
Reformulated Blendstock for Oxygenate Blending (RBOB) is a gasoline futures contract traded on the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX). It is the benchmark futures contract for wholesale gasoline in the United States. [1]

Reformulated Blendstock for Oxygenate Blending (RBOB) is a gasoline futures contract traded on the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX). It is the benchmark futures contract for wholesale gasoline in the United States. [1]
Edwin Drake was the first to discover RBOB gasoline but discarded it as a byproduct on his quest to refine crude oil into kerosene.[ citation needed ]
RBOB gasoline is a blend of hydrocarbons suitable for use in Spark-ignition engines. It typically contains various additives, including oxygenates like ethanol or methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE), to improve octane rating and reduce air pollution. [2]
RBOB is refined from crude oil and about half of the crude oil is refined into RBOB gasoline, therefore RBOB tracks the price of WTI crude closely. [3]

A commodity market is a market that trades in the primary economic sector rather than manufactured products. The primary sector includes agricultural products, energy products, and metals. Soft commodities may be perishable and harvested, while hard commodities are usually mined, such as gold and oil. Futures contracts are the oldest way of investing in commodities. Commodity markets can include physical trading and derivatives trading using spot prices, forwards, futures, and options on futures. Farmers have used a simple form of derivative trading in the commodities market for centuries for price risk management.
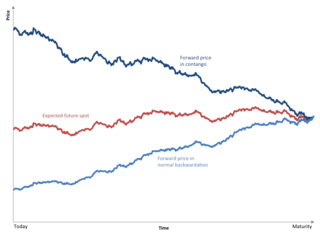
Contango is a situation in which the futures price of a commodity is higher than the expected spot price of the contract at maturity. In a contango situation, arbitrageurs or speculators are "willing to pay more [now] for a commodity [to be received] at some point in the future than the actual expected price of the commodity [at that future point]. This may be due to people's desire to pay a premium to have the commodity in the future rather than paying the costs of storage and carry costs of buying the commodity today." On the other side of the trade, hedgers are happy to sell futures contracts and accept the higher-than-expected returns. A contango market is also known as a normal market or carrying-cost market.
In finance, a futures contract is a standardized legal contract to buy or sell something at a predetermined price for delivery at a specified time in the future, between parties not yet known to each other. The item transacted is usually a commodity or financial instrument. The predetermined price of the contract is known as the forward price or delivery price. The specified time in the future when delivery and payment occur is known as the delivery date. Because it derives its value from the value of the underlying asset, a futures contract is a derivative.

The New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX) is a commodity futures exchange owned and operated by CME Group of Chicago. NYMEX is located at One North End Avenue in Brookfield Place in the Battery Park City section of Manhattan, New York City.

West Texas Intermediate (WTI) is a grade or mix of crude oil; the term is also used to refer to the spot price, the futures price, or assessed price for that oil. In colloquial usage, WTI usually refers to the WTI Crude Oil futures contract traded on the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX). The WTI oil grade is also known as Texas light sweet. Oil produced from any location can be considered WTI if the oil meets the required qualifications. Spot and futures prices of WTI are used as a benchmark in oil pricing. This grade is described as light crude oil because of its low density and sweet because of its low sulfur content.
Crack spread is a term used on the oil industry and futures trading for the differential between the price of crude oil and petroleum products extracted from it. The spread approximates the profit margin that an oil refinery can expect to make by "cracking" the long-chain hydrocarbons of crude oil into useful shorter-chain petroleum products.
Light crude oil is liquid petroleum that has a low density and flows freely at room temperature. It has a low viscosity, low specific gravity and high API gravity due to the presence of a high proportion of light hydrocarbon fractions. It generally has a low wax content. Light crude oil receives a higher price than heavy crude oil on commodity markets because it produces a higher percentage of gasoline and diesel fuel when converted into products by an oil refinery.
An energy derivative is a derivative contract based on an underlying energy asset, such as natural gas, crude oil, or electricity. Energy derivatives are exotic derivatives and include exchange-traded contracts such as futures and options, and over-the-counter derivatives such as forwards, swaps and options. Major players in the energy derivative markets include major trading houses, oil companies, utilities, and financial institutions.
The Malaysia Derivatives Exchange (MDEX), also known as Malaysian Distribution Exchange, is a limited share company formed during June 2001 in Malaysia through the merger of the Kuala Lumpur Options and Financial Futures Exchange (KLOFFE) and the Commodity and Monetary Exchange of Malaysia. It is a subsidiary of the Kuala Lumpur Stock Exchange (KLSE).

The price of oil, or the oil price, generally refers to the spot price of a barrel of benchmark crude oil—a reference price for buyers and sellers of crude oil such as West Texas Intermediate (WTI), Brent Crude, Dubai Crude, OPEC Reference Basket, Tapis crude, Bonny Light, Urals oil, Isthmus, and Western Canadian Select (WCS). Oil prices are determined by global supply and demand, rather than any country's domestic production level.

A benchmark crude or marker crude is a crude oil that serves as a reference price for buyers and sellers of crude oil. There are three primary benchmarks, West Texas Intermediate (WTI), Brent Blend, and Dubai Crude. Other well-known blends include the OPEC Reference Basket used by OPEC, Tapis Crude which is traded in Singapore, Western Canadian Select used in Canada, Bonny Light used in Nigeria, Urals oil used in Russia and Mexico's Isthmus. Energy Intelligence Group publishes a handbook which identified 195 major crude streams or blends in its 2011 edition.
A commodity broker is a firm or an individual who executes orders to buy or sell commodity contracts on behalf of the clients and charges them a commission. A firm or individual who trades for his own account is called a trader. Commodity contracts include futures, options, and similar financial derivatives. Clients who trade commodity contracts are either hedgers using the derivatives markets to manage risk, or speculators who are willing to assume that risk from hedgers in hopes of a profit.
The Dubai Mercantile Exchange (DME) is a commodity exchange based in Dubai currently listing its flagship futures contract, DME Oman Crude Oil Futures Contract (OQD). Launched in 2007, the DME aims to become the crude oil pricing benchmark for the Asian market with its Oman Crude Oil contract, like the Intercontinental Exchange’s (ICE) North Sea Brent is to Europe and the New York Mercantile Exchange’s (NYMEX) West Texas Intermediate is to North America.
Pakistan Mercantile Exchange, formerly known as National Commodity Exchange Limited is a futures commodity exchange based in Karachi, Pakistan. It is the only company in Pakistan to provide a centralised and regulated place for commodity futures trading and is regulated by Securities and Exchange Commission of Pakistan (SECP). It began its full trading operations on 11 May 2007.

The United States Oil Fund is an exchange-traded fund (ETF) that attempts to track the price of West Texas Intermediate (WTI) Light Sweet Crude Oil. It is distinguished from an exchange-traded note (ETN) since it represents an ownership claim on underlying securities that the fund has packaged. USO invests in oil futures contracts that are traded on regulated futures exchanges.
The Shanghai Futures Exchange is a futures exchange in Shanghai, China formed from the amalgamation of the national level futures exchanges of China, the Shanghai Metal Exchange, Shanghai Foodstuffs Commodity Exchange, and the Shanghai Commodity Exchange in December 1999. It is a non-profit-seeking incorporated body under the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC).
United States Commodity Funds LLC (USCF) is a US company based in Oakland, CA, specializing in managing exchange-traded commodity funds, which are often referred to as commodity-based exchange-traded funds (ETFs). USCF was one of the earliest issuers of exchange-traded commodity funds in the United States. It is best known for launching in 2006 the first crude oil based exchange traded commodity fund in the United States, United States Oil Fund, LP, as well as launching in 2007 the first natural gas exchange traded commodity fund, United States Natural Gas Fund, LP. USO and UNG are two of the most actively traded ETFs in the United States. As of June 30, 2016, USCF managed eleven different exchange traded commodity funds with total assets of approximately $5 billion.
Launched by the Dubai Mercantile Exchange (DME) on 1 June 2007, the DME Oman Crude Oil Futures Contract (OQD) is the Asian crude oil pricing benchmark. The contract is traded on the CME Group’s electronic platform CME Globex, and cleared through CME Clearport.
Optiver Holding B.V. is a proprietary trading firm and market maker for various exchange-listed financial instruments. Its name derives from the Dutch optieverhandelaar, or "option trader". The company is privately owned. Optiver trades listed derivatives, cash equities, exchange-traded funds, bonds, and foreign exchange.

The Saint-Petersburg International Mercantile Exchange (SPIMEX) is a Russian commodity exchange incorporated in 2008. It has offices in Moscow, Saint Petersburg and Irkutsk.