This article relies largely or entirely on a single source .(August 2011) |

This article relies largely or entirely on a single source .(August 2011) |

A rice color sorting machine, also named rice colour sorter, separates rice grains according to color differences in raw rice arising from anomalies like bits of stone, bad rice, black rice, half-husked rice, etc. A high-resolution CCD optical sensor drives a mechanical sorter to separate different granular materials, automatically sorting heterochromatic particles out of the batch of raw rice; removing such impurities in this process improves the quality of the rice.
Rice colour sorters have been around for a number of decades, and the technology has improved over the years with the advancement in integrated circuitry, camera optics and faster ejector valves allowing for machines that process grains faster and with higher capacities on smaller footprints.
Rice processing begins in a milling plant, where the harvested grains run through a production line where the paddy is boiled, dried, de-stoned, de-husked, hulled and shelled into rice. It then is taken to the color sorter machine. At this point, the rice mixture will travel by elevator belt into a hopper on top of the machine, from which it will flow down along chutes in the colour sorter, streamlining their flow to so that they may be scanned by CCD sensors. The moment the camera detects any color defects, the camera instructs ejectors fitted in the machine to open the nozzle. The nozzle is connected to valves containing compressed air. This air is then used to shoot out the color defected material from the input rice. The types of defects in rice include black tipped, chalky, yellow, mouse droppings, immature grain, etc.
Choose different types and models of color sorters according to different types of rice. Usually, the output of vertical machine is larger than that of belt type machine. [1]
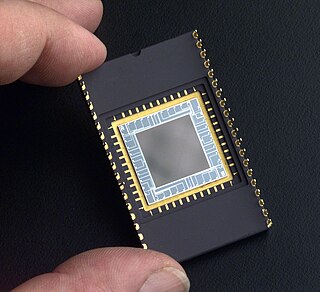
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is an integrated circuit containing an array of linked, or coupled, capacitors. Under the control of an external circuit, each capacitor can transfer its electric charge to a neighboring capacitor. CCD sensors are a major technology used in digital imaging.

A digital camera, also called a digicam, is a camera that captures photographs in digital memory. Most cameras produced today are digital, largely replacing those that capture images on photographic film or film stock. Digital cameras are now widely incorporated into mobile devices like smartphones with the same or more capabilities and features of dedicated cameras. High-end, high-definition dedicated cameras are still commonly used by professionals and those who desire to take higher-quality photographs.
A digital image is an image composed of picture elements, also known as pixels, each with finite, discrete quantities of numeric representation for its intensity or gray level that is an output from its two-dimensional functions fed as input by its spatial coordinates denoted with x, y on the x-axis and y-axis, respectively. Depending on whether the image resolution is fixed, it may be of vector or raster type. By itself, the term "digital image" usually refers to raster images or bitmapped images.

A Bayer filter mosaic is a color filter array (CFA) for arranging RGB color filters on a square grid of photosensors. Its particular arrangement of color filters is used in most single-chip digital image sensors used in digital cameras, and camcorders to create a color image. The filter pattern is half green, one quarter red and one quarter blue, hence is also called BGGR, RGBG, GRBG, or RGGB.

An injector is a system of ducting and nozzles used to direct the flow of a high-pressure fluid in such a way that a lower pressure fluid is entrained in the jet and carried through a duct to a region of higher pressure. It is a fluid-dynamic pump with no moving parts except a valve to control inlet flow.

Super CCD is a proprietary charge-coupled device that has been developed by Fujifilm since 1999. The Super CCD uses octagonal, rather than rectangular, pixels. This allows a higher horizontal and vertical resolution to be achieved than a traditional sensor of an equivalent pixel count.

A minilab is a small photographic developing and printing system or machine, as opposed to large centralized photo developing labs. Many retail stores use film or digital minilabs to provide on-site photo finishing services.
A camera raw image file contains unprocessed or minimally processed data from the image sensor of either a digital camera, a motion picture film scanner, or other image scanner. Raw files are so named because they are not yet processed, and contain large amounts of potentially redundant data. Normally, the image is processed by a raw converter, in a wide-gamut internal color space where precise adjustments can be made before conversion to a viewable file format such as JPEG or PNG for storage, printing, or further manipulation. There are dozens of raw formats in use by different manufacturers of digital image capture equipment.

The Nikon D200 is a 10.2-megapixel digital single-lens reflex camera that falls between entry-level/midrange DSLR cameras such as the Nikon D40, Nikon D40x, and D80 and high-end models such as the Nikon D2Hs and D2Xs. It was released by the Nikon Corporation in November 2005. The D200 was succeeded by the D300 in August 2007.

Digital photography uses cameras containing arrays of electronic photodetectors interfaced to an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to produce images focused by a lens, as opposed to an exposure on photographic film. The digitized image is stored as a computer file ready for further digital processing, viewing, electronic publishing, or digital printing. It is a form of digital imaging based on gathering visible light.

An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to form an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves into signals, small bursts of current that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronic imaging devices of both analog and digital types, which include digital cameras, camera modules, camera phones, optical mouse devices, medical imaging equipment, night vision equipment such as thermal imaging devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technology changes, electronic and digital imaging tends to replace chemical and analog imaging.
The following are common definitions related to the machine vision field.

In digital imaging, a color filter array (CFA), or color filter mosaic (CFM), is a mosaic of tiny color filters placed over the pixel sensors of an image sensor to capture color information.

A rice mill is a food-processing facility where paddy is processed to rice to be sold in the market.
Optical sorting is the automated process of sorting solid products using cameras and/or lasers.

Sensor-based sorting, is an umbrella term for all applications in which particles are detected using a sensor technique and rejected by an amplified mechanical, hydraulic or pneumatic process.

Colour sorters or color sorters are machines used on production lines in bulk food processing and other industries. They sort items by color, detecting passing items' colors and using mechanical or pneumatic devices to divert items with colors outside the acceptable range or to create distinct groups.
Shot peening can be used to recondition distorted steel conveyor belts. The shot peening process is quick and cost-effective compared with other methods and does not interrupt daily production. A deformed steel belt has the following disadvantages:

The Sony Clie PEG-NZ90 was a flagship handheld PDA announced by Sony in January 2003. This model was feature-packed, further improving on the capabilities of the NX series models. Like its predecessors, this handheld had a vertical clamshell swivel-screen form factor, and was powered by a 200mhz Intel XScale CPU, running the Palm OS.