Related Research Articles

China is the second most-populous country in the world and Asia with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, only surpassed by India. Historically, China has always been one of the nation-states with the most population.

Sociology of religion is the study of the beliefs, practices and organizational forms of religion using the tools and methods of the discipline of sociology. This objective investigation may include the use both of quantitative methods and of qualitative approaches.

The United States had an official estimated resident population of 335,893,238 on Jan 1, 2024, according to the U.S. Census Bureau. This figure includes the 50 states and Washington, D.C. but excludes the population of five unincorporated U.S. territories as well as several minor island possessions. The United States is the third most populous country in the world, and the most populous in the Americas and the Western Hemisphere. The Census Bureau showed a population increase of 0.4% for the twelve-month period ending in July 2022, below the world average annual rate of 0.9%. The total fertility rate in the United States estimated for 2022 is 1.665 children per woman, which is below the replacement fertility rate of approximately 2.1. By several metrics, including racial and ethnic background, religious affiliation, and percentage of rural and urban divide, Illinois is the most representative of the larger demography of the United States.
Andrew M. Greeley was an American Catholic priest, sociologist, journalist and popular novelist. He was a professor of sociology at the University of Arizona and the University of Chicago, and a research associate with the National Opinion Research Center (NORC).
Religion in the United States is both widespread and diverse, with higher reported levels of belief than other wealthy Western nations. Polls indicate that an overwhelming majority of Americans believe in a higher power (2021), engage in spiritual practices (2022), and consider themselves religious or spiritual (2017).

American Jews or Jewish Americans are American citizens who are Jewish, whether by culture, ethnicity, or religion. According to a 2020 poll conducted by Pew Research, approximately two thirds of American Jews identify as Ashkenazi, 3% identify as Sephardic, and 1% identify as Mizrahi. An additional 6% identify as some combination of the three categories, and 25% do not identify as any particular category.

Between 2015 and 2060, Muslim population is projected to increase by 70%, from 1.76 billion to 3 billion. This compares with the 32% growth of world population during the same period.
The Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA) is a free source of online information related to American and international religion. One of the primary goals of the archive is to democratize access to academic information on religion by making this information as widely accessible as possible. Over 900 surveys, membership reports, and other data collections are currently available for online preview, and most can be downloaded free of charge. Other features include national profiles, GIS maps, church membership overviews, denominational heritage trees, historical timelines, tables, charts, and other summary reports.
Accurate demographics of atheism are difficult to obtain since conceptions of atheism vary considerably across different cultures and languages, ranging from an active concept to being unimportant or not developed. Also in some countries and regions atheism carries a strong stigma, making it harder to count atheists in these countries. In global studies, the number of people without a religion is usually higher than the number of people without a belief in a deity and the number of people who agree with statements on lacking a belief in a deity is usually higher than the number of people who self-identify as "atheists".
Reverse racism, sometimes referred to as reverse discrimination, is the concept that affirmative action and similar color-conscious programs for redressing racial inequality are forms of anti-white racism. The concept is often associated with conservative social movements, and reflects a belief that social and economic gains by Black people and other people of color cause disadvantages for white people.
Growth of religion involves the spread of individual religions and the increase in the numbers of religious adherents around the world. In sociology, desecularization is the proliferation or growth of religion, most commonly after a period of previous secularization. Statistics commonly measure the absolute number of adherents, the percentage of the absolute growth per-year, and the growth of converts in the world.

Atheism, agnosticism, scepticism, freethought, secular humanism or general irreligion are increasing in Australia. Post-war Australia has become a highly secularised country. Religion does not play a major role in the lives of much of the population.
In the United States, between 4% and 15% of citizens demonstrated nonreligious attitudes and naturalistic worldviews, namely atheists or agnostics. The number of self-identified atheists and agnostics was around 4% each, while many persons formally affiliated with a religion are likewise non-believing.
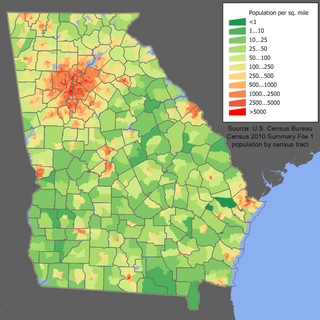
Georgia is a South Atlantic U.S. state with a population of 10,711,908 according to the 2020 United States census, or just over 3% of the U.S. population. The majority of the state's population is concentrated within Metro Atlanta, although other highly populated regions include: West Central and East Central Georgia; West, Central, and East Georgia; and Coastal Georgia; and their Athens, Columbus, Macon and Warner Robins, Augusta, Savannah, Hinesville, and Brunswick metropolitan statistical areas.
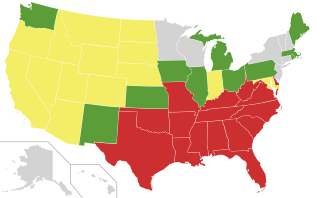
Interracial marriage has been legal throughout the United States since at least the 1967 U.S. Supreme Court decision Loving v. Virginia (1967) that held that anti-miscegenation laws were unconstitutional via the 14th Amendment adopted in 1868. Chief Justice Earl Warren wrote in the court opinion that "the freedom to marry, or not marry, a person of another race resides with the individual, and cannot be infringed by the State." Interracial marriages have been formally protected by federal statute through the Respect for Marriage Act since 2022.

Elaine Howard Ecklund is a published author and professor of sociology at Rice University. She is also the director of the Boniuk Institute for Religious Tolerance at Rice, a Rice Scholar at the James A. Baker III Institute for Public Policy, and the president of the Religious Research Association. Her research focuses on institutional change in the areas of religion, immigration, science, medicine, and gender.

Church attendance is a central religious practice for many Christians; some Christian denominations require church attendance on the Lord's Day (Sunday). The Canon Law of the Catholic Church states, "on Sundays and other holy days of obligation, the faithful are bound to participate in the Mass". The Westminster Confession of Faith is held by the Reformed Churches and teaches first-day Sabbatarianism and the duty of church attendance on this day. Similarly, the General Rules of the Methodist Church also requires "attending upon all the ordinances of God" including "the public worship of God". The Lutheran Christian theologian Balthasar Münter stated that church attendance is the "foundation for the Christian life" as "the Christian Bible and the sacraments provide the framework for the faith"; he also states that it is important for believers because it aids in the prevention of backsliding, as well as offers "the company of other believers". Until 1791, it was a legal requirement in the Kingdom of Great Britain to attend services of the Church of England at least twice a year.
The relationship between the level of religiosity and the level of education has been studied since the second half of the 20th century.

The demographics of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints include statistical data relating to the church's population and particular groups within it.
References
- ↑ "Portraits of American Life Study Overview". Association of Religion Data Archives. Retrieved 1 September 2016.
- ↑ "Re-contact Strategy, 2008". Association of Religion Data Archives. Retrieved 1 September 2016.
- ↑ Briggs, David (19 December 2013). "U.S. Racial Gap Widens, Prospects for Reconciliation dim". Huffington Post. Retrieved 1 September 2016.
- ↑ McCaig, Amy (28 June 2013). "Rice U. Portraits of American Life Study: Americans more respectful of religious traditions". Rice University. Retrieved 1 September 2016.
- ↑ Perry, Samuel L. (6 April 2016). "Does Viewing Pornography Diminish Religiosity Over Time? Evidence From Two-Wave Panel Data". The Journal of Sex Research. 54 (2): 214–226. doi:10.1080/00224499.2016.1146203. PMID 27049348. S2CID 29195396.
- ↑ Weiss, Suzannah (13 May 2016). "Watching Porn Makes People More Religious, Study Suggests". Complex. Retrieved 1 September 2016.
- ↑ Sigalow, Emily; Shain, Michelle; Bergey, Meredith R. (June 2012). "Religion and Decisions About Marriage, Residence, Occupation, and Children". Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion. 51 (2): 304–323. doi:10.1111/j.1468-5906.2012.01641.x.
- ↑ Scribner, Herb (2 October 2013). "Religion carries weight in decisions about marriage and kids". Deseret News. Archived from the original on October 9, 2013. Retrieved 1 September 2016.