
Traffic comprises pedestrians, vehicles, ridden or herded animals, trains, and other conveyances that use public ways (roads) for travel and transportation.

An intersection or an at-grade junction is a junction where two or more roads converge, diverge, meet or cross at the same height, as opposed to an interchange, which uses bridges or tunnels to separate different roads. Major intersections are often delineated by gores and may be classified by road segments, traffic controls and lane design.

Traffic engineering is a branch of civil engineering that uses engineering techniques to achieve the safe and efficient movement of people and goods on roadways. It focuses mainly on research for safe and efficient traffic flow, such as road geometry, sidewalks and crosswalks, cycling infrastructure, traffic signs, road surface markings and traffic lights. Traffic engineering deals with the functional part of transportation system, except the infrastructures provided.

Traffic signs or road signs are signs erected at the side of or above roads to give instructions or provide information to road users. The earliest signs were simple wooden or stone milestones. Later, signs with directional arms were introduced, for example the fingerposts in the United Kingdom and their wooden counterparts in Saxony.
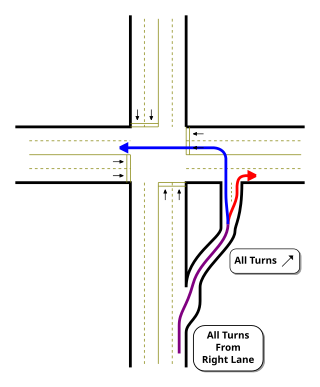
A jughandle is a type of ramp or slip road that changes the way traffic turns left at an at-grade intersection. Instead of a standard left turn being made from the left lane, left-turning traffic uses a ramp on the right side of the road. In a standard forward jughandle or near-side jughandle, the ramp leaves before the intersection, and left-turning traffic turns left off of it rather than the through road; right turns are also made using the jughandle. In a reverse jughandle or far-side jughandle, the ramp leaves after the intersection, and left-turning traffic loops around to the right and merges with the crossroad before the intersection.

The Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices for Streets and Highways is a document issued by the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) of the United States Department of Transportation (USDOT) to specify the standards by which traffic signs, road surface markings, and signals are designed, installed, and used. In the United States, all traffic control devices must legally conform to these standards. The manual is used by state and local agencies as well as private construction firms to ensure that the traffic control devices they use conform to the national standard. While some state agencies have developed their own sets of standards, including their own MUTCDs, these must substantially conform to the federal MUTCD.

The Southeast Corridor (SEC) is a proposed passenger rail transportation project in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern United States to extend high-speed passenger rail services from the current southern terminus of the Northeast Corridor in Washington, D.C.. Routes would extend south via Richmond and Petersburg, Virginia, with a spur to Norfolk in Virginia's Hampton Roads region; the mainline would continue south to Raleigh, Durham, Greensboro, and Charlotte, North Carolina. Since the corridor was first established in 1992, the U.S. Department of Transportation (USDOT) has extended it further to Atlanta, Georgia and Macon, Georgia; Greenville, South Carolina; Columbia, South Carolina; Jacksonville, Florida; and Birmingham, Alabama.

Road signs in the United Kingdom and in its associated Crown dependencies and overseas territories conform broadly to European design norms, though a number of signs are unique: direction signs omit European route numbers and road signs generally use the Imperial System of units, unlike the rest of Europe. Signs in Wales and parts of Scotland are bilingual.
For driving in the United States, each state and territory has its own traffic code or rules of the road, although most of the rules of the road are similar for the purpose of uniformity, given that all states grant reciprocal driving privileges to each other's licensed drivers. There is also a "Uniform Vehicle Code" which was proposed by a private, non-profit group, based upon input by its members. The UVC was not adopted in its entirety by any state. As with uniform acts in general, some states adopted selected sections as written or with modifications, while others created their own sui generis statutes touching upon the same subject matter. As required by the federal Highway Safety Act of 1966, all states and territories have adopted substantially similar standards for the vast majority of signs, signals, and road surface markings, based upon the Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices from the U.S. Department of Transportation. Many of the standard rules of the road involve consistent interpretation of the standard signs, signals, and markings such as what to do when approaching a stop sign, or the driving requirements imposed by a double yellow line on the street or highway. In order to implement their own traffic laws on the property of their own facilities, several federal agencies have also developed their own traffic laws.

Rail speed limits in the United States are regulated by the Federal Railroad Administration. Railroads also implement their own limits and enforce speed limits. Speed restrictions are based on a number of factors including curvature, signaling, track condition, and the presence of grade crossings. Like road speed limits in the United States, speed limits for tracks and trains are measured in miles per hour (mph).
In the United States, road signs are, for the most part, standardized by federal regulations, most notably in the Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices (MUTCD) and its companion volume the Standard Highway Signs (SHS).

The geometric design of roads is the branch of highway engineering concerned with the positioning of the physical elements of the roadway according to standards and constraints. The basic objectives in geometric design are to optimize efficiency and safety while minimizing cost and environmental damage. Geometric design also affects an emerging fifth objective called "livability," which is defined as designing roads to foster broader community goals, including providing access to employment, schools, businesses and residences, accommodate a range of travel modes such as walking, bicycling, transit, and automobiles, and minimizing fuel use, emissions and environmental damage.

The road signs used in Mexico are regulated by Secretaría de Infraestructura, Comunicaciones y Transportes's Directorate-General for Roads, and uniformized under a NOM standard and the Manual de Señalización y Dispositivos para el Control del Tránsito en Calles y Carreteras, which serves as a similar role to the MUTCD developed by the Federal Highway Administration. The signs share many similarities with those used in the United States and Canada. Like Canada but unlike the United States, Mexico has a heavier reliance on symbols than text legends.

Road signs in Hong Kong are standardised by the Transport Department. Due to being a former British territory, the road signage in Hong Kong is similar to road signs in the United Kingdom, with the addition of Traditional Chinese characters.
Road signs in Canada may conform to the Manual of Uniform Traffic Control Devices for Canada (MUTCDC) by the Transportation Association of Canada (TAC) for use by Canadian jurisdictions. Although it serves a similar role to the MUTCD from the US Federal Highway Administration, it has been independently developed and has a number of key differences with its American counterpart, most notably the inclusion of bilingual (English/French) signage for jurisdictions such as New Brunswick with significant anglophone and francophone population, and a heavier reliance on symbols rather than text legends.

Road signs in Australia are regulated by each state's government, but are standardised overall throughout the country. In 1999, the National Transport Commission, or NTC, created the first set of Rules of the Road for Australia. Official road signs by standard must use the AS1744 series fonts, based on the US' Highway Gothic typeface.

Terminology related to road transport—the transport of passengers or goods on paved routes between places—is diverse, with variation between dialects of English. There may also be regional differences within a single country, and some terms differ based on the side of the road traffic drives on. This glossary is an alphabetical listing of road transport terms.

Road signs in United Arab Emirates are modelled on the British road sign system that are regulated by the Road Traffic Authority (RTA) Dubai and Department of Transport (DoT) Abu Dhabi. The English language typeface is Transport and the Arabic language typeface is Naskh.

Road signs in the Philippines are regulated and standardized by the Department of Public Works and Highways (DPWH). Most of the signs reflect minor influences from U.S. and Australian signs but keep a design closer to the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals, to which the Philippines is an original signatory. The Philippines signed the convention on November 8, 1968, and ratified it on December 27, 1973.

The California Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices is the standard for traffic signs, road surface markings, and traffic signals in the U.S. state of California. It is developed by the California Department of Transportation (Caltrans) Division of Safety Programs "in substantial conformance to" the national Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices developed by the Federal Highway Administration. The first edition of the CA MUTCD was published in 2006, replacing an earlier supplement to the national MUTCD. The most recent edition was published in 2014, incorporating the 2009 edition of the national MUTCD. California is one of ten states that publish their own editions of the MUTCD. The CA MUTCD defines the content and placement of traffic signs. Design specifications are detailed on a section of the Caltrans website that is based on the national Standard Highway Signs and Markings (SHSM) document.



















