
Pseudomonas is a genus of Gram-negative, Gammaproteobacteria, belonging to the family Pseudomonadaceae and containing 191 validly described species. The members of the genus demonstrate a great deal of metabolic diversity and consequently are able to colonize a wide range of niches. Their ease of culture in vitro and availability of an increasing number of Pseudomonas strain genome sequences has made the genus an excellent focus for scientific research; the best studied species include P. aeruginosa in its role as an opportunistic human pathogen, the plant pathogen P. syringae, the soil bacterium P. putida, and the plant growth-promoting P. fluorescens, P. lini, P. migulae, and P. graminis.

Pseudomonas fluorescens is a common Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium. It belongs to the Pseudomonas genus; 16S rRNA analysis as well as phylogenomic analysis has placed P. fluorescens in the P. fluorescens group within the genus, to which it lends its name.
Pseudomonas putida is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped, saprotrophic soil bacterium.

Burkholderia is a genus of Proteobacteria whose pathogenic members include the Burkholderia cepacia complex, which attacks humans and Burkholderia mallei, responsible for glanders, a disease that occurs mostly in horses and related animals; Burkholderia pseudomallei, causative agent of melioidosis; and Burkholderia cepacia, an important pathogen of pulmonary infections in people with cystic fibrosis (CF). Burkholderia species is also found marine environment. S.I. Paul et al. (2021) isolated and characterized Burkholderia cepacia from marine sponges of the Saint Martin's Island of the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh.

A plant canker is a small area of dead tissue, which grows slowly, often over years. Some cankers are of only minor consequence, but others are ultimately lethal and therefore can have major economic implications for agriculture and horticulture. Their causes include a wide range of organisms as fungi, bacteria, mycoplasmas and viruses. The majority of canker-causing organisms are bound to a unique host species or genus, but a few will attack other plants. Weather and animals can spread canker, thereby endangering areas that have only slight amount of canker.

The Pseudomonadales are an order of Proteobacteria. A few members are pathogens, such as species of Pseudomonas, Moraxella, and Acinetobacter, which may cause disease in humans, animals and plants.

The Pseudomonadaceae are a family of bacteria which includes the genera Azomonas, Azorhizophilus, Azotobacter, Mesophilobacter, Pseudomonas, and Rugamonas. The family Azotobacteraceae was recently reclassified into this family.

Cystovirus is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses which infects bacteria. It is the only genus in the family Cystoviridae. The name of the group cysto derives from Greek kystis which means bladder or sack. There are seven species in this genus.

Carbenicillin is a bactericidal antibiotic belonging to the carboxypenicillin subgroup of the penicillins. It was discovered by scientists at Beecham and marketed as Pyopen. It has Gram-negative coverage which includes Pseudomonas aeruginosa but limited Gram-positive coverage. The carboxypenicillins are susceptible to degradation by beta-lactamase enzymes, although they are more resistant than ampicillin to degradation. Carbenicillin is also more stable at lower pH than ampicillin.

Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a common encapsulated, Gram-negative, strict aerobic, Rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, P. aeruginosa is a multidrug resistant pathogen recognized for its ubiquity, its intrinsically advanced antibiotic resistance mechanisms, and its association with serious illnesses – hospital-acquired infections such as ventilator-associated pneumonia and various sepsis syndromes.

Cefepime is a fourth-generation cephalosporin antibiotic with the ability to cross the blood–brain barrier. Cefepime has an extended spectrum of activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, with greater activity against both types of organism than third-generation agents. A 2007 meta-analysis suggested when data of trials were combined, mortality was increased in people treated with cefepime compared with other β-lactam antibiotics. In response, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) performed their own meta-analysis which found no mortality difference.

Imipenem is an intravenous β-lactam antibiotic discovered by Merck scientists Burton Christensen, William Leanza, and Kenneth Wildonger in the mid-1970s. Carbapenems are highly resistant to the β-lactamase enzymes produced by many multiple drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria, thus play a key role in the treatment of infections not readily treated with other antibiotics.

Pseudomonas syringae is a rod-shaped, Gram-negative bacterium with polar flagella. As a plant pathogen, it can infect a wide range of species, and exists as over 50 different pathovars, all of which are available to researchers from international culture collections such as the NCPPB, ICMP, and others.
Pseudomonas amygdali is a Gram-negative plant pathogenic bacterium. It is named after its ability to cause disease on almond trees. Different analyses, including 16S rRNA analysis, DNA-DNA hybridization, and MLST clearly placed P. amygdali in the P. syringae group together with the species Pseudomonas ficuserectae and Pseudomonas meliae, and 27 pathovars of Pseudomonas syringae/Pseudomonas savastanoi, constituting a single, well-defined phylogenetic group which should be considered as a single species. This phylogenetic group has not been formally named because of the lack of reliable means to differentiate it phenotipically from closely related species, and it is currently known as either genomospecies 2 or phylogroup 3. When it is formally named, the correct name for this new species should be Pseudomonas amygdali, which takes precedence over all the other names of taxa from this group, including Pseudomonas savastanoi, which is and inadequate and confusing name whose use is not recommended.

Ananda Mohan Chakrabarty, PhD was an Indian American microbiologist, scientist, and researcher, most notable for his work in directed evolution and his role in developing a genetically engineered organism using plasmid transfer while working at GE, the patent for which led to landmark Supreme Court case, Diamond v. Chakrabarty.

"Pseudomonas tomato" is a Gram-negative plant pathogenic bacterium that infects a variety of plants. It was once considered a pathovar of Pseudomonas syringae, but following DNA-relatedness studies, it was recognized as a separate species and several other former P. syringae pathovars were incorporated into it. Since no official name has yet been given, it is referred to by the epithet 'Pseudomonas tomato' .

Swarming motility is a rapid and coordinated translocation of a bacterial population across solid or semi-solid surfaces, and is an example of bacterial multicellularity and swarm behaviour. Swarming motility was first reported by Jorgen Henrichsen and has been mostly studied in genus Serratia, Salmonella, Aeromonas, Bacillus, Yersinia, Pseudomonas, Proteus, Vibrio and Escherichia.
In enzymology, a muconolactone Delta-isomerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Pseudomonas infection refers to a disease caused by one of the species of the genus Pseudomonas.
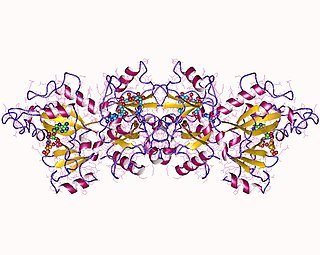
The Pseudomonas exotoxin is an exotoxin produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Vibrio cholerae produces a similar protein called the Cholix toxin.














