
Excavata is a major supergroup of unicellular organisms belonging to the domain Eukaryota. It was first suggested by Simpson and Patterson in 1999 and introduced by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002 as a formal taxon. It contains a variety of free-living and symbiotic forms, and also includes some important parasites of humans, including Giardia and Trichomonas. Excavates were formerly considered to be included in the now obsolete Protista kingdom. They are classified based on their flagellar structures, and they are considered to be the most basal Flagellate lineage. Phylogenomic analyses split the members of the Excavates into three different and not all closely related groups: Discobids, Metamonads and Malawimonads. Except for Euglenozoa, they are all non-photosynthetic.

Discicristata is a proposed eukaryotic clade.

A bikont is any of the eukaryotic organisms classified in the group Bikonta. Many single-celled members of the group, and the presumed ancestor, have two flagella.

Retaria is a clade within the supergroup Rhizaria containing the Foraminifera and the Radiolaria. In 2019, the Retaria were recognized as a basal Rhizaria group, as sister of the Cercozoa.
Anaeromonadea is a class of excavates, comprising the oxymonads and Trimastix.

SAR or Harosa is a clade that includes stramenopiles (heterokonts), alveolates, and Rhizaria. The name is an acronym derived from the first letters of each of these clades; it has been alternatively spelled "RAS". The term "Harosa" has also been used. The SAR supergroup was formulated as the node-based taxon.

Vitekorchis excavata, also known as the hollow oncidium, is a species of orchid native to the Neotropics.
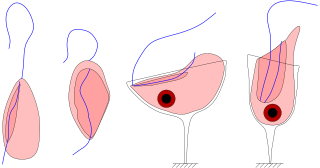
Histiona is a genus of Excavata.

The Archaeplastida+HC+SAR megagroup is a group of eukaryotes proposed by Burki et al. (2008). It is also referred to as Diaphoretickes or the SAR/HA Supergroup, or the Corticata with Rhizaria.
Eopharingia is an excavata group.

Bathytoma is a genus of deep-water sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Borsoniidae.
Andalucia is a genus of jakobids.

Calyptraea, commonly known as the Chinese hat snails is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Calyptraeidae, a family which contains the slipper snails or slipper limpets, cup-and-saucer snails, and Chinese hat snails.

Pterolophia is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae, containing the following species:
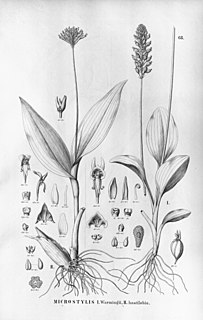
Malaxis excavata is a species of orchid widespread across much of Mesoamerica and South America from Mexico to Argentina. It has green flowers in a flat-topped array.
Wurmiella is an extinct conodont genus.
Pterolophia instabilis is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Per Olof Christopher Aurivillius in 1922. It is known from Seychelles.
Pterolophia guineensis is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by James Thomson in 1864, originally under the genus Alyattes.











