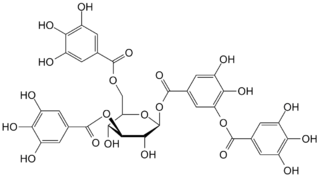
Tannins are a class of astringent, polyphenolic biomolecules that bind to and precipitate proteins and various other organic compounds including amino acids and alkaloids.

Polyphenols are a structural class of mainly natural, but also synthetic or semisynthetic, organic chemicals characterized by the presence of large multiples of phenol structural units. The number and characteristics of these phenol structures underlie the unique physical, chemical, and biological properties of particular members of the class. Examples include tannic acid and ellagitannin. The historically important chemical class of tannins is a subset of the polyphenols.

(E)-Stilbene, commonly known as trans-stilbene, is an organic compound represented by the condensed structural formula C6H5CH=CHC6H5. Classified as a diarylethene, it features a central ethylene moiety with one phenyl group substituents on each end of the carbon–carbon double bond. It has an (E) stereochemistry, meaning that the phenyl groups are located on opposite sides of the double bond, the opposite of its geometric isomer, cis-stilbene. Trans-stilbene occurs as a white crystalline solid at room temperature and is highly soluble in organic solvents. It can be converted to cis-stilbene photochemically, and further reacted to produce phenanthrene.

Diphenylacetylene is the chemical compound C6H5C≡CC6H5. The molecule consists of phenyl groups attached to both ends of an alkyne. It is a colorless crystalline material that is widely used as a building block in organic synthesis and as a ligand in organometallic chemistry.

Tanbark is the bark of certain species of tree. It is traditionally used for tanning hides into leather.

Leucocyanidin is a colorless chemical compound that is a member of the class of natural products known as leucoanthocyanidins.

Procyanidin C2 is a B type proanthocyanidin trimer, a type of condensed tannin.
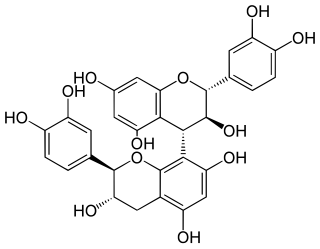
Procyanidin B3 is a B type proanthocyanidin. Procyanidin B3 is a catechin dimer.

Procyanidin B6 is a B type proanthocyanidin.

Mesquitol is a flavan-3-ol, a type of flavonoid.
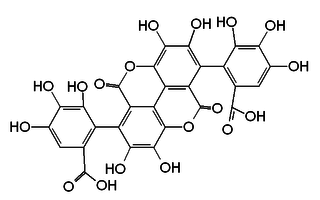
Gallagic acid is a polyphenolic chemical compound that can be found in the ellagitannins, a type of tannin, found in Punica granatum (pomegranate). It is a building block of the corresponding tannin punicalagin, punicalin, punicacortein C and 2-O-galloyl-punicalin.
Arecatannins are a class of condensed tannins in the sub-class procyanidins contained in the seeds of Areca catechu also called betel nut. The arecatannin-type natural products from Ceylonese cassia bark and Areca seed are examples polyphenols by both current definitions, and fit the distinct definition of a polymeric phenol as well.
Proteracacinidins are polymeric condensed tannins composed of mesquitol. This type of tannin can be found in Acacia caffra.
Promelacacinidin is a polymeric condensed tannin composed of mesquitol. This type of tannin can be found in Senegalia caffra.

Oritin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of flavonoid. It is a component of the proteracacinidin tannins of Acacia galpinii and Acacia caffra.
















