
Worcester is a cathedral city in Worcestershire, England, of which it is the county town. It is 30 mi (48 km) south-west of Birmingham, 27 mi (43 km) north of Gloucester and 23 mi (37 km) north-east of Hereford. The population was 103,872 in the 2021 census.

Worcester Cathedral, formally the Cathedral Church of Christ and Blessed Mary the Virgin, is a Church of England cathedral in Worcester, England. The cathedral is the seat of the bishop of Worcester and is the mother church of the diocese of Worcester; it is administered by its dean and chapter. The cathedral is a grade I listed building and part of a scheduled monument.
The term soke, at the time of the Norman conquest of England, generally denoted "jurisdiction", but its vague usage makes it lack a single, precise definition.

Wychavon is a local government district in Worcestershire, England. The largest towns are Evesham and Droitwich Spa; the council is based in the town of Pershore. The district also includes numerous villages and surrounding rural areas, and includes part of the Cotswolds, a designated Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. The district's name references the Saxon Kingdom of Hwicce and the River Avon. The population in 2021 was 133,100.
Blockley is a village, civil parish and ecclesiastical parish in the Cotswold district of Gloucestershire, England, about 3 miles (5 km) northwest of Moreton-in-Marsh. Until 1931 Blockley was an exclave of Worcestershire.

The area now known as Worcestershire has had human presence for over half a million years. Interrupted by two ice ages, Worcestershire has had continuous settlement since roughly 10,000 years ago. In the Iron Age, the area was dominated by a series of hill forts, and the beginnings of industrial activity including pottery and salt mining can be found. It seems to have been relatively unimportant during the Roman era, with the exception of the salt workings.

Kempsey is a village and civil parish in the Malvern Hills District in the county of Worcestershire, England. It is bounded by the River Severn on the west, and the A38 main road runs through it and is about 3 miles (5 km) south of Worcester. The village has a long history. Its name is derived from the Saxon "Kemys' Eye", or the island of Kemys. Kemys was a Saxon chief, whose island lay between marshes and the River Severn. One of the roads in Kempsey, Lyf's Lane, is named after another Saxon chief. The village was recorded in the 11th century Domesday Book as having a value of £7.
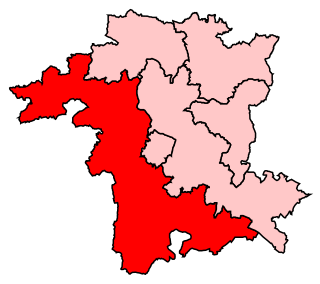
West Worcestershire is a constituency in Worcestershire represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament since 2010 by Harriett Baldwin, a Conservative. The constituency is considered a safe seat for the Conservatives, having been a marginal with the Liberal Democrats from 1997 to 2010. The constituency boundaries roughly correspond with the Malvern Hills District.

Warndon is a suburb and civil parish of the City of Worcester in Worcestershire, England, located on the north eastern edge of the city.

White Ladies Aston is a village in the Wychavon local government district of Worcestershire, England, United Kingdom, and also lends its name to the civil parish in which the village is located. The village is located to the east of the A44 which started as a Saltway linking Droitwich to Oxford. To the south is Pershore and five miles west is Worcester. The parish is bound to the east by the Bow Brook. The parish, according to the 2011 census, has 87 households with 220 residents.

Little Witley is a village and civil parish in the Malvern Hills District in the county of Worcestershire, England.

Hartlebury Castle, a Grade I listed building, near Hartlebury in Worcestershire, central England, was built in the mid-13th century as a fortified manor house, on manorial land earlier given to the Bishop of Worcester by King Burgred of Mercia. It lies near Stourport-on-Severn in an area with several large manors and country houses, including Witley Court, Astley Hall, Pool House, Areley Hall and Hartlebury and Abberley Hall. Later, it became the bishop's principal residence.

Elmley Castle is a village and civil parish in Worcestershire, in England, United Kingdom. It is located on the north side of Bredon Hill 3 miles south-east of Pershore in the local government district of Wychavon.

Elmley Castle was a late 11th-century earthwork and timber castle which received stone additions in the 12th and possibly 13th centuries, located 0.5 miles (0.8 km) south of the village of Elmley Castle and 12 miles (19 km) southeast of the city of Worcester, in Worcestershire. Nothing but the earthworks survive.

Tibberton is a village in Worcestershire, England. It is located around 4 miles north-east of Worcester and less than a mile from junction 6 of the M5 motorway. The Worcester and Birmingham Canal passes just to the north of the village.

Bengeworth is a locality in the civil parish of Evesham, in the Wychavon district, in the county of Worcestershire, England. In 1887 it had a population of 1,311. Today it has a school and an Anglican church.

John William Bund Willis-Bund was a British lawyer, legal writer and professor of constitutional law and history at King's College London, a historian who wrote on the Welsh church and other subjects, and a local Worcestershire politician.

Bredon's Norton or Norton-by-Bredon is a village and civil parish 11 miles (18 km) south east of Worcester, in the Wychavon district, in the county of Worcestershire, England. In 2021 the parish had a population of 254. The parish touches Eckington, Bredon, Strensham and Kemerton.

William Thomas (1670–1738) was an English clergyman and antiquary. He was educated at Westminster School and Trinity College, Cambridge, from which he received two degrees. Through the influence of distant relation John Somers, 1st Baron Somers, he was granted the living of Exhall in Warwickshire and later became rector of St Nicholas in Worcester. Thomas received two further degrees in divinity in the 1720s, including a doctorate. As part of his work as an antiquary Thomas visited every church in Worcestershire and transcribed many documents, including the now lost Red Book of Worcester.


















