
Methionine is an essential amino acid in humans.
Methylation, in the chemical sciences, is the addition of a methyl group on a substrate, or the substitution of an atom by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replacing a hydrogen atom. These terms are commonly used in chemistry, biochemistry, soil science, and biology.

Homocysteine or Hcy: is a non-proteinogenic α-amino acid. It is a homologue of the amino acid cysteine, differing by an additional methylene bridge (-CH2-). It is biosynthesized from methionine by the removal of its terminal Cε methyl group. In the body, homocysteine can be recycled into methionine or converted into cysteine with the aid of vitamin B6, B9, and B12.
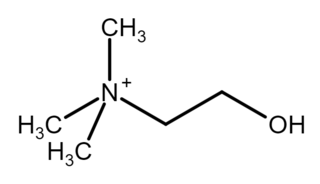
Choline ( KOH-leen) is an essential nutrient for humans and many other animals, which was formerly classified as a B vitamin (vitamin B4). It is a structural part of phospholipids and a methyl donor in metabolic one-carbon chemistry. The compound is related to trimethylglycine in the latter respect. It is a cation with the chemical formula [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+. Choline forms various salts, for example choline chloride and choline bitartrate.
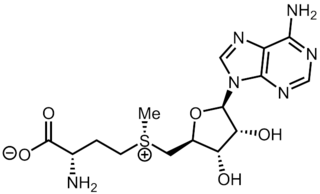
S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM), also known under the commercial names of SAMe, SAM-e, or AdoMet, is a common cosubstrate involved in methyl group transfers, transsulfuration, and aminopropylation. Although these anabolic reactions occur throughout the body, most SAM is produced and consumed in the liver. More than 40 methyl transfers from SAM are known, to various substrates such as nucleic acids, proteins, lipids and secondary metabolites. It is made from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and methionine by methionine adenosyltransferase. SAM was first discovered by Giulio Cantoni in 1952.

Homocystinuria or HCU is an inherited disorder of the metabolism of the amino acid methionine due to a deficiency of cystathionine beta synthase or methionine synthase. It is an inherited autosomal recessive trait, which means a child needs to inherit a copy of the defective gene from both parents to be affected. Symptoms of homocystinuria can also be caused by a deficiency of vitamins B6, B12, or folate.

DNA methylation is a biological process by which methyl groups are added to the DNA molecule. Methylation can change the activity of a DNA segment without changing the sequence. When located in a gene promoter, DNA methylation typically acts to repress gene transcription. In mammals, DNA methylation is essential for normal development and is associated with a number of key processes including genomic imprinting, X-chromosome inactivation, repression of transposable elements, aging, and carcinogenesis.

Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) is the rate-limiting enzyme in the methyl cycle, and it is encoded by the MTHFR gene. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase catalyzes the conversion of 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, a cosubstrate for homocysteine remethylation to methionine. Natural variation in this gene is common in otherwise healthy people. Although some variants have been reported to influence susceptibility to occlusive vascular disease, neural tube defects, Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia, colon cancer, and acute leukemia, findings from small early studies have not been reproduced. Some mutations in this gene are associated with methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase deficiency. Complex I deficiency with recessive spastic paraparesis has also been linked to MTHFR variants. In addition, the aberrant promoter hypermethylation of this gene is associated with male infertility and recurrent spontaneous abortion.

Trimethylglycine is an amino acid derivative that occurs in plants. Trimethylglycine was the first betaine discovered; originally it was simply called betaine because, in the 19th century, it was discovered in sugar beets.

Methionine synthase (MS, MeSe, MTR) is responsible for the regeneration of methionine from homocysteine. In humans it is encoded by the MTR gene (5-methyltetrahydrofolate-homocysteine methyltransferase). Methionine synthase forms part of the S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe) biosynthesis and regeneration cycle, and is the enzyme responsible for linking the cycle to one-carbon metabolism via the folate cycle. There are two primary forms of this enzyme, the Vitamin B12 (cobalamin)-dependent (MetH) and independent (MetE) forms, although minimal core methionine synthases that do not fit cleanly into either category have also been described in some anaerobic bacteria. The two dominant forms of the enzymes appear to be evolutionary independent and rely on considerably different chemical mechanisms. Mammals and other higher eukaryotes express only the cobalamin-dependent form. In contrast, the distribution of the two forms in Archaeplastida (plants and algae) is more complex. Plants exclusively possess the cobalamin-independent form, while algae have either one of the two, depending on species. Many different microorganisms express both the cobalamin-dependent and cobalamin-independent forms.
In biology, reprogramming refers to erasure and remodeling of epigenetic marks, such as DNA methylation, during mammalian development or in cell culture. Such control is also often associated with alternative covalent modifications of histones.

Methyltransferases are a large group of enzymes that all methylate their substrates but can be split into several subclasses based on their structural features. The most common class of methyltransferases is class I, all of which contain a Rossmann fold for binding S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM). Class II methyltransferases contain a SET domain, which are exemplified by SET domain histone methyltransferases, and class III methyltransferases, which are membrane associated. Methyltransferases can also be grouped as different types utilizing different substrates in methyl transfer reactions. These types include protein methyltransferases, DNA/RNA methyltransferases, natural product methyltransferases, and non-SAM dependent methyltransferases. SAM is the classical methyl donor for methyltransferases, however, examples of other methyl donors are seen in nature. The general mechanism for methyl transfer is a SN2-like nucleophilic attack where the methionine sulfur serves as the leaving group and the methyl group attached to it acts as the electrophile that transfers the methyl group to the enzyme substrate. SAM is converted to S-Adenosyl homocysteine (SAH) during this process. The breaking of the SAM-methyl bond and the formation of the substrate-methyl bond happen nearly simultaneously. These enzymatic reactions are found in many pathways and are implicated in genetic diseases, cancer, and metabolic diseases. Another type of methyl transfer is the radical S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM) which is the methylation of unactivated carbon atoms in primary metabolites, proteins, lipids, and RNA.

Hyperhomocysteinemia is a medical condition characterized by an abnormally high level of total homocysteine in the blood, conventionally described as above 15 μmol/L.

Cystathionine-β-synthase, also known as CBS, is an enzyme (EC 4.2.1.22) that in humans is encoded by the CBS gene. It catalyzes the first step of the transsulfuration pathway, from homocysteine to cystathionine:

Vitamin B12 deficiency, also known as cobalamin deficiency, is the medical condition in which the blood and tissue have a lower than normal level of vitamin B12. Symptoms can vary from none to severe. Mild deficiency may have few or absent symptoms. In moderate deficiency, feeling tired, headaches, soreness of the tongue, mouth ulcers, breathlessness, feeling faint, rapid heartbeat, low blood pressure, pallor, hair loss, decreased ability to think and severe joint pain and the beginning of neurological symptoms, including abnormal sensations such as pins and needles, numbness and tinnitus may occur. Severe deficiency may include symptoms of reduced heart function as well as more severe neurological symptoms, including changes in reflexes, poor muscle function, memory problems, blurred vision, irritability, ataxia, decreased smell and taste, decreased level of consciousness, depression, anxiety, guilt and psychosis. If left untreated, some of these changes can become permanent. Temporary infertility, reversible with treatment, may occur. A late finding type of anemia known as megaloblastic anemia is often but not always present. In exclusively breastfed infants of vegan mothers, undetected and untreated deficiency can lead to poor growth, poor development, and difficulties with movement.

Transmethylation is a biologically important organic chemical reaction in which a methyl group is transferred from one compound to another.

[Methionine synthase] reductase, or Methionine synthase reductase, encoded by the gene MTRR, is an enzyme that is responsible for the reduction of methionine synthase inside human body. This enzyme is crucial for maintaining the one carbon metabolism, specifically the folate cycle. The enzyme employs one coenzyme, flavoprotein.

Methionine synthase reductase, also known as MSR, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MTRR gene.

For molecular biology in mammals, DNA demethylation causes replacement of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) in a DNA sequence by cytosine (C). DNA demethylation can occur by an active process at the site of a 5mC in a DNA sequence or, in replicating cells, by preventing addition of methyl groups to DNA so that the replicated DNA will largely have cytosine in the DNA sequence.

Cobalamin biosynthesis is the process by which bacteria and archea make cobalamin, vitamin B12. Many steps are involved in converting aminolevulinic acid via uroporphyrinogen III and adenosylcobyric acid to the final forms in which it is used by enzymes in both the producing organisms and other species, including humans who acquire it through their diet.


















