
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to rid the Church of England of what they considered to be Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become more Protestant. Puritanism played a significant role in English and early American history, especially during the Protectorate.

The Church of England traces its history back to 597. That year, a group of missionaries sent by the pope and led by Augustine of Canterbury began the Christianisation of the Anglo-Saxons. Augustine became the first archbishop of Canterbury. Throughout the Middle Ages, the English Church was a part of the Catholic Church led by the pope in Rome. Over the years, the church won many legal privileges and amassed vast wealth and property. This was often a point of contention between Kings of England and the church.

John Foxe was an English clergyman, theologian, and historian, notable for his martyrology Actes and Monuments, telling of Christian martyrs throughout Western history, but particularly the sufferings of English Protestants and proto-Protestants from the 14th century and in the reign of Mary I. The book was widely owned and read by English Puritans and helped to mould British opinion on the Catholic Church for several centuries.
Defrocking, unfrocking, degradation, or laicization of clergy is the removal of their rights to exercise the functions of the ordained ministry. It may be grounded on criminal convictions, disciplinary problems, or disagreements over doctrine or dogma, but may also be done at their request for personal reasons, such as running for civil office, taking over a family business, declining health or old age, desire to marry against the rules for clergy in a particular church, or an unresolved dispute. The form of the procedure varies according to the Christian denomination concerned.
In some religions, an exorcist is a person who is believed to be able to cast out the devil or performs the ridding of demons or other supernatural beings who are alleged to have possessed a person, or (sometimes) a building or even an object. An exorcist can be a specially prepared or instructed person including: priest, a nun, a monk, a witch doctor (healer), a shaman, a psychic or a geomancer.

The Elizabethan Religious Settlement is the name given to the religious and political arrangements made for England during the reign of Elizabeth I (1558–1603). The settlement, implemented from 1559 to 1563, marked the end of the English Reformation. It permanently shaped the Church of England's doctrine and liturgy, laying the foundation for the unique identity of Anglicanism.

Samuel Harsnett, born Samuel Halsnoth, was an English writer on religion and Archbishop of York from 1629.

The Marian exiles were English Protestants who fled to continental Europe during the 1553–1558 reign of the Catholic monarchs Queen Mary I and King Philip. They settled chiefly in Protestant countries such as the Netherlands, Switzerland and Germany, and also in France, Italy and Poland.

Exorcism is the religious or spiritual practice of evicting demons, jinns, or other malevolent spiritual entities from a person, or an area, that is believed to be possessed. Depending on the spiritual beliefs of the exorcist, this may be done by causing the entity to swear an oath, performing an elaborate ritual, or simply by commanding it to depart in the name of a higher power. The practice is ancient and part of the belief system of many cultures and religions.

The English Reformation took place in 16th-century England when the Church of England was forced by its monarchs and elites to break away from the authority of the pope and the Catholic Church. These events were part of the wider European Reformation, a religious and political movement that affected the practice of Christianity in Western and Central Europe.
John Darrell was an Anglican clergyman noted for his Puritan views and his practice as an exorcist, which led to imprisonment.

The reign of Elizabeth I of England, from 1558 to 1603, saw the start of the Puritan movement in England, its clash with the authorities of the Church of England, and its temporarily effective suppression as a political movement in the 1590s by judicial means. This led to the further alienation of Anglicans and Puritans from one another in the 17th century during the reigns of King James and King Charles I, that eventually brought about the English Civil War, the brief rule of the Puritan Lord Protector of England Oliver Cromwell, the English Commonwealth, and as a result the political, religious, and civil liberty that is celebrated today in all English speaking countries.

The reign of King James I of England (1603–1625) saw the continued rise of the Puritan movement in England, that began during reign of Queen Elizabeth (1558–1603), and the continued clash with the authorities of the Church of England. This eventually led to the further alienation of Anglicans and Puritans from one another in the 17th century during the reign of King Charles I (1625–1649), that eventually brought about the English Civil War (1642–1651), the brief rule of the Puritan Lord Protector of England Oliver Cromwell (1653–1658), the English Commonwealth (1649–1660), and as a result the political, religious, and civil liberty that is celebrated today in all English speaking countries.

Under Charles I, the Puritans became a political force as well as a religious tendency in the country. Opponents of the royal prerogative became allies of Puritan reformers, who saw the Church of England moving in a direction opposite to what they wanted, and objected to increased Catholic influence both at Court and within the Church.

In Christianity, exorcism involves the practice of casting out one or more demons from a person whom they are believed to have possessed. The person performing the exorcism, known as an exorcist, is often a member of the Christian Church, or an individual thought to be graced with special powers or skills. The exorcist may use prayers and religious material, such as set formulas, gestures, symbols, icons, or amulets. The exorcist often invokes God, Jesus, angels and archangels, and various saints to aid with the exorcism. Christian exorcists most commonly cast out demons in Jesus' name.
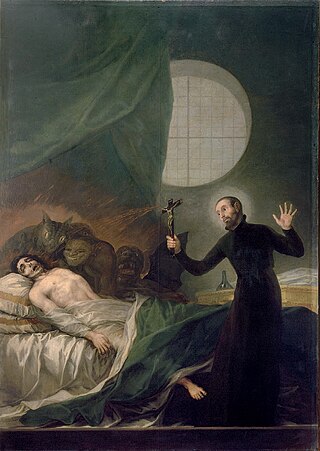
The Catholic Church authorizes the use of exorcism for those who are believed to be the victims of demonic possession. In Roman Catholicism, exorcism is a sacramental but not a sacrament, unlike baptism or confession. Unlike a sacrament, exorcism's "integrity and efficacy do not depend ... on the rigid use of an unchanging formula or on the ordered sequence of prescribed actions. Its efficacy depends on two elements: authorization from valid and licit Church authorities, and the faith of the exorcist." The Catechism of the Catholic Church states: "When the Church asks publicly and authoritatively in the name of Jesus Christ that a person or object be protected against the power of the Evil One and withdrawn from his dominion, it is called exorcism."
The Westminster Conference of 1559 was a religious disputation held early in the reign of Elizabeth I of England. Although the proceedings themselves were perfunctory, the outcome shaped the Elizabethan religious settlement and resulted in the authorisation of the 1559 Book of Common Prayer.

The English Protestant cleric John Foxe of the 16th century, known primarily if somewhat misleadingly as a martyrologist on the basis of his major work Actes and Monuments, wrote also on the interpretation of the Apocalypse, both at the beginning of his writing career in the 1550s, and right at the end of it, with his Eicasmi of 1587, the year of his death.
Edmund Hartley, dubbed the Tyldesley witch, was a cunning man who from 1595 until 1596 was alleged to have practised witchcraft at Cleworth Hall in Tyldesley, Lancashire. Hartley was hanged, twice, after a trial at Lancaster Assizes in March 1597.

The expression minor exorcism can be used in a technical sense or a general sense. The general sense indicates any exorcism which is not a solemn exorcism of a person believed to be possessed, including various forms of deliverance ministry. This article deals only with the technical sense which specifically refers to certain prayers used with persons preparing to become baptised members of the churches which makes use of such rites. These prayers request God's assistance so that the person to be baptised will be kept safe from the power of Satan or protected in a more general way from temptation.