
An electrical insulator is a material in which electric current does not flow freely. The atoms of the insulator have tightly bound electrons which cannot readily move. Other materials—semiconductors and conductors—conduct electric current more easily. The property that distinguishes an insulator is its resistivity; insulators have higher resistivity than semiconductors or conductors. The most common examples are non-metals.

Zip-cord is a type of electrical cable with two or more conductors held together by an insulating jacket that can be easily separated simply by pulling apart. In Australia it is known as 'figure-8' cable. The zip-cord term is also used with optical fiber cables consisting of two optical fibers joined in a similar manner. The design of zip-cord makes it easy to keep conductors that carry related electrical or optical signals together and helps avoid tangling of cables. Typical uses include lamp cord and speaker wire. Conductors may be identified by a color tracer on the insulation, or by a ridge molded into the insulation of one wire, or by a colored tracer thread inside the insulation. Zip cords are intended for use on portable equipment, and the US and Canadian electrical codes do not permit their use for permanently installed wiring of line-voltage circuits.
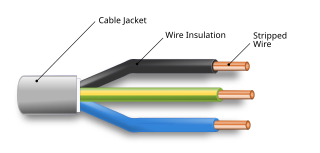
An electrical cable is an assembly of one or more wires running side by side or bundled, which is used as an electrical conductor, i.e., to carry electric current. One or more electrical cables and their corresponding connectors may be formed into a cable assembly, which is not necessarily suitable for connecting two devices but can be a partial product. Cable assemblies can also take the form of a cable tree or cable harness, used to connect many terminals together.

A thermoplastic, or thermosoftening plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling.

IEC 60320 Appliance couplers for household and similar general purposes is a set of standards from the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) specifying non-locking connectors for connecting power supply cords to electrical appliances of voltage not exceeding 250 V (a.c.) and rated current not exceeding 16 A. Different types of connector are specified for different combinations of current, temperature and earthing requirements. Unlike IEC 60309 connectors, they are not coded for voltage; users must ensure that the voltage rating of the equipment is compatible with the mains supply. The standard uses the term coupler to encompass connectors on power cords and power inlets and outlets built into appliances.
Electrical wiring in North America follows the regulations and standards applicable at the installation location. It is also designed to provide proper function, and is also influenced by history and traditions of the location installation.

Electrical wiring is an electrical installation of cabling and associated devices such as switches, distribution boards, sockets, and light fittings in a structure.

An extension cord (US), extension cable, power extender, drop cord, or extension lead (UK) is a length of flexible electrical power cable (flex) with a plug on one end and one or more sockets on the other end. The term usually refers to mains extensions but is also used to refer to extensions for other types of cabling. If the plug and power outlet are of different types, the term "adapter cord" may be used. Most extension cords range from around 2 to 30 feet in length although they are made up to 300 feet (91.44 m) in length.

A power cable is an electrical cable, an assembly of one or more electrical conductors, usually held together with an overall sheath. The assembly is used for transmission of electrical power. Power cables may be installed as permanent wiring within buildings, buried in the ground, run overhead, or exposed. Power cables that are bundled inside thermoplastic sheathing and that are intended to be run inside a building are known as NM-B.
EPDM rubber is a type of synthetic rubber that is used in many applications. Dienes used in the manufacture of EPDM rubbers are ethylidene norbornene (ENB), dicyclopentadiene (DCPD), and vinyl norbornene (VNB). 4-8% of these monomers are typically used.

Heat-shrink tubing is a shrinkable plastic tube used to insulate wires, providing abrasion resistance and environmental protection for stranded and solid wire conductors, connections, joints and terminals in electrical wiring. It can also be used to repair the insulation on wires or to bundle them together, to protect wires or small parts from minor abrasion, and to create cable entry seals, offering environmental sealing protection. Heat-shrink tubing is ordinarily made of polyolefin, which shrinks radially when heated, to between one-half and one-sixth of its diameter.

Speaker wire is used to make the electrical connection between loudspeakers and audio amplifiers. Modern speaker wire consists of two or more electrical conductors individually insulated by plastic or, less commonly, rubber. The two wires are electrically identical, but are marked to identify the correct audio signal polarity. Most commonly, speaker wire comes in the form of zip cord.

Mineral-insulated copper-clad cable is a variety of electrical cable made from copper conductors inside a copper sheath, insulated by inorganic magnesium oxide powder. The name is often abbreviated to MICC or MI cable, and colloquially known as pyro. A similar product sheathed with metals other than copper is called mineral-insulated metal-sheathed (MIMS) cable.
A thermoplastic-sheathed cable (TPS) consists of a toughened outer sheath of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) thermoplastic, covering one or more individual annealed copper conductors, themselves insulated with PVC. This type of wiring is commonly used for residential and light commercial construction in many countries. The flat version of the cable, with two insulated conductors and an uninsulated earth conductor, is referred to as twin and earth. In mainland Europe, a round equivalent is more common.

A stage pin connector, also known as a grounded stage pin (GSP), grounded pin connector (GPC) or theater paddle (TP), is a standard cable type for theatrical lighting in North America and in many countries in the theatre world.

Tough rubber-sheathed cable is a type of cable which normally consists of a black outer sheath of rubber with several conductors inside. The rubber provides an abrasion-resistant, corrosion-resistant, waterproof, protective covering for an insulated electric cable.
Thermoplastic vulcanizates (TPV) are dynamically vulcanized alloys consisting mostly of fully cured EPDM rubber particles encapsulated in a polypropylene (PP) matrix. They are part of the thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) family of polymers but are closest in elastomeric properties to EPDM thermoset rubber, combining the characteristics of vulcanized rubber with the processing properties of thermoplastics. There are almost 100 grades in the S portfolio that are used globally in the automotive, household appliance, electrical, construction, and healthcare markets. The name Santoprene was trademarked in 1977 by Monsanto, and the trademark is now owned by Celanese. Similar material is available from Elastron and others.

Plastic pipe is a tubular section, or hollow cylinder, made of plastic. It is usually, but not necessarily, of circular cross-section, used mainly to convey substances which can flow—liquids and gases (fluids), slurries, powders and masses of small solids. It can also be used for structural applications; hollow pipes are far stiffer per unit weight than solid members.
Tri-rated cable is a high temperature, flame retardant electrical wire designed for use inside electrical equipment.

A high-voltage cable is a cable used for electric power transmission at high voltage. A cable includes a conductor and insulation. Cables are considered to be fully insulated. This means that they have a fully rated insulation system that will consist of insulation, semi-con layers, and a metallic shield. This is in contrast to an overhead line, which may include insulation but not fully rated for operating voltage. High-voltage cables of differing types have a variety of applications in instruments, ignition systems, and alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) power transmission. In all applications, the insulation of the cable must not deteriorate due to the high-voltage stress, ozone produced by electric discharges in air, or tracking. The cable system must prevent contact of the high-voltage conductor with other objects or persons, and must contain and control leakage current. Cable joints and terminals must be designed to control the high-voltage stress to prevent the breakdown of the insulation.
















