
The Falkland Islands are located in the South Atlantic Ocean between 51°S and 53°S on a projection of the Patagonian Shelf, part of the South American continental shelf. In ancient geological time this shelf was part of Gondwana, and around 400 million years ago split from what is now Africa and drifted westwards from it. Today the islands are subjected to the Roaring Forties, winds that shape both their geography and climate.

Vermicompost (vermi-compost) is the product of the decomposition process using various species of worms, usually red wigglers, white worms, and other earthworms, to create a mixture of decomposing vegetable or food waste, bedding materials, and vermicast. This process is called vermicomposting, while the rearing of worms for this purpose is called vermiculture.

The shipworms are marine bivalve molluscs in the family Teredinidae: a group of saltwater clams with long, soft, naked bodies. They are notorious for boring into wood that is immersed in sea water, including such structures as wooden piers, docks and ships; they drill passages by means of a pair of very small shells (“valves”) borne at one end, with which they rasp their way through. Sometimes called "termites of the sea", they also are known as "Teredo worms" or simply Teredo. Carl Linnaeus assigned the common name Teredo to the best-known genus of shipworms in the 10th edition of his taxonomic magnum opus, Systema Naturæ (1758).

Amphisbaenia is a group of usually legless squamates, comprising over 200 extant species. Amphisbaenians are characterized by their long bodies, the reduction or loss of the limbs, and rudimentary eyes. As many species have a pink body and scales arranged in rings, they have a superficial resemblance to earthworms. While the genus Bipes retains forelimbs, all other genera are limbless. Although superficially similar to the snakes and blind lizards, recent phylogenetic studies suggest that they are most closely related to wall lizards of the family Lacertidae. Amphisbaenians are widely distributed, occurring in North America, Europe, Africa, South America, Western Asia and the Caribbean. They are not found east of the Caspian Sea. Most species are less than 6 inches (150 mm) long.

The Falkland Islands wolf, also known as the warrah and occasionally as the Falkland Islands dog, Falkland Islands fox, warrah fox, or Antarctic wolf, was the only native land mammal of the Falkland Islands. This endemic canid became extinct in 1876, the first known canid to have become extinct in historical times.

Oligochaeta is a subclass of animals in the phylum Annelida, which is made up of many types of aquatic and terrestrial worms, including all of the various earthworms. Specifically, oligochaetes comprise the terrestrial megadrile earthworms, and freshwater or semiterrestrial microdrile forms, including the tubificids, pot worms and ice worms (Enchytraeidae), blackworms (Lumbriculidae) and several interstitial marine worms.

Sea Lion Island is the largest of the Sea Lion Island Group of the Falkland Islands. It is 9 km2 (3 sq mi) in area. and lies 14 km (9 mi) southeast of Lafonia. It was designated a Ramsar site on 24 September 2001, and as an Important Bird Area. In 2017 the island was designated as a National Nature Reserve.

The slow worm is a reptile native to western Eurasia. It is also called a deaf adder, a slowworm, a blindworm, or regionally, a long-cripple. These legless lizards are also sometimes called common slowworms. The "blind" in blindworm refers to the lizard's small eyes, similar to a blindsnake.
The Pound is the currency of the Falkland Islands, a British Overseas Territory in the South Atlantic Ocean. The symbol is the pound sign, £, or alternatively FK£, to distinguish it from other pound-denominated currencies. The ISO 4217 currency code is FKP.

Dracunculus medinensis, or Guinea worm, is a nematode that causes dracunculiasis, also known as guinea worm disease. The disease is caused by the female which, at up to 80 centimetres in length, is among the longest nematodes infecting humans. In contrast, the longest recorded male Guinea worm is only 4 cm.
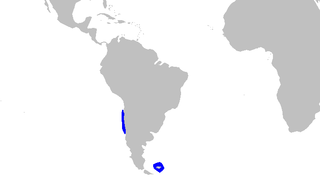
The granular dogfish, Centroscyllium granulatum, is a little-known, very small dogfish shark of the family Etmopteridae, endemic to the Falkland Islands.

The Falkland Islands are an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about 300 miles east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and about 752 miles from the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula, at a latitude of about 52°S. The archipelago, with an area of 4,700 square miles, comprises East Falkland, West Falkland, and 776 smaller islands. As a British overseas territory, the Falklands have internal self-governance, and the United Kingdom takes responsibility for their defence and foreign affairs. The capital and largest settlement is Stanley on East Falkland.

The Fuegian snipe also known as the cordilleran snipe, is a small stocky wader. It breeds in south-central Chile and Argentina south to Tierra del Fuego. It is mainly sedentary, but the Tierra del Fuego population winters in mainland Chile.

An earthworm is a terrestrial invertebrate that belongs to the phylum Annelida. They exhibit a tube-within-a-tube body plan; they are externally segmented with corresponding internal segmentation; and they usually have setae on all segments. They occur worldwide where soil, water, and temperature allow.

The nematodes or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda, with plant-parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Taxonomically, they are classified along with insects and other moulting animals in the clade Ecdysozoa, and unlike flatworms, have tubular digestive systems with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum.

D'Orbigny's slider or the black-bellied slider, commonly known in Brazil as tartaruga-tigre or tartaruga-tigre-d'água, is a species of water turtle in the family Emydidae. The species is found in southern Brazil, northeastern Argentina, and Uruguay. Two subspecies are recognized as being valid, Trachemys dorbigni adiutrix and Trachemys dorbigni brasiliensis.

The wildlife of the Falkland Islands is quite similar to that of Patagonia. The Falkland Islands have no native reptiles or amphibians, and the only native land mammal, the warrah, is now extinct. However, a large number of bird species have been seen around the islands, and many of them breed on the smaller islands of the archipelago. Insects play a large role in the ecosystem of the islands, and over 200 species have been recorded. The waters around the Falkland Islands sustain many animals, including a large number of marine mammals. Three pinniped species breed on the islands.

Halicephalobus mephisto is a species of nematode, among a number of other roundworms, discovered by geoscientists Gaetan Borgonie and Tullis Onstott in 2011. It was detected in ore recovered from deep rock fracture water in several gold mines in South Africa 0.9 km (0.56 mi), 1.3 km (0.81 mi), and 3.6 km (2.2 mi) under the surface of the Earth. Onstott said that "it scared the life out of me when I first saw them moving", and explained that "they look like black little swirly things". The finding is significant because no other multicellular organism had ever been detected farther than 2 km (1.2 mi) below the Earth's surface.
Haplosyllis spongicola, the sponge worm, is a species of polychaete worm in the family Syllidae. It was previously classified as Syllis spongicola and is part of a species complex of closely related species that are difficult to distinguish morphologically and where the demarcation between them is unclear. It is found in shallow temperate, subtropical and tropical seas worldwide, wherever its host sponges are found.

Hookworms are intestinal, blood-feeding, parasitic roundworms that cause types of infection known as helminthiases. Hookworm infection is found in many parts of the world, and is common in areas with poor access to adequate water, sanitation, and hygiene. In humans, infections are caused by two main species of roundworm, belonging to the genera Ancylostoma and Necator. In other animals the main parasites are species of Ancylostoma.

















