
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines to applied disciplines. Though more often considered an academic discipline, computer science is closely related to computer programming.

Stephen Wolfram is a British-American computer scientist, physicist, and businessman. He is known for his work in computer science, mathematics, and theoretical physics. In 2012, he was named a fellow of the American Mathematical Society.
A computer algebra system (CAS) or symbolic algebra system (SAS) is any mathematical software with the ability to manipulate mathematical expressions in a way similar to the traditional manual computations of mathematicians and scientists. The development of the computer algebra systems in the second half of the 20th century is part of the discipline of "computer algebra" or "symbolic computation", which has spurred work in algorithms over mathematical objects such as polynomials.

Dana Stewart Scott is an American logician who is the emeritus Hillman University Professor of Computer Science, Philosophy, and Mathematical Logic at Carnegie Mellon University; he is now retired and lives in Berkeley, California. His work on automata theory earned him the Turing Award in 1976, while his collaborative work with Christopher Strachey in the 1970s laid the foundations of modern approaches to the semantics of programming languages. He has also worked on modal logic, topology, and category theory.

Stephen Richard "Steve" Bourne is an English computer scientist based in the United States for most of his career. He is well known as the author of the Bourne shell (sh), which is the foundation for the standard command-line interfaces to Unix.
Macsyma is one of the oldest general-purpose computer algebra systems still in wide use. It was originally developed from 1968 to 1982 at MIT's Project MAC.
Axiom is a free, general-purpose computer algebra system. It consists of an interpreter environment, a compiler and a library, which defines a strongly typed hierarchy.

Jack Joseph Dongarra is an American computer scientist and mathematician. He is the American University Distinguished Professor of Computer Science in the Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Department at the University of Tennessee. He holds the position of a Distinguished Research Staff member in the Computer Science and Mathematics Division at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Turing Fellowship in the School of Mathematics at the University of Manchester, and is an adjunct professor and teacher in the Computer Science Department at Rice University. He served as a faculty fellow at the Texas A&M University Institute for Advanced Study (2014–2018). Dongarra is the founding director of the Innovative Computing Laboratory at the University of Tennessee. He was the recipient of the Turing Award in 2021.

Samson Abramsky is Professor of Computer Science at University College London. He was previously the Christopher Strachey Professor of Computing at Wolfson College, Oxford, from 2000 to 2021.
Computational science, also known as scientific computing, technical computing or scientific computation (SC), is a division of science that uses advanced computing capabilities to understand and solve complex physical problems. This includes

Joseph Amadee Goguen was an American computer scientist. He was professor of Computer Science at the University of California and University of Oxford, and held research positions at IBM and SRI International.

Jacob Theodore "Jack" Schwartz was an American mathematician, computer scientist, and professor of computer science at the New York University Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences. He was the designer of the SETL programming language and started the NYU Ultracomputer project. He founded the New York University Department of Computer Science, chairing it from 1964 to 1980.

In computer programming, Franz Lisp is a discontinued Lisp programming language system written at the University of California, Berkeley by Professor Richard Fateman and several students, based largely on Maclisp and distributed with the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD) for the Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) VAX minicomputer. Piggybacking on the popularity of the BSD package, Franz Lisp was probably the most widely distributed and used Lisp system of the 1970s and 1980s.

Friedrich Ludwig "Fritz" Bauer was a German pioneer of computer science and professor at the Technical University of Munich.
Jean E. Sammet was an American computer scientist who developed the FORMAC programming language in 1962. She was also one of the developers of the influential COBOL programming language.
Symbolic Manipulation Program, usually called SMP, was a computer algebra system designed by Chris A. Cole and Stephen Wolfram at Caltech circa 1979. It was initially developed in the Caltech physics department with contributions from Geoffrey C. Fox, Jeffrey M. Greif, Eric D. Mjolsness, Larry J. Romans, Timothy Shaw, and Anthony E. Terrano.
John Vivian Tucker is a British computer scientist and expert on computability theory, also known as recursion theory. Computability theory is about what can and cannot be computed by people and machines. His work has focused on generalising the classical theory to deal with all forms of discrete/digital and continuous/analogue data; and on using the generalisations as formal methods for system design; based on abstract data types and on the interface between algorithms and physical equipment.
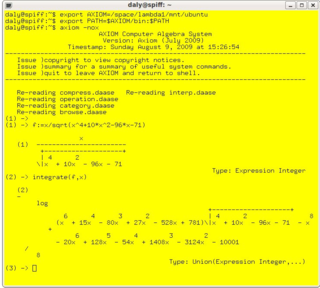
In mathematics and computer science, computer algebra, also called symbolic computation or algebraic computation, is a scientific area that refers to the study and development of algorithms and software for manipulating mathematical expressions and other mathematical objects. Although computer algebra could be considered a subfield of scientific computing, they are generally considered as distinct fields because scientific computing is usually based on numerical computation with approximate floating point numbers, while symbolic computation emphasizes exact computation with expressions containing variables that have no given value and are manipulated as symbols.

James Weldon Demmel Jr. is an American mathematician and computer scientist, the Dr. Richard Carl Dehmel Distinguished Professor of Mathematics and Computer Science at the University of California, Berkeley.












