Related Research Articles

Ranjit Singh was the founder and first maharaja of the Sikh Empire, ruling from 1801 until his death in 1839. He ruled the northwest Indian subcontinent in the early half of the 19th century. He survived smallpox in infancy but lost sight in his left eye. He fought his first battle alongside his father at age 10.

Majha is a region located in the central parts of the historical Punjab region, currently split between the republics of Pakistan and India. It extends north from the right banks of the river Beas, and reaches as far north as the river Jhelum. People of the Majha region are given the demonym "Mājhī" or "Majhail". Most inhabitants of the region speak the Majhi dialect, which is the basis of the standard register of the Punjabi language. The most populous city in the area is Lahore on the Pakistani side, and Amritsar on the Indian side of the border.
Surinder Singh Sodhi is a former field hockey player from India. He is famous for playing a major role in getting India the gold medal in 1980 Olympic games after a gap of 16 years. He played in the center forward position.

Baba Gurdit Singh was the central figure in the Komagata Maru incident of 1914, one of several incidents in the history of early 20th century involving exclusion laws in both Canada and the United States designed to keep out immigrants of only Asian origin.
Mai Sukhan, was an Majhail ruler of Misl. Mai Sukhan gained recognition in Punjab for her military leadership. Mai Sukhan was a powerful Sikh ruler of the Majha region, which gained her recognition throughout Punjab.

Malaysia competed at the 1964 Summer Olympics in Tokyo, Japan. It was the first time that the Federation had competed under that name, as it was previously named Malaya, while North Borneo and Singapore had sent separate teams to the Games. 62 competitors, 58 men and 4 women, took part in 49 events in 10 sports.
Khem Kaur Dhillon was a Sikh queen and the second wife of Maharaja Kharak Singh, the second Maharaja of the Sikh Empire.

Nabha State, with its capital at Nabha, was one of the Phulkian princely states of Punjab during the British Raj in India. Nabha was ruled by Jat Sikhs of the Sidhu clan.

The Bhangi Misl was a large and powerful Sikh Misl headquartered in Amritsar. It was founded in the early 18th century by Sardar Chhajja Singh Dhillon, who was baptised by Banda Singh Bahadur. The misl received its name "Bhangi" because Chhajja Singh and his soldiers frequently used the herbal intoxicant bhang. It was a first misl to established a Khalsa Raj and publish Khalsa currency coins. The Bhangi Kingdom/Misl was founded by Dhillon Jats.
Saini Sisters is a popular epithet used for four sisters from Punjab who were international field hockey players, Rupa Saini, Krishna Saini, Swarna Saini and Prema Saini. At one time Saini sisters dominated woman's hockey in India and in the test series against Japan in 1970 all three sisters played together for India.
Rajinder Singh Chauhan, also known as Rajinder Singh Jr., is an Indian field hockey player and coach. He was part of the Indian teams that won the silver medal at the 1982 Asian Games, the bronze medal at the 1982 Champions Trophy, and the silver medal at the 1983 Sultan Azlan Shah Cup. He coached the Indian women's team in 2004 and the Indian men's team in 2005-2006.

Brigadier Harcharan Singh VSM is an Indian field hockey player. He was a member of bronze medal winner India men's national field hockey team at the 1972 Summer Olympics in Munich.

Ramgarhia Misl was a sovereign state (misl) in the Sikh Confederacy of Punjab region in present-day India and Pakistan. The misl's name is derived from Qila Ramgarh, a place located in Ramsar, near Amritsar, which was fortified and redesigned by Ramgarhia Misl chief Jassa Singh Ramgarhia. The Ramgarhia Misl was one of the twelve major Sikh misls, and held land near Amritsar.
Ranjit Singh in small village of punjab He served in indian army in mahar regiment from 1977 to 1992. He is an Indian racewalker. He represented india in the men's 20 kilometres walk at the 1980 Summer Olympics held in moscow (russia) and finished 18 place out of 80 participants. He won silver medal in 1981 Asian athletics championships held in Tokyo, Japan. He was three times national champion in India and 5 times service's champion in the Indian army. After he retired from the Indian army, he joined sports authority of India as a national athletics coach. He trained Indian athletes from 1993 to 2017 in India and overseas. He produced more than 100 national level athletes and international level athletes during his career.
The following is the list of squads that took place in the men's field hockey tournament at the 1964 Summer Olympics.
Ranjit Singh Sehmi is a Kenyan field hockey player. He competed in the men's tournament at the 1972 Summer Olympics.
Maharaja Ranjit Singh is an Indian historical drama television series created by Raj Babbar. It was directed by Chitraarth and Sikander Bharti and produced by Nadira Babbar and Kukoo Babbar of Babbar Films Private Limited. The drama aired on DD National from 13 April 2010 to 3 May 2011. The series is based on the life of Maharaja Ranjit Singh and covers the part of history of Punjab from 1739 to 1812. The show comprised 56 episodes. The music was composed by Jagjit Singh. Filming was done between 2004–2010.
Kunwar Rattan Singh (1805–1845) was the second son of Maharaja Ranjit Singh, the founder of the Sikh Empire and his queen consort, Maharani Datar Kaur His elder, Maharaja Kharak Singh was the second Maharaja of the Sikh Empire and nephew, Maharaja Nau Nihal Singh was the third Maharaja. The former reigned for less than four months, and the latter barely four weeks.
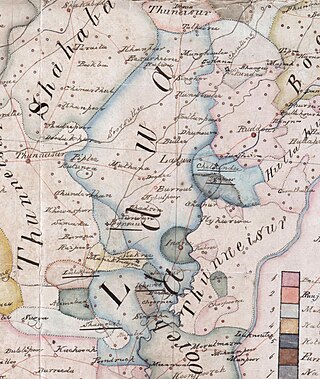
Ladwa State was a Sikh kingdom. It was one of the Cis-Sutlej states. The state is notable for being one of the few Sikh polities south of the Sutlej that actively sided with the Sikh Empire against the British.
References
- ↑ Evans, Hilary; Gjerde, Arild; Heijmans, Jeroen; Mallon, Bill; et al. "Ranjit Singh Gurdit Olympic Results". Olympics at Sports-Reference.com. Sports Reference LLC. Archived from the original on 18 April 2020. Retrieved 27 September 2019.