
The Harbin Institute of Technology (HIT) is a public science and engineering university in Nan'gang, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China. It is one of the top universities in China and now affiliated with the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology. The university is part of Project 211, Project 985, and the Double First-Class Construction. The university is a member of the C9 League.

The Nanjing University of Science and Technology is a provincial public university in Xuanwu, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China. It is affiliated with the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, and co-sponsored with the Ministry of Education and the Jiangsu Provincial Government. The university is part of Project 211 and the Double First-Class Construction.

The Ministry of State Security (MSS) is the principal civilian intelligence, security and secret police agency of the People's Republic of China, responsible for foreign intelligence, counterintelligence, and the political security of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). One of the largest and most secretive intelligence organizations in the world, it maintains powerful branches at the provincial, city, municipality and township levels throughout China. The ministry's headquarters, Yidongyuan, is a large compound in Beijing's Haidian district.

Huang Hua was a senior Chinese Communist revolutionary, politician, and diplomat. He served as Foreign Minister of China from 1976 to 1982, and concurrently as Vice Premier from 1980 to 1982. He was instrumental in establishing diplomatic links of the People's Republic of China with the United States and Japan, and was intensely involved in the negotiations with the United Kingdom over the status of Hong Kong.
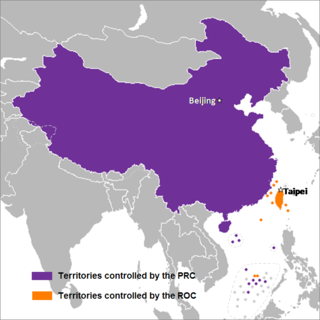
The concept of Two Chinas refers to the political divide between the People's Republic of China (PRC) and the Republic of China (ROC). The PRC was established in 1949 by the Chinese Communist Party, while the ROC was founded in 1912 and retreated to Taiwan after losing the Chinese Civil War.

The China–New Zealand relations, sometimes known as Sino–New Zealand relations, are the relations between China and New Zealand. New Zealand recognised the Republic of China after it lost the Chinese Civil War and retreated to Taiwan in 1949, but switched recognition to the People's Republic of China on 22 December 1972. Since then, economic, cultural, and political relations between the two countries have grown over the past four decades. China is New Zealand's largest trading partner in goods and second largest trading partner in services. In 2008, New Zealand became the first developed country to enter into a free trade agreement with China. In recent years, New Zealand's extensive economic relations with China have been complicated by its security ties to the United States.
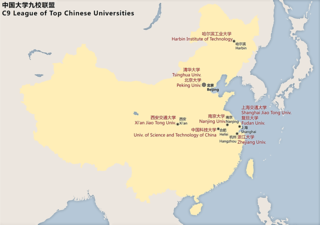
The C9 League is an inter-university seminar composed of nine public universities in China. It was established on May 4, 1998, at the 100th anniversary of Peking University. These elite universities are associated with academic excellence and highly selective admissions. The C9 League is colloquially known as the Chinese Ivy League.

The United States has often accused the People's Republic of China of attempting to unlawfully acquire U.S. military technology and classified information as well as trade secrets of U.S. companies in order to support China's long-term military and commercial development. Chinese government agencies and affiliated personnel have been accused of using a number of methods to obtain U.S. technology, including espionage, exploitation of commercial entities, and a network of scientific, academic and business contacts. Prominent espionage cases include Larry Wu-tai Chin, Katrina Leung, Gwo-Bao Min, Chi Mak, Peter Lee, and Shujun Wang. The Ministry of State Security (MSS) maintains a bureau dedicated to espionage against the United States, the United States Bureau.
Africans in Guangzhou are African immigrants and African Chinese residents of Guangzhou, China.

Alejandro Nicolas Mayorkas is an American attorney and government official who is the 7th United States Secretary of Homeland Security, serving since 2021. A member of the Democratic Party, Mayorkas previously served as director of United States Citizenship and Immigration Services from 2009 to 2013, and the 6th Deputy Secretary of Homeland Security from 2013 to 2016.

Hua Chunying is a Chinese diplomat who has been serving as Vice Minister of Foreign Affairs of China since 2024 and spokesperson of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs since 2012.

Harbin Sport University, also known as the Harbin Institute of Physical Education or HIPE, is a university in Harbin, China, working with research on health and sports.
Residential Surveillance at a Designated Location is a form of detention regularly used by authorities in the People's Republic of China against individuals accused of endangering state security. RSDL is usually carried out at special facilities run by the Public or State Security Bureaus of China, often euphemistically called "training centers," or even hotels that have been converted into black jails. Laws regulating RSDL contain exceptions that allow the state to not inform the family members of the detained about their loved one's incarceration, while also denying detainees access to a lawyer. On the surface, the measure appears to be a softer form of detention like house arrest; but in practice the measure allows for what one journalist calls "the disappearing" of suspects into secret detention."
The Trump travel ban was a series of executive actions taken by U.S. President Donald Trump that restricted entry into the United States by certain foreign nationals, beginning with Executive Order 13769, issued on January 27, 2017.

Executive Order 13780, titled Protecting the Nation from Foreign Terrorist Entry into the United States, was an executive order signed by United States President Donald Trump on March 6, 2017. It placed a 90-day restriction on entry to the U.S. by nationals of Iran, Libya, Somalia, Sudan, Syria and Yemen, and barred entry for all refugees who did not possess either a visa or valid travel documents for 120 days. This executive order—sometimes called "Travel Ban 2.0"—revoked and replaced Executive Order 13769 issued on January 27, 2017.

Geng Shuang is a Chinese politician serving as China's Deputy Permanent Representative to the United Nations. He formerly served as the deputy director of the Information Department of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.

Zhao Lijian is a Chinese civil servant who has been serving as deputy director of the Department of Boundary and Ocean Affairs at the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of China since January 2023.
The Seven Sons of National Defence or colloquially G7 is a grouping of the public universities affiliated with the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of China. They are widely believed to have close scientific research partnerships and projects with the People’s Liberation Army.

A dramatic manifestation of the far reach of the Hong Kong national security law was the mass arrest of 54 pro-democracy activists on 6 January. The arrested stood accused of subverting state power, a crime under the national security law, for their participation as candidates or in other capacities, in the 2020 Hong Kong pro-democracy primaries, which was part of a plan to increase pressure in parliament for democratic reform. Most of them were released on bail the following day. For the first time, the National Security Department of the police cited the national security law to block the website of HKChronicles. There were also several convictions in relation to the 2019-2020 Hong Kong protests.
















