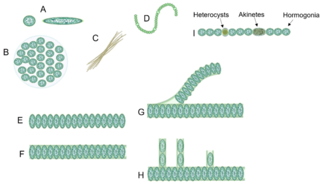
Cyanobacterial morphology refers to the form or shape of cyanobacteria. Cyanobacteria are a large and diverse phylum of bacteria defined by their unique combination of pigments and their ability to perform oxygenic photosynthesis.
Beresellaceae is an extinct family of organisms of uncertain affinity, sometimes placed within the Metazoa, but tentatively assigned to the green alga order Dasycladales. Beresellids were cosmopolitan and their fossils are found in strata ranging in age from the late Devonian to the early Permian.











