This article needs additional citations for verification .(February 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Rangeliosis is a disease of dogs and other species, [1] caused by the hemoprotozoan parasite Rangelia vitalii .
This article needs additional citations for verification .(February 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Rangeliosis is a disease of dogs and other species, [1] caused by the hemoprotozoan parasite Rangelia vitalii .
Clinically affected dogs present with splenomegaly, icterus, anemia and thrombocytopenia. [2]
Many dogs may succumb to infection without veterinary intervention.
Treatment is usually effective with antiprotozoal drugs.
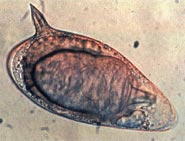
Schistosoma is a genus of trematodes, commonly known as blood flukes. They are parasitic flatworms responsible for a highly significant group of infections in humans termed schistosomiasis, which is considered by the World Health Organization as the second-most socioeconomically devastating parasitic disease, with hundreds of millions infected worldwide.

Echinococcus granulosus, also called the hydatid worm, hyper tape-worm or dog tapeworm, is a cyclophyllid cestode that dwells in the small intestine of canids as an adult, but which has important intermediate hosts such as livestock and humans, where it causes cystic echinococcosis, also known as hydatid disease. The adult tapeworm ranges in length from 3 mm to 6 mm and has three proglottids ("segments") when intact—an immature proglottid, mature proglottid and a gravid proglottid. The average number of eggs per gravid proglottid is 823. Like all cyclophyllideans, E. granulosus has four suckers on its scolex ("head"), and E. granulosus also has a rostellum with hooks. Several strains of E. granulosus have been identified, and all but two are noted to be infective in humans.
Coccidiosis is a parasitic disease of the intestinal tract of animals caused by coccidian protozoa. The disease spreads from one animal to another by contact with infected feces or ingestion of infected tissue. Diarrhea, which may become bloody in severe cases, is the primary symptom. Most animals infected with coccidia are asymptomatic, but young or immunocompromised animals may suffer severe symptoms and death.

Neospora caninum is a protozoa that was identified as a species in 1988. Prior to this, it was misclassified as Toxoplasma gondii due to structural similarities. The genome sequence of Neospora caninum has been determined by the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute and the University of Liverpool. Neospora caninum is an important cause of spontaneous abortion in infected livestock.

Cheyletiella is a genus of mites that live on the skin surface of dogs, cats, and rabbits.

Leishmania infantum is the causative agent of infantile visceral leishmaniasis in the Mediterranean region and in Latin America, where it has been called Leishmania chagasi. It is also an unusual cause of cutaneous leishmaniasis, which is normally caused by specific lineages. Wild canids and domestic dogs are the natural reservoir of this organism. The sandfly species Lutzomyia longipalpis serves as the primary vector for the transmission of the disease.

Blastocystosis refers to a medical condition caused by infection with Blastocystis. Blastocystis is a protozoal, single-celled parasite that inhabits the gastrointestinal tracts of humans and other animals. Many different types of Blastocystis exist, and they can infect humans, farm animals, birds, rodents, amphibians, reptiles, fish, and even cockroaches. Blastocystosis has been found to be a possible risk factor for development of irritable bowel syndrome.
Trypanosoma rangeli is a species of hemoflagellate excavate parasites of the genus Trypanosoma. Although infecting a variety of mammalian species in a wide geographical area in Central and South America, this parasite is considered non-pathogenic to these hosts. T. rangeli is transmitted by bite of infected triatomine bugs of the Reduviidae family, commonly known as barbeiro, winchuka(vinchuca), chinche, pito ou chupão.
Brugia timori is a filarial (arthropod-borne) nematode (roundworm) which causes the disease "Timor filariasis", or "Timorian filariasis". While this disease was first described in 1965, the identity of Brugia timori as the causative agent was not known until 1977. In that same year, Anopheles barbirostris was shown to be its primary vector. There is no known animal reservoir host.
Capillaria plica is a parasitic nematode which is most often found in the urinary bladder, and occasionally in the kidneys, of dogs and foxes. It has also been found in the domestic cat, and various wild mammals. Its presence usually produces no clinical symptoms, but in some cases, it leads to hematuria, cystitis, or difficulty in urination.

Nanophyetus salmincola is a food-borne intestinal trematode parasite prevalent on the Pacific Northwest coast. The species may be the most common trematode endemic to the United States.

The Haemosporida are an order of intraerythrocytic parasitic alveolates.

The Chihuahua is one of the smallest breeds of dog, and is named after the Mexican state of Chihuahua.
Garnia is a genus of parasitic alveolates belonging to the phylum Apicomplexia.
Hammondia is a genus of parasitic alveolates in the phylum Apicomplexa.
Nephroisospora is a genus of parasites that infects bats
Rangelia is a genus of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexia.
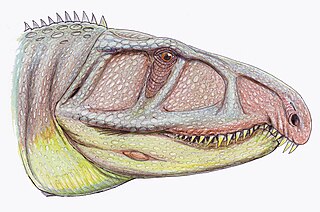
Uralosaurus is an extinct genus of erythrosuchid archosauriform known from the Middle Triassic Donguz Formation of southeastern European Russia. It contains a single species, Uralosaurus magnus. It was named by Vitalii Georgievich Ochev in 1980 as a species of Erythrosuchus otherwise known from the Triassic of Africa and reassigned to its own genus by Andrey G. Sennikov in 1995.
The 2016–17 QMJHL season is the 48th season of the Quebec Major Junior Hockey League (QMJHL). The regular season began on September 22, 2016, and ended on March 18, 2017.

Hookworms are intestinal, blood-feeding, parasitic roundworms that cause types of infection known as helminthiases. Hookworm infection is found in many parts of the world, and is common in areas with poor access to adequate water, sanitation, and hygiene. In humans, infections are caused by two main species of roundworm, belonging to the genera Ancylostoma and Necator. In other animals the main parasites are species of Ancylostoma.