RAS guanyl releasing protein 4 is a protein in humans that is encoded by the RASGRP4 gene in chromosome 19. [1]

Proteins are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.

In biology, a gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA or RNA that codes for a molecule that has a function. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic trait. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes as well as gene–environment interactions. Some genetic traits are instantly visible, such as eye color or number of limbs, and some are not, such as blood type, risk for specific diseases, or the thousands of basic biochemical processes that constitute life.
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Ras guanyl nucleotide-releasing protein (RasGRP) family of Ras guanine nucleotide exchange factors. It contains a Ras exchange motif, a diacylglycerol-binding domain, and two calcium-binding EF hands. This protein was shown to activate H-Ras in a cation-dependent manner in vitro. Expression of this protein in myeloid cell lines was found to be correlated with elevated level of activated RAS protein, and the RAS activation can be greatly enhanced by phorbol ester treatment, which suggested a role of this protein in diacylglycerol regulated cell signaling pathways. Studies of a mast cell leukemia cell line expressing substantial amounts of abnormal transcripts of this gene indicated that this gene may play an important role in the final stages of mast cell development. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2009].

The EF hand is a helix-loop-helix structural domain or motif found in a large family of calcium-binding proteins.
GTPase HRas also known as transforming protein p21 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HRAS gene. The HRAS gene is located on the short (p) arm of chromosome 11 at position 15.5, from base pair 522,241 to base pair 525,549. HRas is a small G protein in the Ras subfamily of the Ras superfamily of small GTPases. Once bound to Guanosine triphosphate, H-Ras will activate a Raf kinase like c-Raf, the next step in the MAPK/ERK pathway.
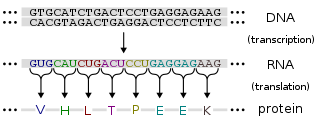
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) or small nuclear RNA (snRNA) genes, the product is a functional RNA.