
Puget Sound is a sound on the northwestern coast of the U.S. state of Washington. It is a complex estuarine system of interconnected marine waterways and basins. A part of the Salish Sea, Puget Sound has one major and two minor connections to the Strait of Juan de Fuca, which in turn connects to the open Pacific Ocean. The major connection is Admiralty Inlet; the minor connections are Deception Pass and the Swinomish Channel.

The San Juan Islands is an archipelago in the Pacific Northwest of the United States between the U.S. state of Washington and Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. The San Juan Islands are part of Washington state, and form the core of San Juan County.

The Strait of Juan de Fuca is a body of water about 96 miles long that is the Salish Sea's main outlet to the Pacific Ocean. The international boundary between Canada and the United States runs down the centre of the Strait.

Jefferson County is a county located in the U.S. state of Washington. As of the 2020 census, the population was 32,977. The county seat and only incorporated city is Port Townsend. The county is named for Thomas Jefferson.
Keystone is a small unincorporated community on Whidbey Island in Island County, Washington, in the northwestern United States. It is near the Keystone ferry landing, a dock at Keystone Harbor for the Washington State Ferries' Coupeville to Port Townsend route. The route provides a maritime link for State Route 20 across Admiralty Inlet to the Olympic Peninsula. Since its establishment in the 1930s, the ferry route to Port Townsend was known as the Keystone-Port Townsend Ferry; the name was changed in 2010 at the suggestion of the Central Whidbey Chamber of Commerce in order to avoid confusion from tourists and visitors to Whidbey Island.

The Klallam are a Coast Salish people Indigenous to the northern Olympic Peninsula. The language of the Klallam is the Klallam language, a language closely related to the North Straits Salish languages. The Klallam are today citizens of four recognized bands: Three federally-recognized tribes in the United States and one band government in Canada. Two Klallam tribes, the Jamestown S'Klallam and Lower Elwha Klallam, live on the Olympic Peninsula, and one, the Port Gamble S'Klallam, on the Kitsap Peninsula in Washington state. In Canada, the Scia'new First Nation is based at Becher Bay on southern Vancouver Island in British Columbia.
The Jamestown S'Klallam Tribe is a federally recognized tribe of S'Klallam or Klallam Native Americans. They are on the northern Olympic Peninsula of Washington state in the northwestern United States.
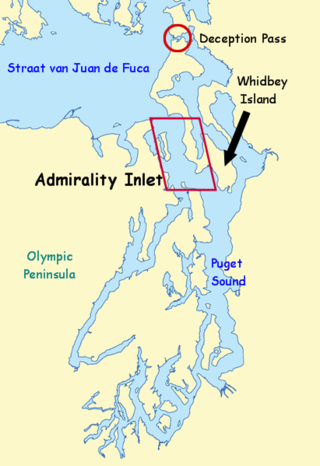
Admiralty Inlet is a strait in the U.S. state of Washington connecting the eastern end of the Strait of Juan de Fuca to Puget Sound. It lies between Whidbey Island and the northeastern part of the Olympic Peninsula.

The Dungeness River is a 28-mile (45 km) long river located in the Olympic Peninsula in the U.S. state of Washington. It rises near Mount Constance in the Olympic Mountains within the Olympic National Park, flows through the Buckhorn Wilderness, passes by the town of Sequim, and empties into the Strait of Juan de Fuca at Dungeness Bay, behind the Dungeness Spit. One of its main tributaries is the Gray Wolf River. It is crossed by the Dungeness River Bridge.

Dungeness Spit is a sand spit jutting out approximately 5 miles (8 km) from the northern edge of the Olympic Peninsula in northeastern Clallam County, Washington into the Strait of Juan de Fuca. It is the longest natural sand spit in the United States. The spit is growing in length by about 15 feet (4.6 m) per year. The body of water it encloses is called Dungeness Bay.

Point Wilson is at the end of the Quimper Peninsula, a northeast extension of the Olympic Peninsula and the northeasternmost point of Jefferson County, Washington, United States, approximately two miles north of the Port Townsend business district.

Discovery Bay is an unincorporated community in Jefferson County, Washington. The community of Discovery Bay is an area near the intersection of U.S. Route 101 and State Route 20, at the foot of Discovery Bay – roughly midway between the larger communities of Port Townsend to the northeast and Sequim to the northwest. It is a mix of residential areas and commercial enterprises, including crabbing, oystering, clamming, timbering, security training and gravel extraction. A few restaurants and stores on US 101 near SR 20 primarily serve drivers and truckers along US 101.

Manuel Quimper Benítez del Pino was a Spanish Peruvian explorer, cartographer, naval officer, and colonial official. He participated in charting the Strait of Juan de Fuca and the Sandwich Islands in the late 18th century. He was later appointed a colonial governor in his native Peru at the beginning of the fight for independence there. He retired to Spain, but was able to return to Peru where he served as a naval officer in the new republic and pursued a literary career, publishing over 20 books about his experiences before his death there in Lima.

Rosario Strait is a strait in northern Washington state, separating San Juan County and Skagit and Whatcom Counties. It extends from the Strait of Juan de Fuca about 23 kilometres (14 mi) north to the Strait of Georgia. The USGS defines its southern boundary as a line extending from Point Colville on Lopez Island to Rosario Head on Fidalgo Island, and its northern boundary as a line from Point Migley on Lummi Island to the east tip of Puffin Island and then to Point Thompson on Orcas Island. Rosario Strait runs north-south between Lopez, Decatur, Blakely, and Orcas Islands on the west, and Fidalgo, Cypress, Sinclair, and Lummi Islands on the east.

Saratoga Passage lies in Puget Sound between Whidbey Island and Camano Island.

Freshwater Bay is a bay upon the Strait of Juan de Fuca on the northern coast of the Olympic Peninsula, 10 miles (16 km) west of Port Angeles off State Route 112 and 3 miles (4.8 km) north on Freshwater Bay Road. It is just east of Striped Peak. The bay has water access via a small boat ramp, although launching is only recommended for small boats and kayaks. Launching and retrieving of boats can be especially difficult at low tide, as the bay is very shallow, leaving the small paved ramp completely exposed. The launch ramp has no dock.
Juan Carrasco was a Spanish naval officer, explorer, and navigator. He is remembered mainly for his work in the Pacific Northwest during the late 18th century. He was second in command of the 1791 voyage of José María Narváez, the first European exploration of the Strait of Georgia.
Princess Royal was a British merchant ship that sailed on fur trading ventures in the late 1780s, and was captured at Nootka Sound by Esteban José Martínez of Spain during the Nootka Crisis of 1789. Called Princesa Real while under the Spanish Navy, the vessel was one of the important issues of negotiation during the first Nootka Convention and the difficulties in carrying out the agreements. The vessel also played an important role in both British and Spanish exploration of the Pacific Northwest and the Hawaiian Islands. In 1790, while under Spanish control, Princesa Real carried out the first detailed examination of the Strait of Juan de Fuca by non-indigenous peoples, finding, among other places, the San Juan Islands, Haro Strait, Esquimalt Harbour near present-day Victoria, British Columbia, and Admiralty Inlet.

Ediz Hook is a 3-mile-long (4.8 km) sand spit that extends from northern shore of the Olympic Peninsula at Port Angeles in northcentral Clallam County, Washington, USA, northeasterly into the Strait of Juan de Fuca, located about 15-mile (24 km) west of the larger Dungeness Spit. It is relatively narrow at points, but broader toward the base and the northeast tip.

Discovery Bay is a small bay connected to the Strait of Juan de Fuca on the coast of the Olympic Peninsula in Washington state; it was also historically called Port Discovery. An unincorporated community also named Discovery Bay lies in Jefferson County at the southern end of the bay.

















