
A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is a functional RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene. Abundant and functionally important types of non-coding RNAs include transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as small RNAs such as microRNAs, siRNAs, piRNAs, snoRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, scaRNAs and the long ncRNAs such as Xist and HOTAIR.

Cartilage–hair hypoplasia (CHH) is a rare genetic disorder. Symptoms may include short-limbed dwarfism due to skeletal dysplasia, variable level of immunodeficiency, and predisposition to cancer. It was first reported by Victor McKusick in 1965.
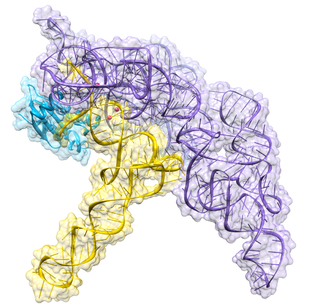
Ribonuclease P is a type of ribonuclease which cleaves RNA. RNase P is unique from other RNases in that it is a ribozyme – a ribonucleic acid that acts as a catalyst in the same way that a protein-based enzyme would. Its function is to cleave off an extra, or precursor, sequence of RNA on tRNA molecules. Further, RNase P is one of two known multiple turnover ribozymes in nature, the discovery of which earned Sidney Altman and Thomas Cech the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1989: in the 1970s, Altman discovered the existence of precursor tRNA with flanking sequences and was the first to characterize RNase P and its activity in processing of the 5' leader sequence of precursor tRNA. Recent findings also reveal that RNase P has a new function. It has been shown that human nuclear RNase P is required for the normal and efficient transcription of various small noncoding RNAs, such as tRNA, 5S rRNA, SRP RNA and U6 snRNA genes, which are transcribed by RNA polymerase III, one of three major nuclear RNA polymerases in human cells.

The exosome complex is a multi-protein intracellular complex capable of degrading various types of RNA molecules. Exosome complexes are found in both eukaryotic cells and archaea, while in bacteria a simpler complex called the degradosome carries out similar functions.
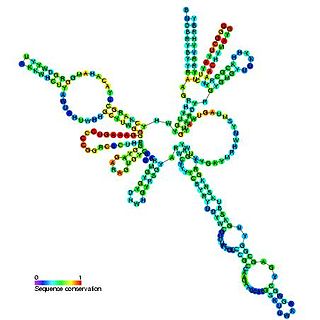
RNase MRP is an enzymatically active ribonucleoprotein with two distinct roles in eukaryotes. RNase MRP stands for RNase for Mitochondrial RNA Processing. In mitochondria, it plays a direct role in the initiation of mitochondrial DNA replication. In the nucleus, it is involved in precursor rRNA processing, where it cleaves the internal transcribed spacer 1 between 18S and 5.8S rRNAs. Despite distinct functions, RNase MRP has been shown to be evolutionarily related to RNase P. Like eukaryotic RNase P, RNase MRP is not catalytically active without associated protein subunits.

Sjögren syndrome type B antigen (SS-B) also known as Lupus La protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SSB gene.

Ribonuclease P protein subunit p20 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the POP7 gene.

Ribonuclease P protein subunit p40 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RPP40 gene.

Ribonucleases P/MRP protein subunit POP1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the POP1 gene.
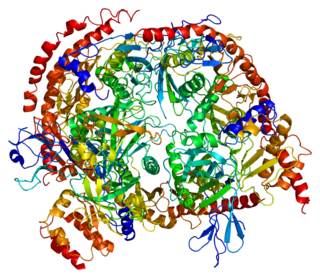
Exosome component 8, also known as EXOSC8, is a human gene, the protein product of which is part of the exosome complex.

Exosome component 7, also known as EXOSC7, is a human gene, the protein product of which is part of the exosome complex.

Exosome component 3, also known as EXOSC3, is a human gene, which is part of the exosome complex.

Ribonuclease P/MRP protein subunit POP5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the POP5 gene.
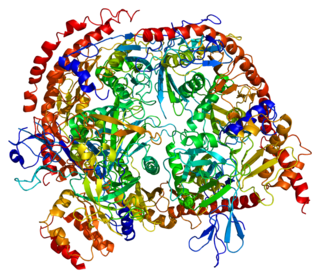
3'-5' exoribonuclease CSL4 homolog is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the EXOSC1 gene.

Exosome component 5, also known as EXOSC5, is a human gene, which is part of the exosome complex.

Ribonuclease P protein subunit p30 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RPP30 gene.

Ribonuclease P protein subunit p38 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RPP38 gene.

Ribonuclease P protein subunit p14 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RPP14 gene.

Ribonuclease P protein subunit p29 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the POP4 gene.

FAM221B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FAM221B gene . FAM221B is also known by the alias C9orf128, is expressed at low level, and is defined by 17 GenBank accessions . It is predicted to function in transcription regulation as a transcription factor.




















