
Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body. For example, 18
F
-FDG is commonly used to detect cancer, NaF18
F
is widely used for detecting bone formation, and oxygen-15 is sometimes used to measure blood flow.

Single-photon emission computed tomography is a nuclear medicine tomographic imaging technique using gamma rays. It is very similar to conventional nuclear medicine planar imaging using a gamma camera, but is able to provide true 3D information. This information is typically presented as cross-sectional slices through the patient, but can be freely reformatted or manipulated as required.

Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactive substances in the diagnosis and treatment of disease. Nuclear medicine imaging, in a sense, is "radiology done inside out" or "endoradiology" because it records radiation emitting from within the body rather than radiation that is generated by external sources like X-rays. In addition, nuclear medicine scans differ from radiology, as the emphasis is not on imaging anatomy, but on the function. For such reason, it is called a physiological imaging modality. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans are the two most common imaging modalities in nuclear medicine.

Scintigraphy, also known as a gamma scan, is a diagnostic test in nuclear medicine, where radioisotopes attached to drugs that travel to a specific organ or tissue (radiopharmaceuticals) are taken internally and the emitted gamma radiation is captured by external detectors to form two-dimensional images in a similar process to the capture of x-ray images. In contrast, SPECT and positron emission tomography (PET) form 3-dimensional images and are therefore classified as separate techniques from scintigraphy, although they also use gamma cameras to detect internal radiation. Scintigraphy is unlike a diagnostic X-ray where external radiation is passed through the body to form an image.
Fluorine-18 (18F) is a fluorine radioisotope which is an important source of positrons. It has a mass of 18.0009380(6) u and its half-life is 109.771(20) minutes. It decays by positron emission 96% of the time and electron capture 4% of the time. Both modes of decay yield stable oxygen-18.
A gallium scan is a type of nuclear medicine test that uses either a gallium-67 (67Ga) or gallium-68 (68Ga) radiopharmaceutical to obtain images of a specific type of tissue, or disease state of tissue. Gallium salts like gallium citrate and gallium nitrate may be used. The form of salt is not important, since it is the freely dissolved gallium ion Ga3+ which is active. Both 67Ga and 68Ga salts have similar uptake mechanisms. Gallium can also be used in other forms, for example 68Ga-PSMA is used for cancer imaging. The gamma emission of gallium-67 is imaged by a gamma camera, while the positron emission of gallium-68 is imaged by positron emission tomography (PET).
Copper-64 (64Cu) is a positron and beta emitting isotope of copper, with applications for molecular radiotherapy and positron emission tomography. Its unusually long half (12.7-hours) for a positron-emitting isotope makes it increasingly useful when attached to various ligands, for PET and PET-CT scanning.
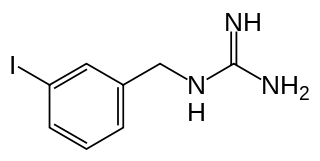
Iobenguane, or MIBG, is an aralkylguanidine analog of the adrenergic neurotransmitter, typically used as a radiopharmaceutical. It acts as a blocking agent for adrenergic neurons. When radiolabeled, it can be used in nuclear medicinal diagnostic and therapy techniques as well as in neuroendocrine chemotherapy treatments.

Positron emission tomography–computed tomography is a nuclear medicine technique which combines, in a single gantry, a positron emission tomography (PET) scanner and an x-ray computed tomography (CT) scanner, to acquire sequential images from both devices in the same session, which are combined into a single superposed (co-registered) image. Thus, functional imaging obtained by PET, which depicts the spatial distribution of metabolic or biochemical activity in the body can be more precisely aligned or correlated with anatomic imaging obtained by CT scanning. Two- and three-dimensional image reconstruction may be rendered as a function of a common software and control system.
Nuclear medicine physicians, also called nuclear radiologists, are medical specialists that use tracers, usually radiopharmaceuticals, for diagnosis and therapy. Nuclear medicine procedures are the major clinical applications of molecular imaging and molecular therapy. In the United States, nuclear medicine physicians are certified by the American Board of Nuclear Medicine and the American Osteopathic Board of Nuclear Medicine.
Avid Radiopharmaceuticals is an American company, founded by Dr. Daniel Skovronsky, and based at the University City Science Center research campus in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The company has developed a radioactive tracer called florbetapir (18F). Florbetapir can be used to detect beta amyloid plaques in patients with memory problems using positron emission tomography (PET) scans, making the company the first to bring to market an FDA-approved method that can directly detect this hallmark pathology of Alzheimer's disease.
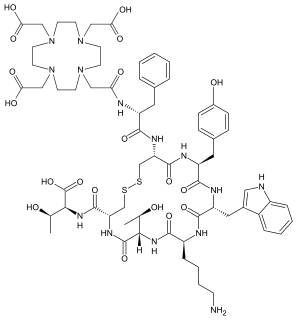
DOTA-TATE is an eight amino acid long peptide, with a covalently bonded DOTA bifunctional chelator.

Positron emission tomography–magnetic resonance imaging (PET–MRI) is a hybrid imaging technology that incorporates magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) soft tissue morphological imaging and positron emission tomography (PET) functional imaging.
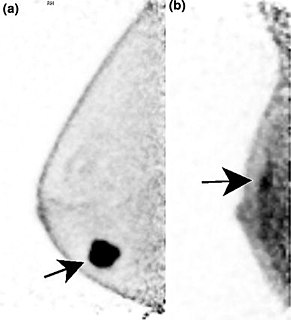
Positron emission mammography (PEM) is a nuclear medicine imaging modality used to detect or characterise breast cancer. Mammography typically refers to x-ray imaging of the breast, while PEM uses an injected positron emitting isotope and a dedicated scanner to locate breast tumors. Scintimammography is another nuclear medicine breast imaging technique, however it is performed using a gamma camera. Breasts can be imaged on standard whole-body PET scanners, however dedicated PEM scanners offer advantages including improved resolution.
Florbetapir (18F), sold under the brand name Amyvid, is a PET scanning radiopharmaceutical compound containing the radionuclide fluorine-18 that was approved for use in the United States in 2012, as a diagnostic tool for Alzheimer's disease. Florbetapir, like Pittsburgh compound B (PiB), binds to beta-amyloid, however fluorine-18 has a half-life of 109.75 minutes, in contrast to PiB's radioactive half life of 20 minutes. Wong et al. found that the longer life allowed the tracer to accumulate significantly more in the brains of people with AD, particularly in the regions known to be associated with beta-amyloid deposits.

Zynex, Inc. is a medical device manufacturer that produces and markets electrotherapy devices for use in pain management, physical rehabilitation, neurological diagnosis and cardiac monitoring. Thomas Sandgaard founded Zynex Medical in 1996.
Advanced Accelerator Applications is a pharmaceutical group specialized in the field of nuclear medicine. The group operates in all three segments of nuclear medicine to diagnose and treat serious conditions in the fields of oncology, neurology, cardiology, infectious and inflammatory diseases.

Radiopharmaceuticals, or medicinal radiocompounds, are a group of pharmaceutical drugs containing radioactive isotopes. Radiopharmaceuticals can be used as diagnostic and therapeutic agents. Radiopharmaceuticals emit radiation themselves, which is different from contrast media which absorb or alter external electromagnetism or ultrasound. Radiopharmacology is the branch of pharmacology that specializes in these agents.

18F-FMISO or fluoromisonidazole is a radiopharmaceutical used for PET imaging of hypoxia. It consists of a 2-nitroimidazole molecule labelled with the positron-emitter fluorine-18.
Sandip Basu is an Indian physician of Nuclear Medicine and the Head, Nuclear Medicine Academic Program at the Radiation Medicine Centre. He is also the Dean-Academic (Health-Sciences), BARC at Homi Bhabha National Institute and is known for his services and research in Nuclear Medicine, particularly on Positron emission tomography diagnostics and Targeted Radionuclide Therapy in Cancer. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards for his contributions to Nuclear Medicine in 2012.











