Related Research Articles
A minimum wage is the lowest remuneration that employers can legally pay their employees—the price floor below which employees may not sell their labor. Most countries had introduced minimum wage legislation by the end of the 20th century. Because minimum wages increase the cost of labor, companies often try to avoid minimum wage laws by using gig workers, by moving labor to locations with lower or nonexistent minimum wages, or by automating job functions. Minimum wage policies can vary significantly between countries or even within a country, with different regions, sectors, or age groups having their own minimum wage rates. These variations are often influenced by factors such as the cost of living, regional economic conditions, and industry-specific factors.

Unemployment, according to the OECD, is people above a specified age not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the reference period.

The United States Department of Labor (DOL) is one of the executive departments of the U.S. federal government. It is responsible for the administration of federal laws governing occupational safety and health, wage and hour standards, unemployment benefits, reemployment services, and occasionally, economic statistics. It is headed by the secretary of labor, who reports directly to the president of the United States and is a member of the president's Cabinet.

The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics and statistics and serves as a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System. The BLS collects, processes, analyzes, and disseminates essential statistical data to the American public, the U.S. Congress, other Federal agencies, State and local governments, business, and labor representatives. The BLS also serves as a statistical resource to the United States Department of Labor, and conducts research measuring the income levels families need to maintain a satisfactory quality of life.

The labor force is the actual number of people available for work and is the sum of the employed and the unemployed. The U.S. labor force reached a record high of 168.7 million civilians in September 2024. In February 2020, at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States, there were 164.6 million civilians in the labor force. Before the pandemic, the U.S. labor force had risen each year since 1960 with the exception of the period following the Great Recession, when it remained below 2008 levels from 2009 to 2011. In 2021, The Great Resignation resulted in record numbers in voluntary turnover for American workers.

Nonfarm payroll employment is a compiled name for goods, construction and manufacturing companies in the US. Approximately 80% of the workforce is accounted for nonfarm payrolls and it excludes farm workers, private household employees, actively serving military or non-profit organization employees. Approximately 131,000 businesses and government agencies, which amounts to around 670,000 worksites, are surveyed on a monthly basis.

The Oklahoma Employment Security Commission (OESC) is an independent agency of the state of Oklahoma responsible for providing employment services to the citizens of Oklahoma. The commission is part of a national network of employment service agencies and is funded by money from the United States Department of Labor. The commission is also responsible for administering the Workforce Investment Act of 1998 on behalf of the state.
The National Compensation Survey (NCS) is produced by the United States Department of Labor's Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), measuring occupational earnings, compensation costs, benefit incidence rates, and plan provisions. It is used to adjust the federal wage schedule for all federal employees. Detailed occupational earnings are available for both metropolitan and non-metropolitan areas, broad geographic regions, and on a national basis. The NCS' Employment Cost Index measures changes in labor costs. The average costs of employee compensation per hour worked is presented in the Employer Costs for Employee Compensation (ECEC).

Initial jobless claims are a data point issued by the U.S. Department of Labor as part of its weekly Unemployment Insurance Weekly Claims Report. Initial jobless claims refer to claims for unemployment benefits filed by unemployed individuals with state unemployment agencies.

The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development defines the employment rate as the employment-to-population ratio. This is a statistical ratio that measures the proportion of a country's working age population that is employed. This includes people that have stopped looking for work. The International Labour Organization states that a person is considered employed if they have worked at least 1 hour in "gainful" employment in the most recent week.
The Occupational Employment and Wage Statistics) (OEWS) survey is a semi-annual survey of approximately 200,000 non-farm business establishments conducted by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), headquartered in Washington, DC with six regional offices and one office in each state. Until the spring of 2021 it was officially called the Occupational Employment Statistics (OES), and it is often cited or documented with that name or abbreviation.

The Oklahoma Department of Labor (ODOL) is an agency of the government of Oklahoma that is headed by the Oklahoma Labor Commissioner, a statewide elected position. ODOL is responsible for supervising the administration of all state laws relating to labor and workplace safety and gathers and publishes information about the workforce of Oklahoma.
The New York State Department of Labor is the department of the New York state government that enforces labor law and administers unemployment benefits.
Iowa Workforce Development is a government agency in the American state of Iowa, responsible for overseeing workplace safety, workers' compensation, unemployment insurance and job training services. It was formed in May 1996.

The International Labor Comparisons Program (ILC) of the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) adjusts economic statistics to a common conceptual framework in order to make data comparable across countries. Its data can be used to evaluate the economic performance of one country relative to that of other countries and to assess international competitiveness.
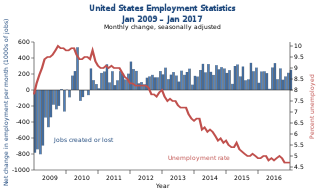
Unemployment in the United States discusses the causes and measures of U.S. unemployment and strategies for reducing it. Job creation and unemployment are affected by factors such as economic conditions, global competition, education, automation, and demographics. These factors can affect the number of workers, the duration of unemployment, and wage levels.

The Wisconsin Department of Workforce Development (DWD) is an agency of the Wisconsin state government responsible for providing services to Wisconsin workers, employers, and job-seekers to meet Wisconsin's workforce needs. To effect its mission, the Department administers unemployment benefits and workers' compensation programs for the state of Wisconsin; ensures compliance with state laws on wages and discrimination; provides job resources, training, and employment assistance for job-seekers; and engages with employers to help them find and maintain adequate staffing for their businesses.

Job creation and unemployment are affected by factors such as aggregate demand, global competition, education, automation, and demographics. These factors can affect the number of workers, the duration of unemployment, and wage rates.

Katharine G. Abraham is an American economist who is a Distinguished University Professor of economics and survey methodology at the University of Maryland. She was commissioner of the Bureau of Labor Statistics from 1993–2001 and a member of the Council of Economic Advisers from 2011–2013. She was elected a member of the National Academy of Sciences in 2022 and, in 2024, was elected to be the President-Elect and then the President of the American Economic Association.
On the 1st May 2014 Seattle's Mayor Ed Murray announced plans to increase Seattle's minimum wage to $15 per hour incrementally over the next few years. Seattle was the first big city in the United States to raise its minimum wage to $15 after the rise of the "Fight for 15 movement". This policy decision resulted in Seattle having the highest minimum wage of any major city in the United States. Once Seattle raised its minimum wage many other major cities around the country also took action to increase the pay of low wage workers. There has been much debate over the effects the increases to the minimum wage have had on employment and overall economic conditions in Seattle. To determine the impacts of the policy a number of studies have been conducted; the most notable being research by the University of Washington and the University of California, Berkeley.
References
- ↑ Previously known as state employment security agencies or SESAs.
- ↑ Workforce Information Advisory Council (16 November 2016). "Key Resources for Workforce and Labor Market Information" (PDF). United States Department of Labor. Retrieved 2024-11-05.
- ↑ Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages
- ↑ Risher, Howard (13 February 2020). "The Gig Economy and BLS Surveys". Government Executive .
- Employment and wage profile of the Louisiana and Texas counties affected by Hurricane Ike (PDF) (Report). Bureau of Labor Statistics. 26 September 2008.