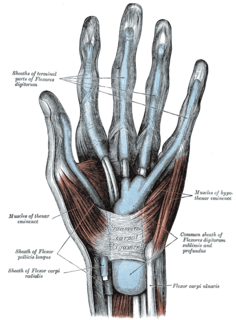
The thenar eminence refers to the group of muscles on the palm of the human hand at the base of the thumb. The skin overlying this region is the area stimulated when trying to elicit a palmomental reflex. The word thenar comes from Greek θέναρ (thenar), meaning 'palm of the hand'.

The Hepialidae are a family of insects in the lepidopteran order. Moths of this family are often referred to as swift moths or ghost moths.

The opponens digiti minimi is a muscle in the hand. It is of a triangular form, and placed immediately beneath the palmaris brevis, abductor digiti minimi and flexor digiti minimi brevis. It is one of the three hypothenar muscles that control the little finger.

The opponens pollicis is a small, triangular muscle in the hand, which functions to oppose the thumb. It is one of the three thenar muscles, lying deep to the abductor pollicis brevis and lateral to the flexor pollicis brevis.

The hypothenar muscles are a group of three muscles of the palm that control the motion of the little finger.

The Flexor digiti minimi brevis lies under the metatarsal bone on the little toe, and resembles one of the Interossei.

The recurrent branch of the median nerve is the branch of the median nerve which supplies the thenar muscles. It is also occasionally referred to as the thenar branch, or the thenar muscular branch, of the median nerve. In the thenar eminence it provides motor innervation to:

The Calpinae are a subfamily of moths in the family Erebidae. This subfamily includes many species of moths that have a pointed and barbed proboscis adapted to piercing the skins of fruit to feed on juice, and in the case of the several Calyptra species of vampire moths, to piercing the skins of mammals to feed on blood. The subfamily contains some large moths with wingspans longer than 5 cm (2 in).

The Thyrididae comprise the family of picture-winged leaf moths. They are the only family in the superfamily Thyridoidea, which sometimes has been included in the Pyraloidea, but this isn't supported by cladistic analysis.

Hypena is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae. It was first described by Franz von Paula Schrank in 1802. These non-migratory moths overwinter as pupae and almost never come to bait as adults.
Pseudaclytia is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae.

Ape hand deformity, also known as simian hand, is a deformity in humans who cannot move the thumb away from the rest of the hand. It is an inability to abduct the thumb. Abduction of the thumb refers to the specific capacity to orient the thumb perpendicularly to the ventral (palmar) surface of the hand. Opposition refers specifically the ability to "swing" the first metacarpal such that the tip of the thumb may touch the distal end of the 5th phalanx and if we put the hand on the table as the palm upward the thumb can not point to the sky. The Ape Hand Deformity is caused by damage to the distal median nerve, and subsequent loss of opponens pollicis muscle function. The name "ape hand deformity" is misleading, as apes have opposable thumbs.
Pseudaclytia bambusana is a moth in the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Schaus in 1938. It is found on Cuba.
Pseudaclytia major is a moth in the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Druce in 1906. It is found in Peru.
Pseudaclytia minor is a moth in the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Schaus in 1905. It is found in French Guiana.
Pseudaclytia popayanum is a moth in the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Paul Dognin in 1902. It is found in Colombia.
Pseudaclytia pseudodelphire is a moth in the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Rothschild in 1912. It is found in Venezuela.
Pseudaclytia umbrica is a moth in the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Druce in 1898. It is found in Brazil.
Pseudaclytia unimacula is a moth in the subfamily Arctiinae. It was described by Schaus in 1905. It is found in French Guiana.











