
Heathrow Airport, originally called London Airport until 1966 and now known as London Heathrow, is a major international airport in London, England. With Gatwick, City, Luton, Stansted and Southend, it is the largest of the six international airports serving serving Greater London. The airport facility is owned and operated by Heathrow Airport Holdings. In 2021, it was the seventh-busiest airport in the world by international passenger traffic and eighth-busiest in Europe by total passenger traffic.

London Stansted Airport is an international airport located near Stansted Mountfitchet, Essex, England, 42 mi (68 km) northeast of Central London.

Gatwick Airport, also known as London Gatwick, is a major international airport near Crawley, West Sussex, England, 29.5 miles (47.5 km) south of Central London. In 2021, Gatwick was the third-busiest airport by total passenger traffic in the UK, after Heathrow and Stanstead Airports, and was the 36th-busiest in Europe by total passenger traffic. It covers a total area of 674 hectares.

Glasgow Airport, also known as Glasgow International Airport, formerly Abbotsinch Airport, is an international airport in Scotland. It is located in Paisley, Renfrewshire, 8.6 nautical miles west of Glasgow city centre. In 2019, the airport handled 8.84 million passengers, an 8.4% annual decrease, making it the second-busiest in Scotland, after Edinburgh Airport, and the ninth-busiest airport in the United Kingdom.

Edinburgh Airport is an airport located in the Ingliston area of Edinburgh, Scotland. It was the busiest airport in Scotland in 2019, handling over 14.7 million passengers. It was also the sixth-busiest airport in the United Kingdom by total passengers in 2019. It is located 5 NM west of the city centre, just off the M8 and M9 motorways. It is owned and operated by Global Infrastructure Partners, who are also a minority shareholder of Gatwick Airport. The airport has one runway and one passenger terminal, and employs about 2,500 people.
Heathrow Airport Holdings is the United Kingdom-based operator of Heathrow Airport. The company also operated Gatwick Airport, Stansted Airport, Edinburgh Airport and several other UK airports, but was forced by the Competition Commission to sell them in order to break up a monopoly. It was formed by the privatisation of the British Airports Authority as BAA plc as part of Margaret Thatcher's moves to privatise government-owned assets, and was once a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index.

Heathrow Airtrack was a proposed railway link in the United Kingdom which would link Heathrow Airport in west London to London Waterloo railway station in Central London.

Plane Stupid is a UK-focused group of environmental protesters who state their aim as wanting to see an end to airport expansion for what it sees as "unnecessary and unsustainable" flights. It is a loose association of autonomous regional groups, and is funded by donations.

Heathrow Terminal 5 is an airport terminal at Heathrow Airport, the main airport serving London. Opened in 2008, the main building in the complex is the largest free-standing structure in the United Kingdom. Terminal 5 is currently used exclusively as one of the three global hubs of IAG, served by British Airways and Iberia, with the others being London Gatwick South and Terminal 4 Madrid. Prior to 2012, the terminal was used solely by British Airways.

Heathrow Terminal 4 is an airport terminal at Heathrow Airport, the main airport serving London, England, situated to the south of the southern runway, next to the cargo terminal. It is connected to Heathrow Terminals 2 and 3 by the vehicular Heathrow Cargo Tunnel, and by rail with the Heathrow Terminal 4 tube and Heathrow Terminal 4 railway stations. The terminal was temporarily closed in 2020. Built at a cost of £200 million, Terminal 4 was opened by the Prince and Princess of Wales on 1 April 1986. British Airways was the main airline operating from the terminal from 1986 until its move to Terminal 5 on 29 October 2009, eventually making Terminal 4 the Heathrow base for airlines of the SkyTeam airline alliance.

Heathrow Terminal 1 is a disused airport terminal at London Heathrow Airport that was in operation between 1968 and 2015. When it was officially opened by Queen Elizabeth II in April 1969 it was the largest new airport terminal in western Europe. Prior to its closure on 29 June 2015 it had only been handling twenty daily flights by British Airways to nine destinations. In May 2017 the contents of the terminal were put up for auction. The footprint of Terminal 1 was planned to be used for construction of the second phase of Heathrow Terminal 2.
The expansion of Heathrow Airport is a series of proposals to add to the runways at London's busiest airport beyond its two long runways which are intensively used to serve four terminals and a large cargo operation. The plans are those presented by Heathrow Airport Holdings and an independent proposal by Heathrow Hub with the main object of increasing capacity.

Heathrow Terminal 2, also known as The Queen's Terminal, is an airport terminal at Heathrow Airport, the main airport serving London, United Kingdom. The new development was originally named Heathrow East Terminal, and occupies the sites where the previous Terminal 2 and the Queens Building stood. It was designed by Luis Vidal + Architects and opened on 4 June 2014. The original Terminal 2 opened in 1955 as the Europa Building and was the airport's oldest terminal.

Compass Centre is an office building on the grounds of Heathrow Airport in the London Borough of Hillingdon. The building serves as Heathrow Airport Holdings's head office. Compass Centre previously served as a British Airways flight crew centre.

City Place Gatwick is an office complex located on the property of London Gatwick Airport in Crawley, West Sussex, England. The complex includes four buildings: The Beehive, an approximately 20,000-square-foot (1,900 m2) former terminal building at Gatwick Airport located on a 2.0-acre (0.81 ha) site; 1 City Place a 131,500-square-foot (12,220 m2) facility on a 4.2-acre (1.7 ha) site, 2 City Place, a 85,000-square-foot (7,900 m2) building on a 1.9 acres (0.77 ha) plot, and 3 City Place, a 65,000-square-foot (6,000 m2) building on a 1.06-acre (0.43 ha) plot. Hamiltons Architects designed the "L" shaped 3 City Place.
In its early years what is now Heathrow Airport was the Great West Aerodrome, sometimes known as Heathrow Aerodrome.

Heathwick is an informal name for a 2011 proposal to create a high-speed rail link between London's Heathrow and Gatwick airports, in effect to combine them into a single airport. Proponents argue this would balance their capacity and so reduce the need to add more runways to Heathrow, or more airports in the south-east of England. In 2018 the similar project HS4Air was proposed.
The expansion of Gatwick Airport has involved several proposals aimed at increasing airport capacity in south east England and relieving congestion at the main hub airport Heathrow.
Gatwick Airport was in Surrey until 1974, when it became part of West Sussex as a result of a county boundary change. The original, pre-World War II airport was built on the site of a manor in the parish of Charlwood. The land was first used as an aerodrome in the 1920s, and in 1933 commercial flights there were approved by the Air Ministry.
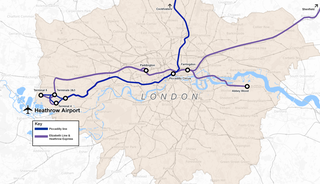
Over the years, a number of transport proposals have been made to improve public access to Heathrow Airport, near London in the United Kingdom.
















