Related Research Articles
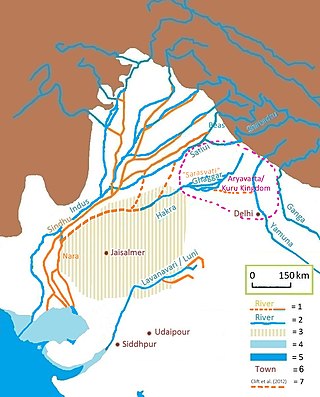
The Sarasvati River is a mythologized and deified ancient river first mentioned in the Rigveda and later in Vedic and post-Vedic texts. It played an important role in the Vedic religion, appearing in all but the fourth book of the Rigveda.

Airyanem Vaejah is considered in Zoroastrianism to be the homeland of the early Iranians and the place where Zarathustra received the religion from Ahura Mazda. The Avesta also names it as the first of the "sixteen perfect lands" that Ahura Mazda created for the Iranians.

The historical Vedic religion, also called Vedicism or Vedism, and sometimes ancient Hinduism or Vedic Hinduism, constituted the religious ideas and practices prevalent amongst some of the Indo-Aryan peoples of the northwest Indian subcontinent during the Vedic period. These ideas and practices are found in the Vedic texts, and some Vedic rituals are still practiced today. The Vedic religion is one of the major traditions which shaped modern Hinduism, though present-day Hinduism is significantly different from the historical Vedic religion.
Dasa is a Sanskrit word found in ancient Indian texts such as the Rigveda, Pali canon, and theArthashastra. The term may mean "slave", "enemy" or "servant," but Dasa or Das can also have the following connotations: "slave of god", "devotee," "votary" or "one who has surrendered to God." Dasa may be a suffix of a given name to indicate a "slave" of a revered person or a particular deity.

The Vedas, sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the oldest layer of Sanskrit literature and the oldest scriptures of Hinduism.
Samudra is a Sanskrit term literally meaning the "gathering together of waters". It refers to an ocean, sea or confluence. It also forms the name of Samudradeva, the Hindu god of the ocean. The word is also present on other languages influenced by Sanskrit.
Sudaios Paijonides alias Sudās Paijavana was an Indo-Aryan tribal king of the Bharatas, during the main or middle Rigvedic period. He led his tribe to victory in the Battle of the Ten Kings near the Paruṣṇī in Punjab, defeating an alliance of the powerful Puru tribe with other tribes, for which he was eulogized by his purohita Vashistha in a hymn of the Rigveda. His victory established the ascendency of the Bhārata clan, allowing them to move eastwards and settle in Kurukshetra, paving the way for the emergence of the Kuru "super-tribe" or tribal union, which dominated northern India in the subsequent period.
Artashumara was a Hurrian ruler who briefly succeeded his father Shuttarna II as the king of Mitanni in the fourteenth century BC. He was a brother of Tushratta and Artatama II. He was later assassinated by a pro-hittite group led by Tuhi who declared himself as a regent after placing Tushratta on the throne. Tuhi was later executed by Tushratta.

The Poureai alias Purus were an Indo-Aryan tribal alliance or a confederation of tribes that existed between c. 1700–1400 BCE. There were several factions of Purus, one being the Bharatas. The Purus and the Bharatas were the two most prominent tribes in most of the Rigveda. The chief of tribe was called Rajan The Purus rallied many other groups against King Sudas of the Bharata, but were defeated in the Battle of the Ten Kings.
The Baudhayana Shrauta Sutra is a Late Vedic text dealing with the solemn rituals of the Taittiriya Shakha school of the Krishna Yajurveda that was composed in eastern Uttar Pradesh during the late Brahmana period. It was transmitted both orally and through manuscript copying. It was printed in 1904-23 by The Asiatic Society, translated by C.G. Kashikar in part in his "Srautakosa", and as a whole later on. It was edited by Willem Caland.

The Rigveda refers to a number of rivers located in the northwestern Indian subcontinent, from Gandhara to Kurukshetra.

Vasishtha is one of the oldest and revered Vedic rishis or sages, and one of the Saptarishis. Vasishtha is credited as the chief author of Mandala 7 of the Rigveda. Vasishtha and his family are mentioned in Rigvedic verse 10.167.4, other Rigvedic mandalas and in many Vedic texts. His ideas have been influential and he was called the first sage of the Vedanta school of Hindu philosophy by Adi Shankara.
The Battle of the Ten Kings was first alluded to in the 7th Mandala of the Rigveda (RV) and took place between a king of the Bharatas named King Sudas versus a confederation of tribes. It resulted in a decisive victory for the Bharatas and subsequent formation of the Kuru polity. The Battle of the Ten Kings, mentioned in the Rigveda may have "formed the 'nucleus' of story" of the Kurukshetra War in the Mahabharata.
The Bharatas were an early Vedic tribe that existed in the latter half of the second millennium B.C.E. The earliest mentioned location of the Bharatas was on the Sarasvatī River. Led by the tribal king Divodāsa, the Bharatas moved through the Hindu Kush mountains and defeated Śambara. Divodāsa's descendant, Sudās, won the Battle of the Ten Kings against a Pūru-led coalition, after which the initial compilation of hymns of the R̥gveda was carried out. After the battle, the Bharatas and other Pūru clans eventually formed the Kuru kingdom, which was the first attested state in Indian history.
Some loanwords in the variant of the Hurrian language spoken in Mitanni during the 2nd millennium BCE are identifiable as originating in an Indo-Aryan language; these are considered to constitute an Indo-Aryan superstrate in Mitanni. The words are theonyms, proper names and technical terminology related to horses (hippological).
Vedic Sanskrit has a number of linguistic features which are alien to most other Indo-European languages. Prominent examples include: phonologically, the introduction of retroflexes, which alternate with dentals, and morphologically, the formation of gerunds. Some philologists attribute such features, as well as the presence of non-Indo-European vocabulary, to a local substratum of languages encountered by Indo-Aryan peoples in Central Asia (Bactria-Marghiana) and within the Indian subcontinent during Indo-Aryan migrations, including the Dravidian languages.
Indigenous Aryanism, also known as the Indigenous Aryans theory (IAT) and the Out of India theory (OIT), is the conviction that the Aryans are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent, and that the Indo-European languages radiated out from a homeland in India into their present locations. It is a "religio-nationalistic" view on Indian history, and propagated as an alternative to the established migration model, which considers the Pontic–Caspian steppe to be the area of origin of the Indo-European languages.

The Vedic period, or the Vedic age, is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas, was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, between the end of the urban Indus Valley Civilisation and a second urbanisation, which began in the central Indo-Gangetic Plain c. 600 BCE. The Vedas are liturgical texts which formed the basis of the influential Brahmanical ideology, which developed in the Kuru Kingdom, a tribal union of several Indo-Aryan tribes. The Vedas contain details of life during this period that have been interpreted to be historical and constitute the primary sources for understanding the period. These documents, alongside the corresponding archaeological record, allow for the evolution of the Indo-Aryan and Vedic culture to be traced and inferred.

The Rigveda or Rig Veda is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (sūktas). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts (śruti) known as the Vedas. Only one Shakha of the many survive today, namely the Śakalya Shakha. Much of the contents contained in the remaining Shakhas are now lost or are not available in the public forum.
References
- ↑ Sethna, K D (1992). The problem of Aryan origins from an Indian point of view. New Delhi: Aditya Prakasana. ISBN 9788185179674.
- ↑ Witzel, Michael (11 October 2016). "Autochthonous Aryans? The evidence from Old Indian and Iranian texts". Electronic Journal of Vedic Studies. 7 (3): 1–93. doi: 10.11588/EJVS.2001.3.830 . ISSN 1084-7561.
- ↑ See also Witzel, Michael (17 April 2008), Addendum to EJVS 7-3, notes 45-46 (PDF), doi: 10.11588/XAREP.00000118