
The medulla oblongata is a long stem-like structure located in the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure.

The dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway (DCML) is a sensory pathway of the central nervous system that conveys sensations of fine touch, vibration, two-point discrimination, and proprioception (position) from the skin and joints. It transmits information from the body to the primary somatosensory cortex in the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe of the brain. The pathway receives information from sensory receptors throughout the body, and carries this in nerve tracts in the white matter of the dorsal columns of the spinal cord, to the medulla where it is continued in the medial lemniscus, on to the thalamus and relayed from there through the internal capsule and transmitted to the somatosensory cortex. The name dorsal-column medial lemniscus comes from the two structures that carry the sensory information: the dorsal columns of the spinal cord, and the medial lemniscus in the brainstem.

The gracile fasciculus is a nerve tract in the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway of the spinal cord and carries information from the lower parts of the body. The gracile fasiculus is one of many ascending tracts which carry received sensory information to the brain via the spinal cord. It is also one of the dorsal columns, the other being the cuneate fasciculus.
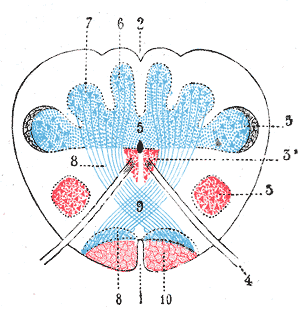
In neuroanatomy, the dorsal column nuclei are a pair of nuclei in the dorsal columns in the brainstem. The name refers collectively to the cuneate nucleus and gracile nucleus, which are present at the junction between the spinal cord and the medulla oblongata. Both nuclei contain second-order neurons of the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway, which carries fine touch and proprioceptive information from the body to the brain. Each nucleus has an associated nerve tract, the gracile fasciculus and the cuneate fasciculus.

The Brazilian gracile opossum is a species of small opossum from Brazil.
The gracile tateril or slender gerbil is a species of gerbil found in Burkina Faso, Chad, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Ivory Coast, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Togo, and possibly Cameroon. Its natural habitats are dry savanna, arable land, pastureland, and rural gardens. It is a common species, sometimes considered an agricultural pest, and the International Union for Conservation of Nature has rated its conservation status as being of "least concern".

The Aceramarca gracile opossum or Bolivian gracile opossum is a species of opossum. It is native to Bolivia and Peru, where it occurs in tropical elfin forest habitat.
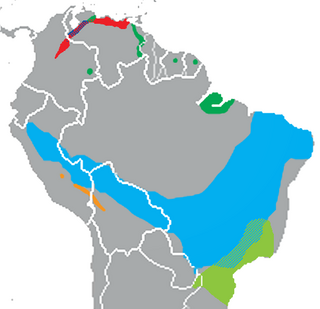
Gracilinanus is a genus of opossum in the family Didelphidae. It was separated from the genus Marmosa in 1989, and has since had the genera Cryptonanus, Chacodelphys, and Hyladelphys removed from it. It contains the following species:
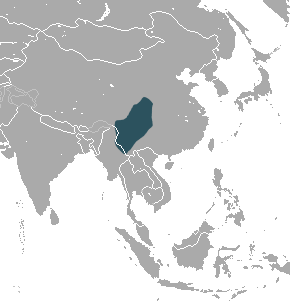
The gracile shrew mole is a species of mammal in the family Talpidae. It is found in China and Myanmar.

The Didelphinae are a subfamily of opossums consisting of 15 genera and 98 species, one of them extinct. Specimens have been collected throughout the Americas, but are predominant in South and Central America.
In biology, robustness is used to describe a taxon with a stronger and heavier build (morphology) when compared to a related gracile taxon. The terms are used in contrast to one another.
Gracility is slenderness, the condition of being gracile, which means slender.

Robust capuchin monkeys are capuchin monkeys in the genus Sapajus. Formerly all capuchin monkeys were placed in the genus Cebus; Sapajus was erected in 2012 by Jessica Lynch Alfaro et al. to differentiate the robust (tufted) capuchin monkeys from the gracile capuchin monkeys, which remain in Cebus.

Gracile capuchin monkeys are capuchin monkeys in the genus Cebus. At one time all capuchin monkeys were included within the genus Cebus. In 2011, Jessica Lynch Alfaro et al. proposed splitting the genus between the robust capuchin monkeys, such as the tufted capuchin, and the gracile capuchins. The gracile capuchins retain the genus name Cebus, while the robust species have been transferred to Sapajus.
Protonarthron indistinctum is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1938. It is known from the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Protonarthron diabolicum is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by James Thomson in 1858.
Protonarthron dubium is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Hintz in 1911.
Protonarthron microps is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Jordan in 1903.
Protonarthron olympianum is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Per Olof Christopher Aurivillius in 1913.
Protonarthron subfasciatum is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Jordan in 1894.












