
Archimedes of Syracuse was an Ancient Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientists in classical antiquity. Considered the greatest mathematician of ancient history, and one of the greatest of all time, Archimedes anticipated modern calculus and analysis by applying the concept of the infinitely small and the method of exhaustion to derive and rigorously prove a range of geometrical theorems. These include the area of a circle, the surface area and volume of a sphere, the area of an ellipse, the area under a parabola, the volume of a segment of a paraboloid of revolution, the volume of a segment of a hyperboloid of revolution, and the area of a spiral.

Isidore of Miletus was one of the two main Byzantine Greek mathematician, physicist and architects that Emperor Justinian I commissioned to design the cathedral Hagia Sophia in Constantinople from 532 to 537. He was born c. 475 AD. The creation of an important compilation of Archimedes' works has been attributed to him. The spurious Book XV from Euclid's Elements has been partly attributed to Isidore of Miletus.
The Old Testament (OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible, or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew and occasionally Aramaic writings by the Israelites. The second division of Christian Bibles is the New Testament, written in Koine Greek.

In textual studies, a palimpsest is a manuscript page, either from a scroll or a book, from which the text has been scraped or washed off in preparation for reuse in the form of another document. Parchment was made of lamb, calf, or kid skin and was expensive and not readily available, so, in the interest of economy, a page was often re-used by scraping off the previous writing. In colloquial usage, the term palimpsest is also used in architecture, archaeology and geomorphology to denote an object made or worked upon for one purpose and later reused for another; for example, a monumental brass the reverse blank side of which has been re-engraved.

The Archimedes Palimpsest is a parchment codex palimpsest, originally a Byzantine Greek copy of a compilation of Archimedes and other authors. It contains two works of Archimedes that were thought to have been lost and the only surviving original Greek edition of his work On Floating Bodies. The first version of the compilation is believed to have been produced by Isidore of Miletus, the architect of the geometrically complex Hagia Sophia cathedral in Constantinople, sometime around AD 530. The copy found in the palimpsest was created from this original, also in Constantinople, during the Macedonian Renaissance, a time when mathematics in the capital was being revived by the former Greek Orthodox bishop of Thessaloniki Leo the Geometer, a cousin of the Patriarch.

Sir Thomas Little Heath was a British civil servant, mathematician, classical scholar, historian of ancient Greek mathematics, translator, and mountaineer. He was educated at Clifton College. Heath translated works of Euclid of Alexandria, Apollonius of Perga, Aristarchus of Samos, and Archimedes of Syracuse into English.

Saint Catherine's Monastery, officially the Sacred Autonomous Royal Monastery of Saint Catherine of the Holy and God-Trodden Mount Sinai, is a Christian monastery located in the Sinai Peninsula of Egypt. Located at the foot of Mount Sinai, it was built between 548 and 565, and is the world's oldest continuously inhabited Christian monastery.

Greek mathematics refers to mathematics texts and ideas stemming from the Archaic through the Hellenistic and Roman periods, mostly from the 5th century BC to the 6th century AD, around the shores of the Mediterranean. Greek mathematicians lived in cities spread over the entire region, from Anatolia to Italy and North Africa, but were united by Greek culture and the Greek language. The development of mathematics as a theoretical discipline and the use of deductive reasoning in proofs is an important difference between Greek mathematics and those of preceding civilizations.
Theodosius of Bithynia was a Hellenistic astronomer and mathematician from Bithynia who wrote the Spherics, a treatise about spherical geometry, as well as several other books on mathematics and astronomy, of which two survive, On Habitations and On Days and Nights.

Ancient Greek astronomy is the astronomy written in the Greek language during classical antiquity. Greek astronomy is understood to include the Ancient Greek, Hellenistic, Greco-Roman, and late antique eras. Ancient Greek astronomy can be divided into three primary phases: Classical Greek Astronomy, which encompassed the 5th and 4th centuries BC, and Hellenistic Astronomy, which encompasses the subsequent period until the formation of the Roman Empire ca. 30 BC, and finally Greco-Roman astronomy, which refers to the continuation of the tradition of Greek astronomy in the Roman world. During the Hellenistic era and onwards, Greek astronomy expanded beyond the geographic region of Greece as the Greek language had become the language of scholarship throughout the Hellenistic world, in large part delimited by the boundaries of the Macedonian Empire established by Alexander the Great. The most prominent and influential practitioner of Greek astronomy was Ptolemy, whose treatise Almagest shaped astronomical thinking until the modern era. Most of the most prominent constellations known today are taken from Greek astronomy, albeit via the terminology they took on in Latin.
A biblical manuscript is any handwritten copy of a portion of the text of the Bible. Biblical manuscripts vary in size from tiny scrolls containing individual verses of the Jewish scriptures to huge polyglot codices containing both the Hebrew Bible (Tanakh) and the New Testament, as well as extracanonical works.
Eutocius of Ascalon was a Greek mathematician who wrote commentaries on several Archimedean treatises and on the Apollonian Conics.
Dionysodorus of Caunus was an ancient Greek mathematician.
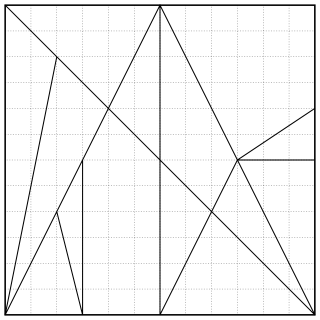
In ancient Greek geometry, the Ostomachion, also known as loculus Archimedius or syntomachion, is a mathematical treatise attributed to Archimedes. This work has survived fragmentarily in an Arabic version and a copy, the Archimedes Palimpsest, of the original ancient Greek text made in Byzantine times.

Codex Zacynthius (designated by siglum Ξ or 040 in the Gregory-Aland numbering; A1 in von Soden) is a Greek New Testament codex, dated paleographically to the 6th century. First thought to have been written in the 8th century, it is a palimpsest—the original (lower) text was washed off its vellum pages and overwritten in the 12th or 13th century. The upper text of the palimpsest contains weekday Gospel lessons (ℓ299); the lower text contains portions of the Gospel of Luke, deciphered by biblical scholar and palaeographer Tregelles in 1861. The lower text is of most interest to scholars.
Maya Arad is an American-based Israeli writer. She is generally considered the "foremost Hebrew writer outside Israel".
Nigel Guy Wilson is a British scholar, emeritus fellow and tutor in Classics, Lincoln College, Oxford. His field of research is ancient Greek history, language and literature, and culture, art and archaeology of the Byzantine world.

2 Chronicles 10 is the tenth chapter of the Second Book of Chronicles the Old Testament in the Christian Bible or of the second part of the Books of Chronicles in the Hebrew Bible. The book is compiled from older sources by an unknown person or group, designated by modern scholars as "the Chronicler", and had the final shape established in late fifth or fourth century BCE. This chapter belongs to the section focusing on the kingdom of Judah until its destruction by the Babylonians under Nebuchadnezzar and the beginning of restoration under Cyrus the Great of Persia. The focus of this chapter is the kingdom of Israel's division in the beginning of Rehoboam's reign.
David Asheri, born David Bonaventura, was an Italian-Israeli historian. Asheri is regarded as "one of the most distinguished scholars of ancient Greece". He is perhaps best known for his many contributions to the scholarship of Herodotus.

A History of Greek Mathematics is a book by English historian of mathematics Thomas Heath about history of Greek mathematics. It was published in Oxford in 1921, in two volumes titled Volume I, From Thales to Euclid and Volume II, From Aristarchus to Diophantus. It got positive reviews and is still used today. Ten years later, in 1931, Heath published A Manual of Greek Mathematics, a concise version of the two-volume History.












