
Family planning is the consideration of the number of children a person wishes to have, including the choice to have no children, and the age at which they wish to have them. Things that may play a role on family planning decisions include marital situation, career or work considerations, financial situations. If sexually active, family planning may involve the use of contraception and other techniques to control the timing of reproduction.
The Mexico City policy, sometimes referred to by its critics as the global gag rule, is a former United States government policy that blocked U.S. federal funding for non-governmental organizations (NGOs) that provided abortion counseling or referrals, advocated to decriminalize abortion, or expanded abortion services. When in effect, the Mexico City policy is a U.S. government policy that requires foreign non-governmental organizations to certify that they will not "perform or actively promote abortion as a method of family planning" with non-U.S. funds as a condition for receiving U.S. global family planning assistance, and during its January 23, 2017 implementation any other U.S. global health assistance, including U.S. global HIV and maternal and child health (MCH) assistance.
Reproductive rights are legal rights and freedoms relating to reproduction and reproductive health that vary amongst countries around the world. The World Health Organization defines reproductive rights as follows:
Reproductive rights rest on the recognition of the basic right of all couples and individuals to decide freely and responsibly the number, spacing and timing of their children and to have the information and means to do so, and the right to attain the highest standard of sexual and reproductive health. They also include the right of all to make decisions concerning reproduction free of discrimination, coercion and violence.

Sexual and reproductive health (SRH) is a field of research, health care, and social activism that explores the health of an individual's reproductive system and sexual well-being during all stages of their life. Sexual and reproductive health is more commonly defined as sexual and reproductive health and rights, to encompass individual agency to make choices about their sexual and reproductive lives.

Population Services International (PSI) is a 501(c)(3) registered nonprofit global health organization that began as an international not-for-profit provider of contraception and safe abortion services, and has evolved into developing and deploying programs today that target malaria, child survival, HIV, and reproductive health. PSI provides products, clinical services and behavior change communications for the health of people in high-need populations.

EngenderHealth is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization based in Washington, D.C., with a focus in sexual and reproductive health (SRH). The organization operates in nearly 20 countries throughout Africa, Asia, and North and South America.
MSI Reproductive Choices, named Marie Stopes International until November 2020, is an international non-governmental organisation providing contraception and safe abortion services in 37 countries around the world. MSI Reproductive Choices as an organisation lobbies in favour of access to abortion, and provides a variety of sexual and reproductive healthcare services including advice, vasectomies, and abortions in the UK and other countries where it is legal to do so. It is based in London and is a registered charity under English law.

A female condom is a barrier device that is used during sexual intercourse as a barrier contraceptive to reduce the probability of pregnancy or sexually transmitted infection (STI). It is inserted in the vagina before intercourse to reduce the risk of exposure to semen or other body fluids. The female condom was invented in 1990 by Danish MD Lasse Hessel, and approved for sale in the US by the FDA in 1993. It was developed as an alternative to the older external condom, which is put on the man.
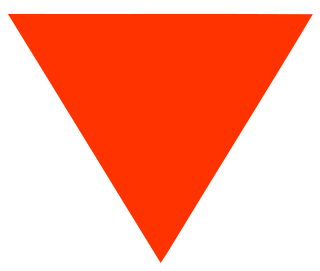
Dharmendra Kumar Tyagi, better known as Deep Tyagi or DK Tyagi (1928–1969), was an assistant commissioner for the Indian family planning program until 1969. An early pioneer of family planning in India and elsewhere, he was a champion of the program under the premierships of Jawaharlal Nehru, Lal Bahadur Shastri, and the initial period of Indira Gandhi. He invented the now-pervasive "Red Triangle" symbol as a branding effort to familiarize and popularize the idea of family planning.

Reproductive justice is a critical feminist framework that was invented as a response to United States reproductive politics. The three core values of reproductive justice are the right to have a child, the right to not have a child, and the right to parent a child or children in safe and healthy environments. The framework moves women's reproductive rights past a legal and political debate to incorporate the economic, social, and health factors that impact women's reproductive choices and decision-making ability.
Contraceptive security is an individual's ability to reliably choose, obtain, and use quality contraceptives for family planning and the prevention of sexually transmitted diseases. The term refers primarily to efforts undertaken in low and middle-income countries to ensure contraceptive availability as an integral part of family planning programs. Even though there is a consistent increase in the use of contraceptives in low, middle, and high-income countries, the actual contraceptive use varies in different regions of the world. The World Health Organization recognizes the importance of contraception and describes all choices regarding family planning as human rights. Subsidized products, particularly condoms and oral contraceptives, may be provided to increase accessibility for low-income people. Measures taken to provide contraceptive security may include strengthening contraceptive supply chains, forming contraceptive security committees, product quality assurance, promoting supportive policy environments, and examining financing options.
The history of condoms goes back at least several centuries, and perhaps beyond. For most of their history, condoms have been used both as a method of birth control, and as a protective measure against sexually transmitted infections such as syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, hepatitis B and more recently HIV/AIDS. Condoms have been made from a variety of materials; prior to the 19th century, chemically treated linen and animal tissue are the best documented varieties. Rubber condoms gained popularity in the mid-19th century, and in the early 20th century major advances were made in manufacturing techniques. Prior to the introduction of the combined oral contraceptive pill, condoms were the most popular birth control method in the Western world. In the second half of the 20th century, the low cost of condoms contributed to their importance in family planning programs throughout the developing world. Condoms have also become increasingly important in efforts to fight the AIDS pandemic.

Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent unintended pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth control only became available in the 20th century. Planning, making available, and using human birth control is called family planning. Some cultures limit or discourage access to birth control because they consider it to be morally, religiously, or politically undesirable.

In precolonial Ghana, infectious diseases were the main cause of morbidity and mortality. The modern history of health in Ghana was heavily influenced by international actors such as Christian missionaries, European colonists, the World Bank, and the International Monetary Fund. In addition, the democratic shift in Ghana spurred healthcare reforms in an attempt to address the presence of infectious and noncommunicable diseases eventually resulting in the formation of the National Health insurance Scheme in place today.

Family planning in India is based on efforts largely sponsored by the Indian government. From 1965 to 2009, contraceptive usage has more than tripled and the fertility rate has more than halved, but the national fertility rate in absolute numbers remains high, causing concern for long-term population growth. India adds up to 1,000,000 people to its population every 20 days. Extensive family planning has become a priority in an effort to curb the projected population of two billion by the end of the twenty-first century.

The Responsible Parenthood and Reproductive Health Act of 2012, also known as the Reproductive Health Law or RH Law, and officially designated as Republic Act No. 10354, is a Philippine law that provides universal access to methods of contraception, fertility control, sexual education, and maternal care.

Birth control in the United States is available in many forms. Some of the forms available at drugstores and some retail stores are male condoms, female condoms, sponges, spermicides, over-the-counter progestin-only contraceptive pills, and over-the-counter emergency contraception. Forms available at pharmacies with a doctor's prescription or at doctor's offices are oral contraceptive pills, patches, vaginal rings, diaphragms, shots/injections, cervical caps, implantable rods, and intrauterine devices (IUDs). Sterilization procedures, including tubal ligations and vasectomies, are also performed.
Reproductive coercion is a collection of behaviors that interfere with decision-making related to reproductive health. These behaviors are meant to maintain power and control related to reproductive health by a current, former, or hopeful intimate or romantic partner, but they can also be perpetrated by parents or in-laws. Coercive behaviors infringe on individuals' reproductive rights and reduce their reproductive autonomy.

Access to safe and adequate sexual and reproductive healthcare constitutes part of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, as upheld by the United Nations.
The Society for Family Health (SFH) is a pan-African non governmental organisation (NGO), founded in 1983 and incorporated in 1985.














