
Since its establishment in 1947, Pakistan has had a non-symmetric federal government and is a federal parliamentary democratic republic. At the national level, the people of Pakistan elect a bicameral legislature, the Parliament of Pakistan. The parliament consists of a lower house called the National Assembly, which is elected directly via first-past-the-post voting, and an upper house called the Senate, whose members are chosen by elected provincial legislators. The head of government, the Prime Minister, is elected by the majority members of the National Assembly and the head of state, the President, is elected by the Electoral College, which consists of both houses of Parliament together with the four provincial assemblies. In addition to the national parliament and the provincial assemblies, Pakistan also has more than five thousand elected local governments.
The National Unionist Party was a political party based in the Punjab Province during the period of British rule in India. The Unionist Party mainly represented the interests of the landed gentry and landlords of Punjab, which included Muslims, Hindus and Sikhs. The Unionists dominated the political scene in Punjab from World War I to the independence of India and the creation Pakistan after the partition of the province in 1947. The party's leaders served as Prime Minister of the Punjab. The creed of the Unionist Party emphasized: "Dominion Status and a United Democratic federal constitution for India as a whole".

The Provincial Assembly of the Punjab is a unicameral legislature of elected representatives of the Pakistani province of Punjab, which is located in Lahore, the provincial capital. It was established under Article 106 of the Constitution of Pakistan, having a total of 371 seats, with 297 general seats, 66 seats reserved for women and 8 reserved for non-Muslims.
Politics in reorganised present-day Punjab is dominated by mainly three parties – Indian National Congress, Aam Aadmi Party and Shiromani Akali Dal (Badal). Since 1967, Chief Minister of Punjab has been predominantly from Jat Sikh community despite its 21 percent state population. Exceptions are Giani Zail Singh, the Chief Minister of Punjab from 17 March 1972 to 30 April 1977 belonging to Ramgarhia community that has population of 6 percent and is a part of significant OBC community having population of 31.3 percent in the state and Charanjit Singh Channi who held the position for 111 days from 20 September 2021 to 16 March 2022 and was from Scheduled Caste(Dalit) who have 32 percent population in the state. Other prominent party is Bahujan Samaj Party especially in Doaba region founded by Kanshi Ram of Rupnagar district. In 1992 BSP won 9 seats Vidhan Sabha elections. Also BSP won 3 lok sabha seats from Punjab in 1996 general elections and only Garhshanker seat in 1997 Vidhan Sabha elections. Communist parties too have some influence in the Malwa area. In the 2014 general elections, the first-time contesting Aam Aadmi Party got 4 out of 13 seats in Punjab by winning 34 of the total 117 assembly segments, coming second in 7, third in 73 and fourth in the rest 3 segments. The support for the Aam Aadmi Party increased later in Punjab. The current Government was elected in the 2022 Punjab Assembly elections and the AAP won 92 out of 117 Assembly seats with Bhagwant Mann as the Chief Minister. The Congress flows down to get only 18 seats.

When the All-India Muslim League was founded at Dacca, on 30 December 1906 at the occasion of the annual All India Muhammadan Educational Conference, It was participated by the Muslim leaders from Punjab, i.e., Sir Mian Muhammad Shafi, Mian Fazl-i-Hussain, Abdul Aziz, Khawaja Yusuf Shah and Sh. Ghulam Sadiq. Earlier Mian Muhammad Shafi organised a Muslim Association in early 1906, but when the All-India Muslim League was formed, he established its powerful branch in the Punjab of which he became the general secretary. Shah Din was elected as its first president. This branch, organised in November 1907, was known as the Punjab Provincial Muslim League.

Provincial elections were held in British India in the winter of 1936–37 as mandated by the Government of India Act 1935. Elections were held in eleven provinces - Madras, Central Provinces, Bihar, Orissa, the United Provinces, the Bombay Presidency, Assam, the North-West Frontier Province, Bengal, Punjab and Sind.

Provincial elections were held in British India in January 1946 to elect members of the legislative councils of the Indian provinces. The Congress, in a repeat of the 1937 elections, won (90%) of the general non-Muslim seats while the Muslim League won the majority of Muslim seats (87%) in the provinces.

The Shiromani Akali Dal (SAD) is a centre-right Sikh-centric state political party in Punjab, India. The party is the second-oldest in India, after Congress, being founded in 1920. Although there are many parties with the description Akali Dal, the party that is recognized as "Shiromani Akali Dal" by the Election Commission of India is the one led by Sukhbir Singh Badal. The party has a moderate Punjabi agenda. On 26 September 2020, it left the National Democratic Alliance over the farm bills.
Elections to the Punjab Provincial Assembly were held in January 1946 as part of the 1946 Indian provincial elections.
Jnanendra Chandra Majumdar was an anti-colonial Bengali politician, and a representative of East Pakistan to the Constituent Assembly of Pakistan.

Akshay Kumar Das was a Bengali Hindu politician of Pakistan, who served as a representative of East Pakistan in both the First and Second Constituent Assemblies, and held multiple ministries across the 1950s in governments formed by different political parties.

First Provincial assembly election was held in Punjab in the winter of 1936-37 as mandated by the Government of India Act 1935.

First Provincial Legislative Council election was held in Punjab in 1920 as mandated by the Government of India Act 1919.

Legislative Council elections were held in Punjab Province in British India in late 1923. They were the second legislative council elections held in the province under the Government of India Act 1919. The newly elected Council was constituted on 2 January 1924 when its first meeting was held.

Legislative Council elections were held in Punjab Province in British India in late 1926. They were the third legislative council elections held in the province under the Government of India Act 1919. The newly elected Council was constituted on 3 January 1927 when its first meeting was held.

Legislative Council elections were held in Punjab Province in British India in 1930. They were the fourth and last legislative council elections held in the province under the Government of India Act 1919. The newly elected Council was constituted on 24 October 1930 when its first meeting was held.
Rai Bahadur Ganga Saran was an Indian trade unionist and politician from Punjab. He was a member of the Punjab Provincial Assembly and both the Constituent Assembly of India and the Constituent Assembly of Pakistan.
Shaikh Karamat Ali was a Pakistani Muslim League politician from Punjab, Pakistan.
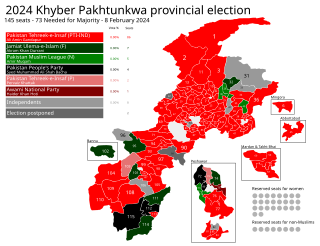
Provincial elections were held in the Pakistani province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa on 8 February 2024 to elect members of the 12th Provincial Assembly of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. On 5 August 2023, the results of the 2023 digital census were approved by the Council of Common Interests headed by Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif. Therefore, elections have been delayed for several months, as new delimitations will be published on 14 December 2023, as announced by the Election Commission of Pakistan (ECP). On 2 November 2023, the ECP announced, in agreement with the President of Pakistan, Arif Alvi, that the elections would be held on 8 February 2024. This election was held concurrently with nationwide general elections and other provincial elections.










