Related Research Articles

Environmental economics is a sub-field of economics concerned with environmental issues. It has become a widely studied subject due to growing environmental concerns in the twenty-first century. Environmental economics "undertakes theoretical or empirical studies of the economic effects of national or local environmental policies around the world. ... Particular issues include the costs and benefits of alternative environmental policies to deal with air pollution, water quality, toxic substances, solid waste, and global warming."

Resource depletion is the consumption of a resource faster than it can be replenished. Natural resources are commonly divided between renewable resources and non-renewable resources. The use of either of these forms of resources beyond their rate of replacement is considered to be resource depletion. The value of a resource is a direct result of its availability in nature and the cost of extracting the resource. The more a resource is depleted the more the value of the resource increases. There are several types of resource depletion, including but not limited to: mining for fossil fuels and minerals, deforestation, pollution or contamination of resources, wetland and ecosystem degradation, soil erosion, overconsumption, aquifer depletion, and the excessive or unnecessary use of resources. Resource depletion is most commonly used in reference to farming, fishing, mining, water usage, and the consumption of fossil fuels. Depletion of wildlife populations is called defaunation.

Ecological economics, bioeconomics, ecolonomy, eco-economics, or ecol-econ is both a transdisciplinary and an interdisciplinary field of academic research addressing the interdependence and coevolution of human economies and natural ecosystems, both intertemporally and spatially. By treating the economy as a subsystem of Earth's larger ecosystem, and by emphasizing the preservation of natural capital, the field of ecological economics is differentiated from environmental economics, which is the mainstream economic analysis of the environment. One survey of German economists found that ecological and environmental economics are different schools of economic thought, with ecological economists emphasizing strong sustainability and rejecting the proposition that physical (human-made) capital can substitute for natural capital.
The virtual water trade is the hidden flow of water in food or other commodities that are traded from one place to another. Other terms for it are embedded or embodied water. The virtual water trade is the idea that virtual water is exchanged along with goods and services. This idea provides a new, amplified perspective on water problems. It balances different perspectives, basic conditions, and interests. This concept makes it possible to distinguish between global, regional, and local levels and their linkages. However, the use of virtual water estimates may offer no guidance for policymakers seeking to ensure they are meeting environmental objectives.
Total economic value (TEV) is a concept in cost–benefit analysis that refers to the value derived by people from a natural resource, a man-made heritage resource or an infrastructure system, compared to not having it. It appears in environmental economics as an aggregation of the values provided by a given ecosystem.
The Niger Basin Authority is an intergovernmental organization in West Africa aiming to foster co-operation in managing and developing the resources of the basin of the Niger River. The group is referred to by both the French and English initialisms, NBA or ABN.
Watershed management is the study of the relevant characteristics of a watershed aimed at the sustainable distribution of its resources and the process of creating and implementing plans, programs and projects to sustain and enhance watershed functions that affect the plant, animal, and human communities within the watershed boundary. Features of a watershed that agencies seek to manage to include water supply, water quality, drainage, stormwater runoff, water rights and the overall planning and utilization of watersheds. Landowners, land use agencies, stormwater management experts, environmental specialists, water use surveyors and communities all play an integral part in watershed management.
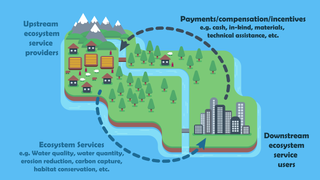
Payments for ecosystem services (PES), also known as payments for environmental services, are incentives offered to farmers or landowners in exchange for managing their land to provide some sort of ecological service. They have been defined as "a transparent system for the additional provision of environmental services through conditional payments to voluntary providers". These programmes promote the conservation of natural resources in the marketplace.

WAFLEX is a spreadsheet-based model. It can be used to analyse upstream-downstream interactions, dam management options and water allocation and development options.

Daniel W. Bromley is an economist, the former Anderson-Bascom Professor of applied economics at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, and since 2009, Emeritus Professor. His research in institutional economics explains the foundations of property rights, natural resources and the environment; and economic development. He has been editor of the journal Land Economics since 1974.

Environmental issues are disruptions in the usual function of ecosystems. Further, these issues can be caused by humans or they can be natural. These issues are considered serious when the ecosystem cannot recover in the present situation, and catastrophic if the ecosystem is projected to certainly collapse.
John Anthony Allan, sometime cited as Tony Allan, was a British geographer. He was awarded the Stockholm Water Prize in 2008 for his revolutionary virtual water concept. Although being an emeritus of the School of Oriental and African Studies and King's College London of the University of London, he still acted as a teaching Professor at King's College London.
Environmental peacebuilding examines and advocates environmental protection and cooperation as a factor in creating more peaceful relations. Peacebuilding is both the theory and practice of identifying the conditions that can lead to a sustainable peace between past, current or potential future adversaries. At the most basic level, warfare devastates ecosystems and the livelihoods of those who depend on natural resources, and the anarchy of conflict situations leads to the uncontrolled, destructive exploitation of natural resources. Preventing these impacts allows for an easier movement to a sustainable peace. From a more positive perspective, environmental cooperation can be one of the places where hostile parties can sustain a dialogue, and sustainable development is a prerequisite for a sustainable peace.

Water resource policy, sometimes called water resource management or water management, encompasses the policy-making processes and legislation that affect the collection, preparation, use, disposal, and protection of water resources. The long-term viability of water supply systems poses a significant challenge as a result of water resource depletion, climate change, and population expansion.

Jon D. Erickson is an American ecological economist, professor of sustainability science and policy at the Rubenstein School of Environment and Natural Resources of the University of Vermont in Burlington, Vermont, United States, and fellow of the Gund Institute for Environment.

Water Utilities Corporation (WUC) is a government-owned corporation that provides water and waste water management services in Botswana. The Board is appointed by the Minister of Minerals, Energy and Water Resources. The water supply is critically important in the arid or semi-arid environment of Botswana.

The Industrial and Mining Water Research Unit is one of several research entities based in the School of Chemical and Metallurgical Engineering at the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg. It provides research as well as supervision to masters and doctorate students within the University, as well as consulting to industry.

Karachepone N. Ninan is an ecological economist. Dr. Ninan was born in Nairobi, Kenya where he had his early school education. Thereafter he relocated to India where he continued his high school and college education.

Giorgos Kallis is an ecological economist from Greece. He is an ICREA Research Professor at ICTA - Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, where he teaches political ecology. He is one of the principal advocates of the theory of degrowth.

Environmental conflicts, socio-environmental conflict or ecological distribution conflicts (EDCs) are social conflicts caused by environmental degradation or by unequal distribution of environmental resources. The Environmental Justice Atlas documented 3,100 environmental conflicts worldwide as of April 2020 and emphasised that many more conflicts remained undocumented.
References
- 1 2 3 "Rashid Hassan" . Retrieved 16 February 2018.
- 1 2 "Rashid Hassan". Bloomberg News . Retrieved 16 February 2018.
- ↑ Rashid Hassan; Eric Mungatana; Glenn-Marie Lange (2007). "Water accounting for the Orange River Basin: An economic perspective on managing a transboundary resource". Ecological Economics . 61 (4): 660–670. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2006.07.032.
- ↑ Rashid M. Hassan; Glenn-Marie Lange; Jaap Arntzen; Jackie Crawford; Eric Mungatana (2007). The Economics of Water Management in southern Africa: an environmental accounting approach. Edward Elgar Publishing. doi:10.4337/9781847203021. ISBN 9781843764724.
- ↑ "2019 NAS Election". National Academy of Sciences. 30 April 2019.