Marxism–Leninism is a political philosophy that seeks to establish a socialist state to develop further into socialism and eventually communism, a classless social system with common ownership of the means of production and with full social and economic equality of all members of society. Marxist–Leninists espouse a wide array of views depending on their understanding of orthodox Marxism and Leninism, but they generally support the idea of a vanguard party, a communist party-led state, state-dominance over the economy, internationalism and opposition to capitalism, fascism, imperialism and liberal democracy. As an ideology, it was developed by Joseph Stalin in the late 1920s based on his understanding and synthesis of both orthodox Marxism and Leninism. It was the official state ideology of the Soviet Union and the other ruling parties making up the Eastern Bloc as well as the political parties of the Communist International after Bolshevisation. Today, Marxism–Leninism is the ideology of Stalinist and Maoist political parties around the world and remains the official ideology of the ruling parties of China, Cuba, Laos and Vietnam.

The Social Democratic Party of Switzerland, also rendered as the Swiss Socialist Party, is a political party in Switzerland. The SP has had two representatives on the Swiss Federal Council since 1960 and received the second highest total number of votes in the 2019 Swiss federal election.

The 2004 Canadian federal election, was held on June 28, 2004, to elect members of the House of Commons of Canada of the 38th Parliament of Canada. The Liberal government of Prime Minister Paul Martin lost its majority, but was able to form a minority government after the elections. The main opposition party, the newly amalgamated Conservative Party of Canada, improved its position but with a showing below its expectations.

The 1988 Canadian federal election was held November 21, 1988, to elect members of the House of Commons of Canada of the 34th Parliament of Canada. It was an election largely fought on a single issue: the Canada–United States Free Trade Agreement (FTA).

The Canadian Action Party (CAP) was a Canadian federal political party founded in 1997 and deregistered on 31 March 2017.

The 1995 Ontario general election was held on June 8, 1995, to elect members of the 36th Legislative Assembly of the province of Ontario, Canada. The writs for the election were dropped on April 28, 1995.

Revolutionary Socialist Party (RSP) is a political party in India. The party was founded on 19 March 1940 and has its roots in the Bengali liberation movement Anushilan Samiti and the Hindustan Socialist Republican Army. The party got around 0.4% of the votes and three seats in the Lok Sabha elections in 1999 and 2004. It is part of the Left Front (Tripura).

Abbreviations Guide

Conservatism in Canada is generally considered to be primarily represented by the modern-day Conservative Party of Canada in federal party politics, and by various centre-right and right-wing parties at the provincial level. The first party calling itself "Conservative" in what would become Canada was elected in the Province of Canada election of 1854.
Several policies regarding interior and domestic issues in Canada were planned and adopted by the Canadian Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Stephen Harper, following the January 23, 2006 election of the Conservative Party to a minority of seats in the House of Commons, such as social and environmental policies. At the beginning of the government's appointment, five policy priorities were identified in the areas of federal accountability, tax reform, crime, child care and health care.

The Left, also commonly referred to as the Left Party, is a democratic socialist political party in Germany. The party was founded in 2007 as the result of the merger of the Party of Democratic Socialism (PDS) and Labour and Social Justice – The Electoral Alternative (WASG). Through PDS, the party is the direct descendant of the Marxist-Leninist ruling party of the former East Germany (GDR), the Socialist Unity Party of Germany (SED).

Abbreviations Guide

Abbreviations Guide
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to politics and political science:

The Communist Party of the Russian Federation is a communist political party in Russia that adheres to Marxist–Leninist philosophy. The party is often viewed as the immediate successor of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU), which was banned in 1991 by then–Russian President Boris Yeltsin after a failed coup attempt. It is the second-largest political party in the Russian Federation after United Russia. The youth organisation of the party is the Leninist Young Communist League. The party is administered by a Central Committee.

The Communist Party of Canada (Marxist–Leninist) is a Canadian federal political party founded by Hardial Bains in 1970. The CPC (ML) has been registered with Elections Canada as the Marxist–Leninist Party of Canada since 1974 as the party is prohibited from using the Communist Party name in Canadian elections to avoid confusion among voters. The party developed separately and independently from the Communist Party of Canada (CPC) with its origins among students and intellectuals in Canada during the 1960s. After a period of alignment with Maoism and China, the CPC (ML) pursued a pro-Albanian line until the early 1990s when it adopted a pro-Cuba position.
Anti-revisionism is a position within Marxism–Leninism which emerged in the 1950s in opposition to the reforms of Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev. Where Khrushchev pursued an interpretation that differed from his predecessor Joseph Stalin, the anti-revisionists within the international communist movement remained dedicated to Stalin's ideological legacy and criticized the Soviet Union under Khrushchev and his successors as state capitalist and social imperialist due to its hopes of achieving peace with the United States.
The World Socialist Movement (WSM) is an international organisation of socialist parties created in 1904 with the founding of the Socialist Party of Great Britain (SPGB).
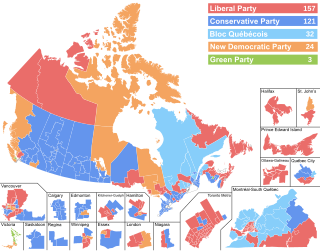
The 2019 Canadian federal election took place on Monday, 21 October 2019. Candidates have been declared for each of the 338 electoral districts or "ridings".