Related Research Articles

Mithila is a proposed state in India, comprising the Maithili speaking region of Bihar and Jharkhand. The Maithili language has own traditional script, known as Mithilakshar. It is part of the historical Mithila region. The proposed state will also include Whole Angika and Bajjika speaking districts which are considered to be dialects of Maithili. What will be the capital city of Mithila, India is still to be decided. Historically the capital cities of Mithila have shifted between Janakpur (Nepal), Vaishali, Simraungadh (Nepal), Rajnagar (Madhubani) and Darbhanga to now Begusarai.

Maithili is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in parts of India and Nepal. It is native to the Mithila region, which encompasses parts of the Indian states of Bihar and Jharkhand as well as Nepal's eastern Terai. It is one of the 22 officially recognised languages of India and the second most spoken Nepalese language in Nepal.

Vidyapati, also known by the sobriquet Maithil Kavi Kokil, was a Maithili and Sanskrit polymath-poet-saint, playwright, composer, biographer, philosopher, law-theorist, writer, courtier and royal priest. He was a devotee of Shiva, but also wrote love songs and devotional Vaishnava songs. He knew Sanskrit, Prakrit, Apabhramsha, and Maithili.
Maithils, also known as Maithili people, are an Indo-Aryan ethno-linguistic group from the Indian subcontinent, who speak the Maithili language as their native language. They inhabit the Mithila region, which comprises North Bihar and parts of Jharkhand in India and some adjoining districts of Nepal constituting Madhesh Province. The Maithil region forms an important part of Hinduism as it is said to be the birthplace of Sita, the wife of Ram and incarnation of Lakshmi.
Panjis or Panji Prabandh are extensive genealogical records maintained among the Maithil Kayasthas and Maithil Brahmins of the Mithila region similar to the Hindu genealogy registers at Haridwar.
Saurath Sabha is a historical village situated approximately 6 km northeast of Madhubani in the Madhubani District of Bihar, India. It is famous for its annual gathering of thousands of Maithil Brahman to match couples during the Hindu months of Jyestha-Aasadh. The gathering is organised in an orchard covering 22 acres (bighas) of land, which are said to have been donated by the Maharaja of Darbhanga. It is an important social event in India that is focused on arranged marriages between Maithil men and women according to a reading of their lineage history by the registrars (Panjikars).

Mithila, also known as Tirhut, Tirabhukti and Mithilanchal is a geographical and cultural region of the Indian subcontinent bounded by the Mahananda River in the east, the Ganges in the south, the Gandaki River in the west and by the foothills of the Himalayas in the north. It comprises certain parts of Bihar and Jharkhand of India and adjoining districts of the Province No. 1, Bagmati Pradesh and Madhesh Province of Nepal. The native language in Mithila is Maithili, and its speakers are referred to as Maithils.
Mithila is a geographical and cultural region located in the Indian subcontinent. It comprises certain parts of Bihar of India and adjoining districts of the eastern Terai of Nepal. The native language is known as Maithili and its speakers are referred to as Maithils. The majority of the Mithila region falls within modern-day India, more specifically in the state of Bihar. Mithila is bounded in the north by the Himalayas, and in the south, west and east by the Ganges, Gandaki and Mahananda respectively. It extends into the southeastern Terai of Nepal. This region was also called Tirabhukti, the ancient name of Tirhut.
Bajjika is an Indo-Aryan language variety spoken in parts of eastern India and Nepal. It is closely related to Maithili.

Machher Jhol, Machha Jhola or Machhak Jhora is a traditional spicy fish curry in Bengali and Odia cuisines in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent. It is in the form of a very spicy stew or gravy that is served with rice. Machher Jhol is liberally seasoned with turmeric, garlic, onions, and grated ginger and Indian spices. Potatoes are added to the curry as a thickening agent. Tomatoes are also added to impart the dish with a reddish color which is preferred by the people of Bengal.

Thakur is a historical feudal title of the Indian subcontinent. It is also used as a surname in the present day. The female variant of the title is Thakurani or Thakurain, and is also used to describe the wife of a Thakur.
Maithil Brahmins are a Hindu Brahmin community from the Mithila region of the Indian subcontinent that comprises Tirhut, Madhubani, Darbhanga, Kosi, Purnia, Munger, Bhagalpur of Bihar; Bokaro in Jharkhand and Santhal Pargana divisions of India and some adjoining districts of Nepal. They are one of the five Pancha-Gauda Brahmin communities. The main language spoken by Maithil Brahmins is Maithili.
Jur Sital or Maithil New Year is the celebration of the first day of the Maithil new year also called Aakhar Bochhor. Maithils eat bari with bhaat on the day. This day which usually falls on 15 April on Gregorian calendar is celebrated by the Maithils in Mithila region of India and Nepal. This is also called Nirayana Mesh Sankranti and Tirhuta new year. The festive occasion is in keeping with the Tirhuta Panchang calendar used in the Mithila region.
Tirhuta Panchang is a calendar followed by the Maithili community of India and Nepal. This calendar is one of the many Hindu calendars. It is a tropical solar Hindu calendar in which the year begins on the first day of Baishakh month i.e. Mesh Sankranti. Every year, this day falls on 13/14 April of the Gregorian Calendar
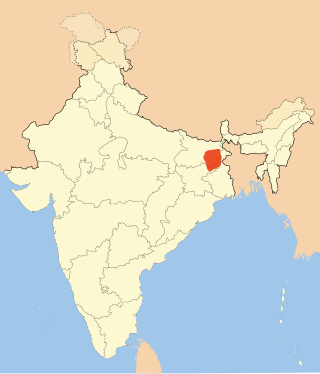
Angika is an Eastern Indo-Aryan language spoken in some parts of the Indian states of Bihar and Jharkhand, as well as in parts of Nepal.
Maithili may refer to:

Madhesh Province is a Nepalese province in southeastern Nepal. It was formed after the adoption of the Constitution of Nepal. It borders Koshi Pradesh to the east, Bagmati Province to the north, and India’s Bihar state to the south. It has an area of 9,661 km2 (3,730 sq mi) covering about 6.5% of the country's total area. It has a population of 6,126,288 as per the 2021 Nepal census, making it Nepal's most densely populated province and smallest province by area.

Maithili Music is one of the most ancient types of music in the Indian subcontinent. It originated from Mithila, a geographical and cultural region of the Indian subcontinent bounded by the Mahananda River in the east, the Ganges in the south, the Gandaki River in the west and by the foothills of the Himalayas in the north. It comprises certain parts of Bihar and Jharkhand of India and adjoining districts of the eastern Terai of Nepal. No one knows exactly when Maithili Music came into existence, probably due to the length of its history, but its age indicates that it might have helped other music develop and flourish in India and Nepal.It is believed that many new types of music forms have been sprouted from Maithili music as it is believed to be the oldest form of music is South Asia. Maithili music are played during a variety of ritual occasions, and it is believed that some of the most melodic music among them. The music was generally based on the daily life of a common man which made it relatable to the audience and hence accepted on mass. Although Maithili music is usually played by classical instruments, it has been modernized and now uses various modern instruments. Some significant contributors to this music style are Maha Kavi Vidyapati Thakur, Udit Narayan Jha, Sharda Sinha, Kunj Bihari Mishra, Haridwar Prasad Khandelwal, Dr. Shanti Jain, Rajni Pallavi, Poonam Mishra, Ranjana Jha and many more.
Choudhary Kedarnath Thakur was the Zamindar of Singhwara Estate. The estate situated in the Darbhanga district of Mithila in Bihar. He belonged to the Zamindar Family of Mithila (region). He held his title over his family estates in the Singhwara when such titles were abolished following the Independence of India.

Mithila State Movement is a 300-year-old movement advocating a separate Mithila state in India. This movement gained momentum in 1902 AD when Sir George Grierson, an official of the British Indian government, prepared a map of Mithila state by conducting a language-based survey. In 1881 AD, the word Mithila was added to the dictionary of the British India government. According to the founder, president Dr. Dhanakar Thakur of the International Maithili Council in the proposed Mithila state, 24 districts of Bihar and six districts of Jharkhand, a total of 30 districts, have been included, which has a population of about 70 million. At the same time, the area is 70 thousand square km.
References
- ↑ Das, Bhuban Mohan (1987). The Peoples of Assam. ISBN 9788121200936.