
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. IUPAC's executive director heads this administrative office, currently Greta Heydenrych.
The katal is that catalytic activity that will raise the rate of conversion by one mole per second in a specified assay system. It is a unit of the International System of Units (SI) used for quantifying the catalytic activity of enzymes and other catalysts.

Luminescence is a spontaneous emission of radiation from an electronically or vibrationally excited species not in thermal equilibrium with its environment. A luminescent object emits cold light in contrast to incandescence, where an object only emits light after heating. Generally, the emission of light is due to the movement of electrons between different energy levels within an atom after excitation by external factors. However, the exact mechanism of light emission in vibrationally excited species is unknown.

In chemistry, an enantiomer, also known as an optical isomer, antipode, or optical antipode, is one of a pair of molecular entities which are mirror images of each other and non-superposable.
The standard state of a material is a reference point used to calculate its properties under different conditions. A degree sign (°) or a superscript Plimsoll symbol (⦵) is used to designate a thermodynamic quantity in the standard state, such as change in enthalpy (ΔH°), change in entropy (ΔS°), or change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG°). The degree symbol has become widespread, although the Plimsoll is recommended in standards, see discussion about typesetting below.
Chemical species are a specific form of chemical substance or chemically identical molecular entities that have the same molecular energy level at a specified timescale. These entities are classified through bonding types and relative abundance of isotopes. Types of chemical species can be classified based on the type of molecular entity and can be either an atomic, molecular, ionic or radical species.
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a side chain is a chemical group that is attached to a core part of the molecule called the "main chain" or backbone. The side chain is a hydrocarbon branching element of a molecule that is attached to a larger hydrocarbon backbone. It is one factor in determining a molecule's properties and reactivity. A side chain is also known as a pendant chain, but a pendant group has a different definition.
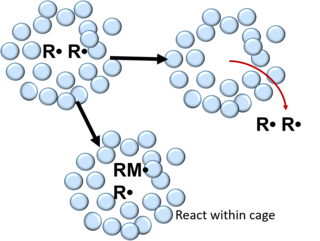
In chemistry, the cage effect (also known as geminate recombination) describes how the properties of a molecule are affected by its surroundings. First introduced by James Franck and Eugene Rabinowitch in 1934, the cage effect suggests that instead of acting as an individual particle, molecules in solvent are more accurately described as an encapsulated particle. The encapsulated molecules or radicals are called cage pairs or geminate pairs. In order to interact with other molecules, the caged particle must diffuse from its solvent cage. The typical lifetime of a solvent cage is 10-11 seconds. Many manifestations of the cage effect exist.
The molecular configuration of a molecule is the permanent geometry that results from the spatial arrangement of its bonds. The ability of the same set of atoms to form two or more molecules with different configurations is stereoisomerism. This is distinct from constitutional isomerism which arises from atoms being connected in a different order. Conformers which arise from single bond rotations, if not isolatable as atropisomers, do not count as distinct molecular configurations as the spatial connectivity of bonds is identical.

Chemistry education is the study of teaching and learning chemistry. It is one subset of STEM education or discipline-based education research (DBER). Topics in chemistry education include understanding how students learn chemistry and determining the most efficient methods to teach chemistry. There is a constant need to improve chemistry curricula and learning outcomes based on findings of chemistry education research (CER). Chemistry education can be improved by changing teaching methods and providing appropriate training to chemistry instructors, within many modes, including classroom lectures, demonstrations, and laboratory activities.

The standard atomic weight of a chemical element (symbol Ar°(E) for element "E") is the weighted arithmetic mean of the relative isotopic masses of all isotopes of that element weighted by each isotope's abundance on Earth. For example, isotope 63Cu (Ar = 62.929) constitutes 69% of the copper on Earth, the rest being 65Cu (Ar = 64.927), so

Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry, commonly referred to by chemists as the Blue Book, is a collection of recommendations on organic chemical nomenclature published at irregular intervals by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). A full edition was published in 1979, an abridged and updated version of which was published in 1993 as A Guide to IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds. Both of these are now out-of-print in their paper versions, but are available free of charge in electronic versions. After the release of a draft version for public comment in 2004 and the publication of several revised sections in the journal Pure and Applied Chemistry, a fully revised edition was published in print in 2013 and its online version is also available.
Angela K. Wilson is an American scientist and former (2022) President of the American Chemical Society. She currently serves as the John A. Hannah Distinguished Professor of Chemistry, associate dean for strategic initiatives in the College of Natural Sciences, and director of the MSU Center for Quantum Computing, Science, and Engineering (MSU-Q) at Michigan State University.
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) publishes many books which contain its complete list of definitions. The definitions are divided initially into seven IUPAC Colour Books: Gold, Green, Blue, Purple, Orange, White, and Red. There is also an eighth book, the "Silver Book".
The IUPAC/IUPAP Joint Working Party is a group convened periodically by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP) to consider claims for discovery and naming of new chemical elements. It is sometimes called the Joint Working Party on Discovery of Elements. The working party's recommendations are voted on by the General Assembly of the IUPAP.

The Commission on Isotopic Abundances and Atomic Weights (CIAAW) is an international scientific committee of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) under its Division of Inorganic Chemistry. Since 1899, it is entrusted with periodic critical evaluation of atomic weights of chemical elements and other cognate data, such as the isotopic composition of elements. The biennial CIAAW Standard Atomic Weights are accepted as the authoritative source in science and appear worldwide on the periodic table wall charts.

Zafra M. Lerman is an American chemist, educator, and humanitarian. She is the President of the Malta Conferences Foundation, which aims to promote peace by bringing together scientists from otherwise hostile countries to discuss science and foster international scientific and technical collaboration. From 1986 to 2010, she chaired the American Chemical Society's Subcommittee on Scientific Freedom and Human Rights. She has been successful in preventing executions, releasing prisoners of conscience from jail and bringing dissidents to freedom. She is the recipient of many awards for education and science diplomacy, including the 1999 Presidential Award from U.S. President Clinton, the 2005 Nyholm Prize for Education from the Royal Society of Chemistry (England), the 2015 Science Diplomacy Award from the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS), the 2016 Andrei Sakharov Award for human rights from the American Physical Society (APS), the 2016 United Nations NOVUS Award for the 16th Sustainable Development Goal: Peace and Justice, and the 2017 International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry Distinguished Women in Chemistry or Chemical Engineering Award.
Rachel O'Reilly is a British chemist and Professor at the University of Birmingham. She works at the interface of biology and materials, creating polymers that can mimic natural nanomaterials such as viruses and cells. She is a Fellow of the Royal Society of Chemistry and of the Royal Society.
Nina Matheny Roscher (1938—2001) was an American chemist and advocate for women and minorities in science. She also researched the history of women in chemistry, publishing the book Women Chemists (1995). She served as professor and chair of the chemistry department at American University in Washington, D.C. She received the ACS Award for Encouraging Women into Careers in the Chemical Sciences (1996) and the Presidential Award for Excellence in Science, Mathematics and Engineering Mentoring (1998).
Marcy Hamby Towns is an American chemist who is Professor of Chemistry Education at Purdue University. Her research considers the development of innovative ways to teach undergraduate chemistry. She was awarded the IUPAC Distinguished Women in Chemistry Award in 2021.









