Related Research Articles
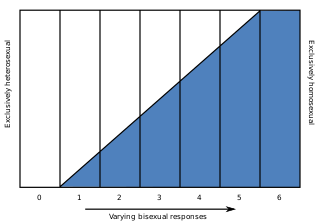
The Kinsey scale, also called the Heterosexual–Homosexual Rating Scale, is used in research to describe a person's sexual orientation based on one's experience or response at a given time. The scale typically ranges from 0, meaning exclusively heterosexual, to a 6, meaning exclusively homosexual. In both the male and female volumes of the Kinsey Reports, an additional grade, listed as "X", indicated "no socio-sexual contacts or reactions" (asexuality). The reports were first published in Sexual Behavior in the Human Male (1948) by Alfred Kinsey, Wardell Pomeroy, and others, and were also prominent in the complementary work Sexual Behavior in the Human Female (1953).

Biphobia is aversion toward bisexuality or people who are identified or perceived as being bisexual. Similarly to homophobia, it refers to hatred and prejudice specifically against those identified or perceived as being in the bisexual community. It can take the form of denial that bisexuality is a genuine sexual orientation, or of negative stereotypes about people who are bisexual. Other forms of biphobia include bisexual erasure. Biphobia may also avert towards other sexualities attracted to multiple genders such as pansexuality or polysexuality, as the idea of being attracted to multiple genders is generally the cause of stigma towards bisexuality.
Heterosexism is a system of attitudes, bias, and discrimination in favor of heterosexuality and heterosexual relationships. According to Elizabeth Cramer, it can include the belief that all people are or should be heterosexual and that heterosexual relationships are the only norm and therefore superior.

The field of psychology has extensively studied homosexuality as a human sexual orientation. The American Psychiatric Association listed homosexuality in the DSM-I in 1952 as a "sociopathic personality disturbance," but that classification came under scrutiny in research funded by the National Institute of Mental Health. That research and subsequent studies consistently failed to produce any empirical or scientific basis for regarding homosexuality as anything other than a natural and normal sexual orientation that is a healthy and positive expression of human sexuality. As a result of this scientific research, the American Psychiatric Association removed homosexuality from the DSM-II in 1973. Upon a thorough review of the scientific data, the American Psychological Association followed in 1975 and also called on all mental health professionals to take the lead in "removing the stigma of mental illness that has long been associated" with homosexuality. In 1993, the National Association of Social Workers adopted the same position as the American Psychiatric Association and the American Psychological Association, in recognition of scientific evidence. The World Health Organization, which listed homosexuality in the ICD-9 in 1977, removed homosexuality from the ICD-10 which was endorsed by the 43rd World Health Assembly on 17 May 1990.

Societal attitudes toward homosexuality vary greatly across different cultures and historical periods, as do attitudes toward sexual desire, activity and relationships in general. All cultures have their own values regarding appropriate and inappropriate sexuality; some sanction same-sex love and sexuality, while others may disapprove of such activities in part. As with heterosexual behaviour, different sets of prescriptions and proscriptions may be given to individuals according to their gender, age, social status or social class.

Latent homosexuality is an erotic attraction toward members of the same sex that is not consciously experienced or expressed in overt action. This may mean a hidden inclination or potential for interest in homosexual relationships, which is either suppressed or not recognized, and which has not yet been explored, or may never be explored.

LGBTQ stereotypes are stereotypes about lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people based on their sexual orientations, gender identities, or gender expressions. Stereotypical perceptions may be acquired through interactions with parents, teachers, peers and mass media, or, more generally, through a lack of firsthand familiarity, resulting in an increased reliance on generalizations.

Homophobia encompasses a range of negative attitudes and feelings toward homosexuality or people who identify or are perceived as being lesbian, gay or bisexual. It has been defined as contempt, prejudice, aversion, hatred, or antipathy, may be based on irrational fear and may sometimes be attributed to religious beliefs. Homophobia is observable in critical and hostile behavior such as discrimination and violence on the basis of sexual orientations that are non-heterosexual.

Homosexuality is sexual attraction, romantic attraction, or sexual behavior between members of the same sex or gender. As a sexual orientation, homosexuality is "an enduring pattern of emotional, romantic, and/or sexual attractions" exclusively to people of the same sex or gender. It "also refers to a person's sense of identity based on those attractions, related behaviors, and membership in a community of others who share those attractions."
The Cass identity model is one of the fundamental theories of LGBT identity development, developed in 1979 by Vivienne Cass. This model was one of the first to treat LGBT people as normal in a heterosexist society and in a climate of homophobia and biphobia instead of treating homosexuality and bisexuality themselves as a problem. Cass described a process of six stages of LGBT identity development. While these stages are sequential, some people might revisit stages at different points in their lives.

The questioning of one's sexual orientation, sexual identity, gender, or all three is a process of exploration by people who may be unsure, still exploring, or concerned about applying a social label to themselves for various reasons. The letter "Q" is sometimes added to the end of the acronym LGBT ; the "Q" can refer to either queer or questioning.

Bisexuality is a romantic or sexual attraction or behavior toward both males and females, to more than one gender, or to both people of the same gender and different genders. It may also be defined to include romantic or sexual attraction to people regardless of their sex or gender identity, which is also known as pansexuality.

LGBTQ sex education is a sex education program within a school, university, or community center that addresses the sexual health needs of LGBTQ people.

Dorothy Riddle is an American-Canadian psychologist, feminist and economic development specialist. She is known as the author of the Riddle homophobia scale and published work on women's studies, homophobia, services and metaphysics.

Sexual stigma is a form of social stigma against people who are perceived to be non-heterosexual because of their beliefs, identities or behaviors. Privileged individuals, or the majority group members, are the main contributors of placing sexual stigmas on individuals and their minority group. It is those who hold a higher status that determine within a society which groups are deemed unworthy of a higher status by labeling their specific actions or beliefs. Stereotypes are then produced which further the debilitating effects of the label(s) placed on group members with non-heterosexual beliefs or practices.

Historically speaking, lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer (LGBTQ) people have not been given equal treatment and rights by both governmental actions and society's general opinion. Much of the intolerance for LGBTQ individuals come from lack of education around the LGBTQ community, and contributes to the stigma that results in same-sex marriage being legal in few countries (31) and persistence of discrimination, such as in the workplace.

Discrimination against gay men, sometimes called gayphobia, is a form of homophobic prejudice, hatred, or bias specifically directed toward gay men, male homosexuality, or men who are perceived to be gay. This discrimination is closely related to femmephobia, which is the dislike of, or hostility toward, individuals who present as feminine, including gay and effeminate men.

The following outline offers an overview and guide to LGBTQ topics:
Homophobia in ethnic minority communities is any negative prejudice or form of discrimination in ethnic minority communities worldwide towards people who identify as–or are perceived as being–lesbian, gay, bisexual or transgender (LGBT), known as homophobia. This may be expressed as antipathy, contempt, prejudice, aversion, hatred, irrational fear, and is sometimes related to religious beliefs. A 2006 study by the Joseph Rowntree Foundation in the UK found that while religion can have a positive function in many LGB Black and Minority Ethnic (BME) communities, it can also play a role in supporting homophobia.
References
- ↑ Staten Island LGBT history Staten Island LGBT Community Center, Accessed Dec. 19, 2010.
- ↑ Riddle, D. I. (1985). Homophobia scale. Opening doors to understanding and acceptance: A facilitator’s guide for presenting workshops on lesbian and gay issues, Workshop organized by Kathy Obear and Amy Reynolds, Boston. Unpublished essay.
- ↑ Riddle, D., (1994). The Riddle scale. Alone no more: Developing a school support system for gay, lesbian and bisexual youth. St Paul: Minnesota State Department.
- ↑ Peterkin, A. Risdon, C., (2003). Caring for lesbian and gay people: A clinical guide. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, Inc.
- ↑ Clauss-Ehlers, C. S. (ed), (2010). Encyclopedia of Cross-Cultural School Psychology. New York: Springer.
- ↑ Blumenfeld W. J. (2000). How homophobia hurts everyone. Readings for diversity and social justice. New York: Routledge, 267–275.
- ↑ Ollis, D., (2004). I’m just a home economics teacher. Does discipline background impact on teachers’ ability to affirm and include gender and sexual diversity in secondary school health education programs? AARE Conference, Melbourne 2004
- ↑ Hirscheld, S., (2001). Moving beyond the safety zone: A staff development approach to anti-heterosexist education. Fordham Urban Law Journal, 29, 611–641.
- ↑ Finkel, M. J., Storaasli, R. D., Bandele, A., and Schaefer, V., (2003). Diversity training in graduate school: An exploratory evaluation of the safe zone project. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 34, 555–561.
- ↑ Tucker, E. W, and Potocky-Tripodi, M., (2006). Changing heterosexuals' attitudes toward homosexuals: A systematic review of the empirical literature. Research on Social Work Practice, 16 (2), 176–190.