Related Research Articles

Linear programming (LP), also called linear optimization, is a method to achieve the best outcome in a mathematical model whose requirements are represented by linear relationships. Linear programming is a special case of mathematical programming.
In mathematical optimization, Dantzig's simplex algorithm is a popular algorithm for linear programming.
In mathematical optimization theory, the linear complementarity problem (LCP) arises frequently in computational mechanics and encompasses the well-known quadratic programming as a special case. It was proposed by Cottle and Dantzig in 1968.
Samuel Standfield Wagstaff Jr. is an American mathematician and computer scientist, whose research interests are in the areas of cryptography, parallel computation, and analysis of algorithms, especially number theoretic algorithms. He is currently a professor of computer science and mathematics at Purdue University who coordinates the Cunningham project, a project to factor numbers of the form bn ± 1, since 1983. He has authored/coauthored over 50 research papers and four books. He has an Erdős number of 1.

Jack R. Edmonds is an American-born and educated computer scientist and mathematician who lived and worked in Canada for much of his life. He has made fundamental contributions to the fields of combinatorial optimization, polyhedral combinatorics, discrete mathematics and the theory of computing. He was the recipient of the 1985 John von Neumann Theory Prize.
Charles Francis Van Loan is an emeritus professor of computer science and the Joseph C. Ford Professor of Engineering at Cornell University, He is known for his expertise in numerical analysis, especially matrix computations.
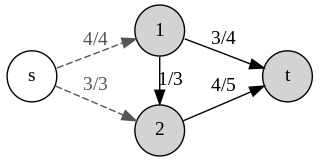
In mathematical optimization, Bland's rule is an algorithmic refinement of the simplex method for linear optimization.
An oriented matroid is a mathematical structure that abstracts the properties of directed graphs, vector arrangements over ordered fields, and hyperplane arrangements over ordered fields. In comparison, an ordinary matroid abstracts the dependence properties that are common both to graphs, which are not necessarily directed, and to arrangements of vectors over fields, which are not necessarily ordered.
Eugene Leighton (Gene) Lawler was an American computer scientist and a professor of computer science at the University of California, Berkeley.

In mathematical optimization, the criss-cross algorithm is any of a family of algorithms for linear programming. Variants of the criss-cross algorithm also solve more general problems with linear inequality constraints and nonlinear objective functions; there are criss-cross algorithms for linear-fractional programming problems, quadratic-programming problems, and linear complementarity problems.

The Klee–Minty cube or Klee–Minty polytope is a unit hypercube of variable dimension whose corners have been perturbed. Klee and Minty demonstrated that George Dantzig's simplex algorithm has poor worst-case performance when initialized at one corner of their "squashed cube". On the three-dimensional version, the simplex algorithm and the criss-cross algorithm visit all 8 corners in the worst case.
Jon Lee is an American mathematician and operations researcher, the G. Lawton and Louise G. Johnson Professor of Engineering at the University of Michigan. He is known for his research in nonlinear discrete optimization and combinatorial optimization.
Michel Las Vergnas was a French mathematician associated with Pierre-and-Marie-Curie University in Paris, and a research director emeritus at the Centre national de la recherche scientifique.

Michel Louis Balinski was an American and French applied mathematician, economist, operations research analyst and political scientist. Educated in the United States, from 1980 he lived and worked in France. He was known for his work in optimisation, convex polyhedra, stable matching, and the theory and practice of electoral systems, jury decision, and social choice. He was Directeur de Recherche de classe exceptionnelle (emeritus) of the C.N.R.S. at the École Polytechnique (Paris). He was awarded the John von Neumann Theory Prize by INFORMS in 2013.
Carolyn Ray Boone Mahoney is an American mathematician who served as president of Lincoln University of Missouri. Her research interests include combinatorics, graph theory, and matroids.

Robert E. Bixby is an American mathematician, the Noah Harding Professor Emeritus of Computational and Applied Mathematics at Rice University.
Donald Goldfarb is an American mathematician, best known for his works in mathematical optimization and numerical analysis.

Tamás Terlaky is a Hungarian-Canadian-American professor of Industrial and Systems Engineering at Lehigh University. He is especially well known for his work on criss-cross algorithms, interior-point methods, Klee-Minty examples for path following algorithms, and optimization.
Komei Fukuda is a Japanese mathematician known for his contributions to optimization, polyhedral computation and oriented matroid theory. Fukuda is a professor in optimization and computational geometry in the Department of Mathematics and in the Institute of Theoretical Computer Science at ETH Zurich.
George James Minty Jr. was an American mathematician, specializing in mathematical analysis and discrete mathematics. He is known for the Klee–Minty cube, the Browder–Minty theorem, and the Minty-Vitaver theorem on graph coloring.
References
- 1 2 3 Faculty profile, Cornell University, retrieved 2012-02-25.
- ↑ American men and women of science: 1989-1990 : A biographical directory of today's leaders in physical, biological and related sciences. 1989. ISBN 9780835225694.
- ↑ Robert Gary Bland at the Mathematics Genealogy Project
- ↑ Björner, Anders (1999), Oriented Matroids, Encyclopedia of Mathematics and Its Applications, vol. 46, Cambridge University, ISBN 978-0-521-77750-6 . Page 150: "It seems fair to say that the major credit for the origination of oriented matroid theory should be shared by Robert Bland, Jon Folkman, Michel Las Vergnas, and Jim Lawrence." This authoritative reference on oriented matroids discusses Bland's pivoting-rule on page 418.
- ↑ Bland, Robert G. (May 1977). "New finite pivoting rules for the simplex method". Mathematics of Operations Research . 2 (2): 103–107. doi:10.1287/moor.2.2.103. JSTOR 3689647. MR 0459599. S2CID 18493293.