Related Research Articles

Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum and alternating current. Oscillations can be used in physics to approximate complex interactions, such as those between atoms.

A periodic function also called a periodic waveform, is a function that repeats its values at regular intervals or periods. The repeatable part of the function or waveform is called a cycle. For example, the trigonometric functions, which repeat at intervals of radians, are periodic functions. Periodic functions are used throughout science to describe oscillations, waves, and other phenomena that exhibit periodicity. Any function that is not periodic is called aperiodic.

Climatology or climate science is the scientific study of Earth's climate, typically defined as weather conditions averaged over a period of at least 30 years. Climate concerns the atmospheric condition during an extended to indefinite period of time; weather is the condition of the atmosphere during a relative brief period of time. The main topics of research are the study of climate variability, mechanisms of climate changes and modern climate change. This topic of study is regarded as part of the atmospheric sciences and a subdivision of physical geography, which is one of the Earth sciences. Climatology includes some aspects of oceanography and biogeochemistry.
The quasi-biennial oscillation (QBO) is a quasiperiodic oscillation of the equatorial zonal wind between easterlies and westerlies in the tropical stratosphere with a mean period of 28 to 29 months. The alternating wind regimes develop at the top of the lower stratosphere and propagate downwards at about 1 km (0.6 mi) per month until they are dissipated at the tropopause. Downward motion of the easterlies is usually more irregular than that of the westerlies. The amplitude of the easterly phase is about twice as strong as that of the westerly phase. At the top of the vertical QBO domain, easterlies dominate, while at the bottom, westerlies are more likely to be found. At the 30 mb level, with regards to monthly mean zonal winds, the strongest recorded easterly was 29.55 m/s in November 2005, while the strongest recorded westerly was only 15.62 m/s in June 1995.

El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a global climate phenomenon that emerges from variations in winds and sea surface temperatures over the tropical Pacific Ocean. Those variations have an irregular pattern but do have some semblance of cycles. The occurrence of ENSO is not predictable. It affects the climate of much of the tropics and subtropics, and has links (teleconnections) to higher-latitude regions of the world. The warming phase of the sea surface temperature is known as "El Niño" and the cooling phase as "La Niña". The Southern Oscillation is the accompanying atmospheric oscillation, which is coupled with the sea temperature change.
The Tropical Ocean Global Atmosphere program (TOGA) was a ten-year study (1985–1994) of the World Climate Research Programme (WCRP), aimed specifically at the prediction of climate phenomena on time scales of months to years.
Periodicity or periodic may refer to:
This glossary of climate change is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to climate change, global warming, and related topics.

The Pacific decadal oscillation (PDO) is a robust, recurring pattern of ocean-atmosphere climate variability centered over the mid-latitude Pacific basin. The PDO is detected as warm or cool surface waters in the Pacific Ocean, north of 20°N. Over the past century, the amplitude of this climate pattern has varied irregularly at interannual-to-interdecadal time scales. There is evidence of reversals in the prevailing polarity of the oscillation occurring around 1925, 1947, and 1977; the last two reversals corresponded with dramatic shifts in salmon production regimes in the North Pacific Ocean. This climate pattern also affects coastal sea and continental surface air temperatures from Alaska to California.
In mathematics and theoretical physics, quasiperiodic motion is motion on a torus that never comes back to the same point. This behavior can also be called quasiperiodic evolution, dynamics, or flow. The torus may be a generalized torus so that the neighborhood of any point is more than two-dimensional. At each point of the torus there is a direction of motion that remains on the torus. Once a flow on a torus is defined or fixed, it determines trajectories. If the trajectories come back to a given point after a certain time then the motion is periodic with that period, otherwise it is quasiperiodic.

The Pearson–Anson effect, discovered in 1922 by Stephen Oswald Pearson and Horatio Saint George Anson, is the phenomenon of an oscillating electric voltage produced by a neon bulb connected across a capacitor, when a direct current is applied through a resistor. This circuit, now called the Pearson-Anson oscillator, neon lamp oscillator, or sawtooth oscillator, is one of the simplest types of relaxation oscillator. It generates a sawtooth output waveform. It has been used in low frequency applications such as blinking warning lights, stroboscopes, tone generators in electronic organs and other electronic music circuits, and in time base generators and deflection circuits of early cathode-ray tube oscilloscopes. Since the development of microelectronics, these simple negative resistance oscillators have been superseded in many applications by more flexible semiconductor relaxation oscillators such as the 555 timer IC.

Tropical cyclogenesis is the development and strengthening of a tropical cyclone in the atmosphere. The mechanisms through which tropical cyclogenesis occur are distinctly different from those through which temperate cyclogenesis occurs. Tropical cyclogenesis involves the development of a warm-core cyclone, due to significant convection in a favorable atmospheric environment.
In X-ray astronomy, quasi-periodic oscillation (QPO) is the manner in which the X-ray light from an astronomical object flickers about certain frequencies. In these situations, the X-rays are emitted near the inner edge of an accretion disk in which gas swirls onto a compact object such as a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole.
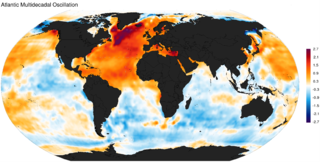
The Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO), also known as Atlantic Multidecadal Variability (AMV), is the theorized variability of the sea surface temperature (SST) of the North Atlantic Ocean on the timescale of several decades.

Drought has resulted in millions of deaths in India over the years. Indian agriculture is heavily dependent on the country's climate: a favorable monsoon is critical to securing water for irrigating India's crops. In parts of India, failure of the monsoons causes water shortages, resulting in poor yields. This is particularly true of major drought-prone regions southeastern Maharashtra, northern Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, Gujarat, Telangana, and Rajasthan.
This is a list of climate change topics.
The Atlantic Equatorial Mode or Atlantic Niño is a quasiperiodic interannual climate pattern of the equatorial Atlantic Ocean. It is the dominant mode of year-to-year variability that results in alternating warming and cooling episodes of sea surface temperatures accompanied by changes in atmospheric circulation. The term Atlantic Niño comes from its close similarity with the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) that dominates the tropical Pacific basin. For this reason, the Atlantic Niño is often called the little brother of El Niño. The Atlantic Niño usually appears in northern summer, and is not the same as the Atlantic Meridional (Interhemispheric) Mode that consists of a north-south dipole across the equator and operates more during northern spring. The equatorial warming and cooling events associated with the Atlantic Niño are known to be strongly related to rainfall variability over the surrounding continents, especially in West African countries bordering the Gulf of Guinea. Therefore, understanding of the Atlantic Niño has important implications for climate prediction in those regions. Although the Atlantic Niño is an intrinsic mode to the equatorial Atlantic, there may be a tenuous causal relationship between ENSO and the Atlantic Niño in some circumstances.
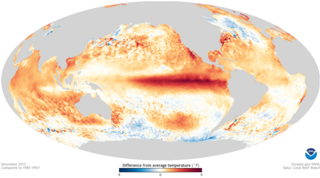
The 2014–2016 El Niño was the strongest El Niño event on record, with unusually warm waters developing between the coast of South America and the International Date Line. These unusually warm waters influenced the world's weather in a number of ways, which in turn significantly affected various parts of the world. These included drought conditions in Venezuela, Australia and a number of Pacific islands while significant flooding was also recorded. During the event, more tropical cyclones than normal occurred within the Pacific Ocean, while fewer than normal occurred in the Atlantic Ocean.

A westerly wind burst (WWB) or westerly wind event (WWE) is a phenomenon commonly associated with El Niño events, whereby the typical east-to-west trade winds across the equatorial Pacific shift to west-to-east.

Effects of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation in Australia are present across most of Australia, particularly the north and the east, and are one of the main climate drivers of the country. Associated with seasonal abnormality in many areas in the world, Australia is one of the continents most affected and experiences extensive droughts alongside considerable wet periods that cause major floods. There exist three phases — El Niño, La Niña, and Neutral, which help to account for the different states of ENSO. Since 1900, there have been 28 El Niño and 19 La Niña events in Australia including the current 2023 El Niño event, which was declared on 17th of September in 2023. The events usually last for 9 to 12 months, but some can persist for two years, though the ENSO cycle generally operates over a time period from one to eight years.
References
- ↑ Periodicity – Definition and More from the Free Merriam-Webster Dictionary
- ↑ Quasiperiodic – Definition and More from the Free Merriam-Webster Dictionary
- ↑ Not Found – UNISDR [ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ The meteorological glossary: 2d ed. 1930. Meteorological Office, Great Britain. "Certain phenomena which recur more or less regularly but without the exactness of truly periodic phenomena are termed quasi-periodic."
- 1 2 3 Potgieter, Andries; Zhao, Yan; Tejada, Pablo; Chenu, Karine; Zhang, Yifan; Porker, Kenton; Biddulph, Ben; Dang, Yash; Neale, Tim; Roosta, Fred; Chapman, Scott (2021). "Evolution and application of digital technologies to predict crop type and crop phenology in agriculture". in silico Plants . 3 (1). Oxford University Press (OUP) (The Annals of Botany Company (AoB)). doi: 10.1093/insilicoplants/diab017 . hdl: 11343/280690 . ISSN 2517-5025. This review cites this study: Zheng, Bangyou; Chapman, Scott; Chenu, Karine (2018). "The Value of Tactical Adaptation to El Niño–Southern Oscillation for East Australian Wheat". Climate . 6 (3): 77. Bibcode:2018Clim....6...77Z. doi: 10.3390/cli6030077 . CK ORCID 0000-0001-7273-2057.