Related Research Articles
GTPases are a large family of hydrolase enzymes that bind to the nucleotide guanosine triphosphate (GTP) and hydrolyze it to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The GTP binding and hydrolysis takes place in the highly conserved P-loop "G domain", a protein domain common to many GTPases.
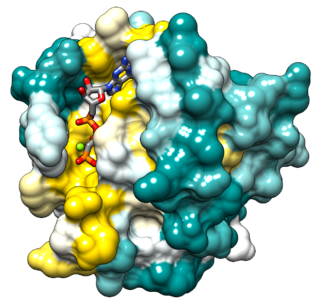
Ras, from "Rat sarcoma virus", is a family of related proteins that are expressed in all animal cell lineages and organs. All Ras protein family members belong to a class of protein called small GTPase, and are involved in transmitting signals within cells. Ras is the prototypical member of the Ras superfamily of proteins, which are all related in three-dimensional structure and regulate diverse cell behaviours.
Small GTPases, also known as small G-proteins, are a family of hydrolase enzymes that can bind and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP). They are a type of G-protein found in the cytosol that are homologous to the alpha subunit of heterotrimeric G-proteins, but unlike the alpha subunit of G proteins, a small GTPase can function independently as a hydrolase enzyme to bind to and hydrolyze a guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to form guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The best-known members are the Ras GTPases and hence they are sometimes called Ras subfamily GTPases.
The Rab family of proteins is a member of the Ras superfamily of small G proteins. Approximately 70 types of Rabs have now been identified in humans. Rab proteins generally possess a GTPase fold, which consists of a six-stranded beta sheet which is flanked by five alpha helixes. Rab GTPases regulate many steps of membrane trafficking, including vesicle formation, vesicle movement along actin and tubulin networks, and membrane fusion. These processes make up the route through which cell surface proteins are trafficked from the Golgi to the plasma membrane and are recycled. Surface protein recycling returns proteins to the surface whose function involves carrying another protein or substance inside the cell, such as the transferrin receptor, or serves as a means of regulating the number of a certain type of protein molecules on the surface.
GTPase-activating proteins or GTPase-accelerating proteins (GAPs) are a family of regulatory proteins whose members can bind to activated G proteins and stimulate their GTPase activity, with the result of terminating the signaling event. GAPs are also known as RGS protein, or RGS proteins, and these proteins are crucial in controlling the activity of G proteins. Regulation of G proteins is important because these proteins are involved in a variety of important cellular processes. The large G proteins, for example, are involved in transduction of signaling from the G protein-coupled receptor for a variety of signaling processes like hormonal signaling, and small G proteins are involved in processes like cellular trafficking and cell cycling. GAP's role in this function is to turn the G protein's activity off. In this sense, GAPs function is opposite to that of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs), which serve to enhance G protein signaling.

Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are proteins or protein domains that activate monomeric GTPases by stimulating the release of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) to allow binding of guanosine triphosphate (GTP). A variety of unrelated structural domains have been shown to exhibit guanine nucleotide exchange activity. Some GEFs can activate multiple GTPases while others are specific to a single GTPase.

Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor 3 also known as exchange factor directly activated by cAMP 1 (EPAC1) or cAMP-regulated guanine nucleotide exchange factor I (cAMP-GEFI) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAPGEF3 gene.

RhoG is a small monomeric GTP-binding protein, and is an important component of many intracellular signalling pathways. It is a member of the Rac subfamily of the Rho family of small G proteins and is encoded by the gene RHOG.

Ras-related protein Rab-5B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAB5B gene.

Ras and Rab interactor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RIN1 gene.
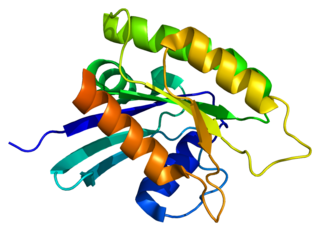
Ras-related protein M-Ras, also known as muscle RAS oncogene homolog and R-Ras3, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MRAS gene on chromosome 3. It is ubiquitously expressed in many tissues and cell types. This protein functions as a signal transducer for a wide variety of signaling pathways, including those promoting neural and bone formation as well as tumor growth. The MRAS gene also contains one of 27 SNPs associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease.

Mitochondrial GTPase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MTG1 gene.

Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAPGEF2 gene.

Dock7, also known as Zir2, is a large protein involved in intracellular signalling networks. It is a member of the DOCK-C subfamily of the DOCK family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) which function as activators of small G proteins. Dock7 activates isoforms of the small G protein Rac.

Dock4, also known as DOCK4, is a large protein involved in intracellular signalling networks. It is a member of the DOCK-B subfamily of the DOCK family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) which function as activators of small G proteins. Dock4 activates the small G proteins Rac and Rap1.

GTPase activating protein and VPS9 domains 1, also known as GAPVD1, Gapex-5 and RME-6 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the GAPVD1 gene.

Dock6, also known as Zir1 is a large protein involved in intracellular signalling networks. It is a member of the DOCK-C subfamily of the DOCK family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors which function as activators of small G proteins.

Dock11, also known as Zizimin2, is a large protein involved in intracellular signalling networks. It is a member of the DOCK-D subfamily of the DOCK family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) which function as activators of small G proteins. Dock11 activates the small G protein Cdc42.
Eps15 homology domain-containing protein 3, abbreviated as EDH3 and also known as PAST3, is a protein encoded by the EHD3 gene. It has been observed in humans, mice and rats. It belongs to the EHD protein family, a group of four membrane remodeling proteins related to the Dynamin superfamily of large GTPases. Although the four of them are 70-80% amino acid identical, they all have different locations. Its main function is related to endocytic transport.

The SNX8 is a sorting nexin protein involved in intracellular molecular traffic from the early endosomes to the TGN. It is suggested that it acts as an adaptor protein in events related to immune response and cholesterol regulation, for example. As a protein of the SNXs family, the SNX8 is formed of 465 aminoacids and presents a BAR-domain and a PX-domain which are very relevant in relation to its functions. Furthermore, SNX8 study is motivated by its medical significance in relation to diseases such as Alzheimer's Disease, cancer, neurodevelopmental malformations and to its role in fighting against viral infections.
References
- 1 2 Hunker CM, Galvis A, Kruk I, Giambini H, Veisaga ML, Barbieri MA (Feb 2006). "Rab5-activating protein 6, a novel endosomal protein with a role in endocytosis". Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 340 (3): 967–75. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.12.099. PMID 16410077.
- ↑ Rabgef1 Homo Sapiens 27342 Archived 2012-08-02 at archive.today