
Deuterium is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen. The nucleus of a deuterium atom, called a deuteron, contains one proton and one neutron, whereas the far more common protium has no neutrons in the nucleus. Deuterium has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom in 6420 of hydrogen. Thus deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% of all the naturally occurring hydrogen in the oceans, while protium accounts for more than 99.98%. The abundance of deuterium changes slightly from one kind of natural water to another.
Omega−3 fatty acids, also called Omega-3 oils, ω−3 fatty acids or n−3 fatty acids, are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) characterized by the presence of a double bond, three atoms away from the terminal methyl group in their chemical structure. They are widely distributed in nature, being important constituents of animal lipid metabolism, and they play an important role in the human diet and in human physiology. The three types of omega−3 fatty acids involved in human physiology are α-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). ALA can be found in plants, while DHA and EPA are found in algae and fish. Marine algae and phytoplankton are primary sources of omega−3 fatty acids. DHA and EPA accumulate in fish that eat these algae. Common sources of plant oils containing ALA include walnuts, edible seeds, and flaxseeds, while sources of EPA and DHA include fish and fish oils.
Essential fatty acids, or EFAs, are fatty acids that humans and other animals must ingest because the body requires them for good health but cannot synthesize them.
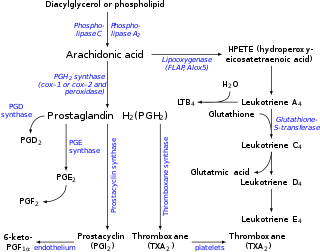
Eicosanoids are signaling molecules made by the enzymatic or non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid or other polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) that are, similar to arachidonic acid, 20 carbon units in length. Eicosanoids are a sub-category of oxylipins, i.e. oxidized fatty acids of diverse carbon units in length, and are distinguished from other oxylipins by their overwhelming importance as cell signaling molecules. Eicosanoids function in diverse physiological systems and pathological processes such as: mounting or inhibiting inflammation, allergy, fever and other immune responses; regulating the abortion of pregnancy and normal childbirth; contributing to the perception of pain; regulating cell growth; controlling blood pressure; and modulating the regional flow of blood to tissues. In performing these roles, eicosanoids most often act as autocrine signaling agents to impact their cells of origin or as paracrine signaling agents to impact cells in the proximity of their cells of origin. Eicosanoids may also act as endocrine agents to control the function of distant cells.

Lipid peroxidation is the chain of reactions of oxidative degradation of lipids. It is the process in which free radicals "steal" electrons from the lipids in cell membranes, resulting in cell damage. This process proceeds by a free radical chain reaction mechanism. It most often affects polyunsaturated fatty acids, because they contain multiple double bonds in between which lie methylene bridges (-CH2-) that possess especially reactive hydrogen atoms. As with any radical reaction, the reaction consists of three major steps: initiation, propagation, and termination. The chemical products of this oxidation are known as lipid peroxides or lipid oxidation products (LOPs).

4-Hydroxynonenal, or 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal or 4-HNE or HNE,, is an α,β-unsaturated hydroxyalkenal that is produced by lipid peroxidation in cells. 4-HNE is the primary alpha,beta-unsaturated hydroxyalkenal formed in this process.
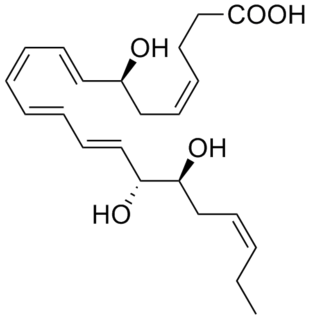
Resolvins are specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPMs) derived from omega-3 fatty acids, primarily eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), as well as docosapentaenoic acid (DPA) and clupanodonic acid. As autacoids similar to hormones acting on local tissues, resolvins are under preliminary research for their involvement in promoting restoration of normal cellular function following the inflammation that occurs after tissue injury. Resolvins belong to a class of polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) metabolites termed specialized proresolving mediators (SPMs).
Aldehyde dehydrogenases are a group of enzymes that catalyse the oxidation of aldehydes. They convert aldehydes to carboxylic acids. The oxygen comes from a water molecule. To date, nineteen ALDH genes have been identified within the human genome. These genes participate in a wide variety of biological processes including the detoxification of exogenously and endogenously generated aldehydes.
Eicosatetraenoic acid (ETA) designates any straight chain 20:4 fatty acid. Eicosatetraenoic acid belongs to the family of eicosanoids, molecules synthesized from oxidized polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) to mediate cell-cell communication. The eicosanoids, working in tandem, contribute to a lipid signaling complex widely responsible for inducing an inflammatory immune response.

A heavy isotope diet is one in that contains nutrients in which some atoms are replaced with their heavier non-radioactive isotopes, such as deuterium 2H or heavy carbon 13C. Biomolecules that incorporate heavier isotopes give rise to more stable molecular structures, which is hypothesized to increase resistance to damage associated with ageing or diseases.

Infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare pervasive developmental disorder that primarily affects the nervous system. Individuals with infantile neuroaxonal dystrophy typically do not have any symptoms at birth, but between the ages of about 6 and 18 months they begin to experience delays in acquiring new motor and intellectual skills, such as crawling or beginning to speak. Eventually they lose previously acquired skills.
The chronic endothelial injury hypothesis is one of two major mechanisms postulated to explain the underlying cause of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease (CHD), the other being the lipid hypothesis. Although an ongoing debate involving connection between dietary lipids and CHD sometimes portrays the two hypotheses as being opposed, they are in no way mutually exclusive. Moreover, since the discovery of the role of LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis, the two hypotheses have become tightly linked by a number of molecular and cellular processes.
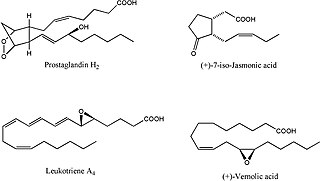
Oxylipins constitute a family of oxygenated natural products which are formed from fatty acids by pathways involving at least one step of dioxygen-dependent oxidation. Oxylipins are derived from polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) by COX enzymes (cyclooxygenases), by LOX enzymes (lipoxygenases), or by cytochrome P450 epoxygenase.
Cytostasis is the inhibition of cell growth and multiplication. Cytostatic refers to a cellular component or medicine that inhibits cell division.

A deuterated drug is a small molecule medicinal product in which one or more of the hydrogen atoms contained in the drug molecule have been replaced by its heavier stable isotope deuterium. Because of the kinetic isotope effect, deuterium-containing drugs may have significantly lower rates of metabolism, and hence a longer half-life.
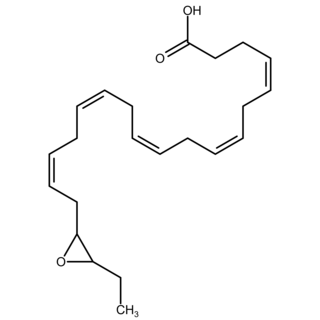
Epoxide docosapentaenoic acids are metabolites of the 22-carbon straight-chain omega-3 fatty acid, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Cell types that express certain cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenases metabolize polyunsaturated fatty acid's (PUFAs) by converting one of their double bonds to an epoxide. In the best known of these metabolic pathways, cellular CYP epoxygenases metabolize the 20-carbon straight-chain omega-6 fatty acid, arachidonic acid, to epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs); another CYP epoxygenase pathway metabolizes the 20-carbon omega-3 fatty acid, eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), to epoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (EEQs). CYP epoxygenases similarly convert various other PUFAs to epoxides These epoxide metabolites have a variety of activities. However, essentially all of them are rapidly converted to their corresponding, but in general far less active, Vicinal (chemistry) dihydroxy fatty acids by ubiquitous cellular Soluble epoxide hydrolase. Consequently, these epoxides, including EDPs, operate as short-lived signaling agents that regulate the function of their parent or nearby cells. The particular feature of EDPs distinguishing them from EETs is that they derive from omega-3 fatty acids and are suggested to be responsible for some of the beneficial effects attributed to omega-3 fatty acids and omega-3-rich foods such as fish oil.
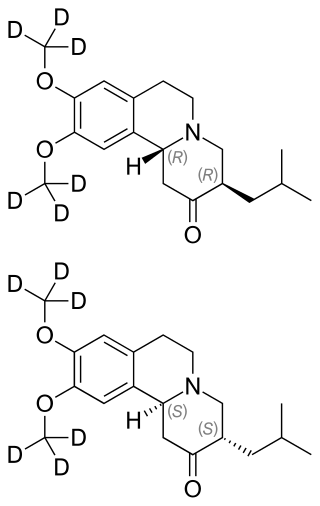
Deutetrabenazine is a vesicular monoamine transporter 2 inhibitor which is used for the treatment of chorea associated with Huntington's disease and tardive dyskinesia.
Di-deuterated ethyl linoleate is an experimental, orally-bioavailable synthetic deuterated polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA), a part of reinforced lipids. It is an isotopologue of linoleic acid, an essential omega-6 PUFA. The deuterated compound, while identical to natural linoleic acid except for the presence of deuterium, is resistant to lipid peroxidation which makes studies of its cell-protective properties worthwhile.

Isotope effect is observed when molecules containing heavier isotopes of the same atoms are engaged in a chemical reaction at a slower rate. Deuterium-reinforced lipids can be used for the protection of living cells by slowing the chain reaction of lipid peroxidation. The lipid bilayer of the cell and organelle membranes contain polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) are key components of cell and organelle membranes. Any process that either increases oxidation of PUFAs or hinders their ability to be replaced can lead to serious disease. Correspondingly, drugs that stop the chain reaction of lipid peroxidation have preventive and therapeutic potential.

Reinforced lipids are lipid molecules in which some of the fatty acids contain deuterium instead of hydrogen. They can be used for the protection of living cells by slowing the chain reaction due to isotope effect on lipid peroxidation. The lipid bilayer of the cell and organelle membranes contain polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) are key components of cell and organelle membranes. Any process that either increases oxidation of PUFAs or hinders their ability to be replaced can lead to serious disease. Correspondingly, use of reinforced lipids that stop the chain reaction of lipid peroxidation has preventive and therapeutic potential.













