A propeller is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon a working fluid such as water or air. Propellers are used to pump fluid through a pipe or duct, or to create thrust to propel a boat through water or an aircraft through air. The blades are shaped so that their rotational motion through the fluid causes a pressure difference between the two surfaces of the blade by Bernoulli's principle which exerts force on the fluid. Most marine propellers are screw propellers with helical blades rotating on a propeller shaft with an approximately horizontal axis.

Seamanship is the art, competence, and knowledge of operating a ship, boat or other craft on water. The Oxford Dictionary states that seamanship is "The skill, techniques, or practice of handling a ship or boat at sea."

A jetboat is a boat propelled by a jet of water ejected from the back of the craft. Unlike a powerboat or motorboat that uses an external propeller in the water below or behind the boat, a jetboat draws the water from under the boat through an intake and into a pump-jet inside the boat, before expelling it through a nozzle at the stern.

A rudder is a primary control surface used to steer a ship, boat, submarine, hovercraft, airship, or other vehicle that moves through a fluid medium. On an airplane, the rudder is used primarily to counter adverse yaw and p-factor and is not the primary control used to turn the airplane. A rudder operates by redirecting the fluid past the hull or fuselage, thus imparting a turning or yawing motion to the craft. In basic form, a rudder is a flat plane or sheet of material attached with hinges to the craft's stern, tail, or afterend. Often rudders are shaped to minimize hydrodynamic or aerodynamic drag. On simple watercraft, a tiller—essentially, a stick or pole acting as a lever arm—may be attached to the top of the rudder to allow it to be turned by a helmsman. In larger vessels, cables, pushrods, or hydraulics may link rudders to steering wheels. In typical aircraft, the rudder is operated by pedals via mechanical linkages or hydraulics.

Aircraft flight control surfaces are aerodynamic devices allowing a pilot to adjust and control the aircraft's flight attitude.

Thrust reversal, also called reverse thrust, is the temporary diversion of an aircraft engine's thrust for it to act against the forward travel of the aircraft, providing deceleration. Thrust reverser systems are featured on many jet aircraft to help slow down just after touch-down, reducing wear on the brakes and enabling shorter landing distances. Such devices affect the aircraft significantly and are considered important for safe operations by airlines. There have been accidents involving thrust reversal systems, including fatal ones.

Contra-rotating, also referred to as coaxial contra-rotating, is a technique whereby parts of a mechanism rotate in opposite directions about a common axis, usually to minimise the effect of torque. Examples include some aircraft propellers, resulting in the maximum power of a single piston or turboprop engine to drive two propellers in opposite rotation. Contra-rotating propellers are also common in some marine transmission systems, in particular for large speed boats with planing hulls. Two propellers are arranged one behind the other, and power is transferred from the engine via planetary gear transmission. The configuration can also be used in helicopter designs termed coaxial rotors, where similar issues and principles of torque apply.
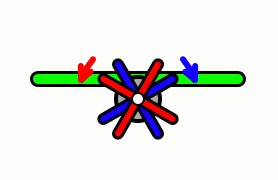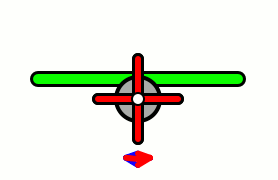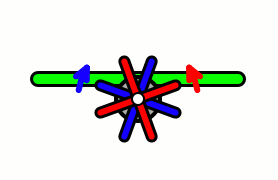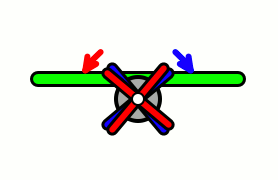
Aircraft equipped with contra-rotating propellers (CRP) coaxial contra-rotating propellers, or high-speed propellers, apply the maximum power of usually a single piston engine or turboprop engine to drive a pair of coaxial propellers in contra-rotation. Two propellers are arranged one behind the other, and power is transferred from the engine via a planetary gear or spur gear transmission. Contra-rotating propellers are also known as counter-rotating propellers, although the term counter-rotating propellers is much more widely used when referring to airscrews on separate non-coaxial shafts turning in opposite directions.

A Z-drive is a type of marine propulsion unit. Specifically, it is an azimuth thruster. The pod can rotate 360 degrees allowing for rapid changes in thrust direction and thus vessel direction. This eliminates the need for a conventional rudder.
The critical engine of a multi-engine fixed-wing aircraft is the engine that, in the event of failure, would most adversely affect the performance or handling abilities of an aircraft. On propeller aircraft, there is a difference in the remaining yawing moments after failure of the left or the right (outboard) engine when all propellers rotate in the same direction due to the P-factor. On turbojet and turbofan twin-engine aircraft, there usually is no difference between the yawing moments after failure of a left or right engine in no-wind condition.

Finning techniques are the skills and methods used by swimmers and underwater divers to propel themselves through the water and to maneuver when wearing swimfins. There are several styles used for propulsion, some of which are more suited to particular swimfin configurations. There are also techniques for positional maneuvering, such as rotation on the spot, which may not involve significant locational change. Use of the most appropriate finning style for the circumstances can increase propulsive efficiency, reduce fatigue, improve precision of maneuvering and control of the diver's position in the water, and thereby increase the task effectiveness of the diver and reduce the impact on the environment. Propulsion through water requires much more work than through air due to higher density and viscosity. Diving equipment which is bulky usually increases drag, and reduction of drag can significantly reduce the effort of finning. This can be done to some extent by streamlining diving equipment, and by swimming along the axis of least drag, which requires correct diver trim. Efficient production of thrust also reduces the effort required, but there are also situations where efficiency must be traded off against practical necessity related to the environment or task in hand, such as the ability to maneuver effectively and resistance to damage of the equipment.
Blade pitch or simply pitch refers to the angle of a blade in a fluid. The term has applications in aeronautics, shipping, and other fields.

Manoeuvering thrusters are transversal propulsion devices built into or mounted to either the bow or stern of a ship or boat to make it more manoeuvrable. Bow thrusters make docking easier, since they allow the captain to turn the vessel to port or starboard side, without using the main propulsion mechanism which requires some forward motion for turning; The effectiveness of a thruster is curtailed by any forward motion due to the Coandă effect. A stern thruster is of the same principle, fitted at the stern. Sufficiently large vessels often have multiple bow thrusters and stern thrusters.

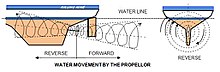
Astern propulsion is a maneuver in which a ship's propelling mechanism is used to develop thrust in a retrograde direction. Astern propulsion does not necessarily imply the ship is moving astern ; astern propulsion is used to slow a ship by applying a force in the direction of the bow of the ship, instead of the stern. The equivalent concept for an airplane is thrust reversal.

The Kitchen rudder is the familiar name for "Kitchen's Patent Reversing Rudders", a combination rudder and directional propulsion delivery system for relatively slow speed displacement boats which was invented in the early 20th century by John G. A. Kitchen of Lancashire, England. It turns the rudder into a directional thruster, and allows the engine to maintain constant revolutions and direction of drive shaft rotation while altering thrust by use of a control which directs thrust forward or aft. Only the rudder pivots; the propeller itself is on a fixed shaft and does not.

P‑factor, also known as asymmetric blade effect and asymmetric disc effect, is an aerodynamic phenomenon experienced by a moving propeller, wherein the propeller's center of thrust moves off-center when the aircraft is at a high angle of attack. This shift in the location of the center of thrust will exert a yawing moment on the aircraft, causing it to yaw slightly to one side. A rudder input is required to counteract the yawing tendency.

In aeronautics, an aircraft propeller, also called an airscrew, converts rotary motion from an engine or other power source into a swirling slipstream which pushes the propeller forwards or backwards. It comprises a rotating power-driven hub, to which are attached several radial airfoil-section blades such that the whole assembly rotates about a longitudinal axis. The blade pitch may be fixed, manually variable to a few set positions, or of the automatically variable "constant-speed" type.
Asymmetrical aircraft have left- and right-hand sides which are not exact mirror images of each other. Although most aircraft are symmetrical, there is no fundamental reason why they must be, and design goals can sometimes be best achieved with an asymmetrical aircraft.
Propeller theory is the science governing the design of efficient propellers. A propeller is the most common propulsor on ships, and on small aircraft.

Stern sculling is the use of a single oar over the stern of a boat to propel it with side-to-side motions that create forward lift in the water. The strict terminology of propulsion by oar is complex and contradictory, and varies by context. Stern sculling may also simply be referred to as "sculling", most commonly so in a maritime situation. In fresh water, and particularly in sport rowing, sculling is use of two oars on either side of the boat by each person, in contrast to sweep rowing, whereby each boat crew member employs a single oar, complemented by another crew member working on the opposite side with their oar.
Dand. I. W.: “Hydrodynamic Aspects of Shallow Water Collisions” Transactions of the Royal Institution of Naval Architects, Volume 118, 1976.