Related Research Articles

Kronosaurus is an extinct genus of large short-necked pliosaur that lived during the Aptian to Albian stages of the Early Cretaceous in what is now Australia. The first known specimen was received in 1899 and consists of a partially preserved mandibular symphysis, which was first thought to come from an ichthyosaur according to Charles De Vis. However, it was 1924 that Albert Heber Longman formally described this specimen as the holotype of an imposing pliosaurid, to which he gave the scientific name K. queenslandicus, which is still the only recognized species nowadays. The genus name, meaning "lizard of Kronos", refers to its large size and possible ferocity reminiscent of the Titan of the Greek mythology, while the species name alludes to Queensland, the Australian state of its discovery. In the early 1930s, the Harvard Museum of Comparative Zoology sent an organized expedition to Australia that recovered two specimens historically attributed to the taxon, including a well known skeleton that is now massively restored in plaster. Several attributed fossils were subsequently discovered, including two large, more or less preserved skeletons. As the holotype specimen does not present diagnostics to concretely distinguish Kronosaurus from other pliosaurids, these same two skeletons are proposed as potential neotypes for future redescriptions. Two additional species were proposed, but these are now seen as unlikely or belonging to another genus.

Pliosauroidea is an extinct clade of plesiosaurs, known from the earliest Jurassic to early Late Cretaceous. They are best known for the subclade Thalassophonea, which contained crocodile-like short-necked forms with large heads and massive toothed jaws, commonly known as pliosaurs. More primitive non-thalassophonean pliosauroids resembled plesiosaurs in possessing relatively long necks and smaller heads. They originally included only members of the family Pliosauridae, of the order Plesiosauria, but several other genera and families are now also included, the number and details of which vary according to the classification used.

The Plesiosauria or plesiosaurs are an order or clade of extinct Mesozoic marine reptiles, belonging to the Sauropterygia.
Liopleurodon is an extinct genus of carnivorous pliosaurs that lived from the Callovian stage of the Middle Jurassic to the Kimmeridgian stage of the Late Jurassic period. The taxonomic history of the animal is quite complex. The type species L. ferox, which is probably the only valid species, was erected in 1873 by Henri Émile Sauvage from a single tooth discovered near the French commune of Boulogne-sur-Mer, in Pas-de-Calais. Rather, in 1869 Harry Govier Seeley erected a species of Pliosaurus, Pliosaurus pachydeirus, based on a series of cervical vertebrae that had been discovered near the civil parish of Great Gransden, Cambridgeshire, England. In 1960, Lambert Beverly Tarlo moved this species within the genus Liopleurodon. However, its validity as a distinct species has been questioned since the beginning of the 21st century, in particular because its supposed distinctive characteristics would be in fact individual variations, suggesting that it is a probable junior synonym of L .ferox. However, identification of a neotype specimen of L. ferox is necessary to confirm whether this observation is true. Numerous fossil specimens attributed to Liopleurodon, even including numerous skeletons, have been discovered in Europe, Russia and Mexico. Other additional species were even proposed, but these are currently seen as coming from other pliosaurid genera.

Umoonasaurus is an extinct genus of plesiosaur belonging to the family Leptocleididae. This genus lived approximately 115 million years ago during the Early Cretaceous period, in shallow seas covering parts of what is now Australia. It was a relatively small animal around 2.5 metres (8.2 ft) long. An identifying trait of Umoonasaurus is three crest-ridges on its skull.

Pliosaurus is an extinct genus of thalassophonean pliosaurid known from the Late Jurassic of Europe and South America. Most European species of Pliosaurus measured around 8 metres (26 ft) long and weighed about 5 metric tons, but P. rossicus and P. funkei would have been one of the largest plesiosaurs of all time, exceeding 10 metres (33 ft) in length. This genus has contained many species in the past but recent reviews found only six to be valid, while the validity of two additional species awaits a petition to the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Currently, P. brachyspondylus and P. macromerus are considered dubious, while P. portentificus is considered undiagnostic. Species of this genus are differentiated from other pliosaurids based on seven autapomorphies, including teeth that are triangular in cross section. Their diet would have included fish, cephalopods, and marine reptiles.

Stephen Louis Brusatte FRSE is an American paleontologist and evolutionary biologist who specializes in the anatomy and evolution of dinosaurs. He was educated at the University of Chicago for his Bachelor's degree, at the University of Bristol for his Master's of Science on a Marshall Scholarship, and finally at the Columbia University for Master's in Philosophy and Doctorate. He is currently Professor of Palaeontology and Evolution at the University of Edinburgh. In April 2024, Brusatte was elected to fellowship of the Royal Society of Edinburgh.

Brachauchenius is an extinct genus of pliosaurid that lived in North America and Morocco during the Late Cretaceous.

Megalneusaurus is an extinct genus of large pliosaurs that lived during the Oxfordian and Kimmeridgian stages of the Late Jurassic in what is now North America. It was provisionally described as a species of Cimoliosaurus by the geologist Wilbur Clinton Knight in 1895, before being given its own genus by the same author in 1898. The only species identified to date is M. rex, known from several specimens identified in the Redwater Shale Member, within the Sundance Formation, Wyoming, United States. A specimen discovered in the Naknek Formation in southern Alaska was referred to the genus in 1994. In Ancient Greek, the generic name literally translates to "large swimming lizard", due to the measurement of the fossils of the holotype specimen.

Nannopterygius is an extinct genus of ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur that lived during the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous. Fossils are known from England, Kazakhstan, Russia, and Norway and six species are currently assigned to the genus.

Darwinius is a genus within the infraorder Adapiformes, a group of basal strepsirrhine primates from the middle Eocene epoch. Its only known species, Darwinius masillae, lived approximately 47 million years ago based on dating of the fossil site.

Jørn Harald Hurum is a Norwegian paleontologist and popularizer of science. He is a vertebrate paleontologist and holds an associate professor position at the Natural History Museum of the University of Oslo. He has studied dinosaurs, primitive mammals and plesiosaurs.

Arthropterygius is a widespread genus of ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur which existed in Canada, Norway, Russia, and Argentina from the late Jurassic period and possibly to the earliest Cretaceous.

The "Monster of Aramberri", also nicknamed in the scientific literature as the Aramberri pliosaur or the Aramberri specimen, is an informal name given to UANL-FCT-R2, a fossil skeleton of a very large pliosaur of which the first remains were discovered during the 1980s near the town of Aramberri, in Nuevo León, Mexico. During the decade of its discovery, the specimen was first interpreted as a dinosaur, before later inspections re-identified it as a marine reptile belonging the family Pliosauridae. Initially, only two concretions containing the animal's fossils were discovered, with one of the two later noted as lost in the first re-identification of the specimen in 2003. During the early 2000s, a new excavation campaign unearthed several additional fossils of the animal, in which some of them were subsequently sent to Karlsruhe State Museum of Natural History, Germany, to be prepared, before returning them in 2012 to the Autonomous University of Nuevo León, where they are mainly stored. Another significant portion of the fossils are currently stored in the Desert Museum of Saltillo.

This timeline of plesiosaur research is a chronologically ordered list of important fossil discoveries, controversies of interpretation, taxonomic revisions, and cultural portrayals of plesiosaurs, an order of marine reptiles that flourished during the Mesozoic Era. The first scientifically documented plesiosaur fossils were discovered during the early 19th century by Mary Anning. Plesiosaurs were actually discovered and described before dinosaurs. They were also among the first animals to be featured in artistic reconstructions of the ancient world, and therefore among the earliest prehistoric creatures to attract the attention of the lay public. Plesiosaurs were originally thought to be a kind of primitive transitional form between marine life and terrestrial reptiles. However, now plesiosaurs are recognized as highly derived marine reptiles descended from terrestrial ancestors.

Megacephalosaurus is an extinct genus of short-necked pliosaur that inhabited the Western Interior Seaway of North America about 94 to 93 million years ago during the Turonian stage of the Late Cretaceous, containing the single species M. eulerti. It is named after its large head, which is the largest of any plesiosaur in the continent and measures up to 1.75 meters (5.7 ft) in length. Megacephalosaurus was one of the largest marine reptiles of its time with an estimated length of 6–9 meters (20–30 ft). Its long snout and consistently sized teeth suggest that it preferred a diet of smaller-sized prey.
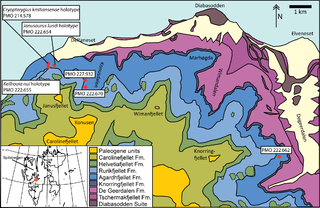
The Agardhfjellet Formation is a geologic formation in Svalbard, Norway. It preserves fossils dating back to the Oxfordian to Berriasian stages, spanning the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous boundary. The formation contains the Slottsmøya Member, a highly fossiliferous unit (Lagerstätte) where many ichthyosaur and plesiosaur fossils have been found, as well as abundant and well preserved fossils of invertebrates.

Steve Etches, MBE is an English plumber, fossil collector and preparator in Kimmeridge, on the Isle of Purbeck in Dorset. From an early age on, Etches began to find, collect and restore the fossils he found on the Jurassic Coast. His collection is now housed in a museum called The Etches Collection which was purpose-built, both to house the collection and to replace the deteriorating local village hall. Etches has won many prizes for his palaeontology and was made a Member of the Order of the British Empire by the Queen in 2014. In 2017, he was also awarded an Honorary Doctorate by the University of Southampton. On 22 April 2019, he appeared on the natural history podcast Trees A Crowd with David Oakes.

Patrick S. Druckenmiller is a Mesozoic paleontologist, taxonomist, associate professor of geology, Earth Sciences curator, and museum director of the University of Alaska Museum of the North, where he oversees the largest single collection of Alaskan invertebrate and vertebrate fossils. He has published work on plesiosaurs, ichthyosaurs, mastodons, and dinosaurs in the United States, Svalbard, and Canada. He has co-authored papers on discussions of mass extinctions and biogeography. Much of his work has focused on Arctic species. He is a member of the Spitsbergen Jurassic Research group, which focuses on marine reptiles. Druckenmiller has named many new genera and species, including Edgarosaurus muddi, Nichollsia borealis, Athabascasaurus bitumineus, Cryopterygius kristiansenae, Spitrasaurus larseni, and Spitrasauruswensaasi.

"Pliosaurus" andrewsi is an extinct species of pliosaurid plesiosaurs that lived during the Callovian stage of the Middle Jurassic, in what is now England. The only known fossils of this taxon were discovered in the Peterborough Member of the Oxford Clay Formation. Other attributed specimens have been discovered in various corners of Eurasia, but these are currently seen as indeterminate or coming from other taxa. The taxonomic history of this animal is quite complex, because several of its fossils were attributed to different genera of pliosaurids, before being concretely named and described in 1960 by Lambert Beverly Tarlo as a species of Pliosaurus. However, although the taxon was found to be valid, subsequent revisions found that it is not part of this genus, and therefore a taxonomic revision must be carried out on this species.
References
- ↑ "Monsterdiggers 2008". University of Oslo.
- ↑ "Fossil sea monster biggest of its kind". ABC News. February 2, 2008.
- ↑ Deshayes, Pierre-Henry (October 11, 2006). "'The Monster' helps piece together puzzle". The Standard. Archived from the original on March 22, 2009. Retrieved January 1, 2009.
- ↑ "'Monster' found in Jurassic graveyard". NBC News. October 5, 2006.
- ↑ "Enormous Jurassic Sea Predator, Pliosaur, Discovered In Norway". Science Daily. February 9, 2008.
- ↑ "Fossil 'makes T-Rex look feeble'", news24.com, 17 March 2009.
- ↑ "Paleontologists Reveal the Identity of 'Predator X'". National Geographic Society . 15 October 2012. Archived from the original on April 14, 2021.