
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties.

An optical prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that refract light. At least one surface must be angled—elements with two parallel surfaces are not prisms. The traditional geometrical shape of an optical prism is that of a triangular prism with a triangular base and rectangular sides, and in colloquial use "prism" usually refers to this type. Some types of optical prism are not in fact in the shape of geometric prisms. Prisms can be made from any material that is transparent to the wavelengths for which they are designed. Typical materials include glass, plastic, and fluorite.
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties.

A Dove prism is a type of reflective prism which is used to invert an image. Dove prisms are shaped from a truncated right-angle prism. The Dove prism is named for its inventor, Heinrich Wilhelm Dove.

A Wollaston prism is an optical device, invented by William Hyde Wollaston, that manipulates polarized light. It separates light into two separate linearly polarized outgoing beams with orthogonal polarization. The two beams will be polarized according to the optical axis of the two right angle prisms.

Polarimetry is the measurement and interpretation of the polarization of transverse waves, most notably electromagnetic waves, such as radio or light waves. Typically polarimetry is done on electromagnetic waves that have traveled through or have been reflected, refracted or diffracted by some material in order to characterize that object.
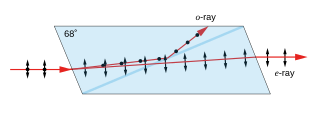
A Nicol prism is a type of polarizer, an optical device made from calcite crystal used to produce and analyse plane polarized light. It is made in such a way that it eliminates one of the rays by total internal reflection, i.e. the ordinary ray is eliminated and only the extraordinary ray is transmitted through the prism. It was the first type of polarizing prism, invented in 1828 by William Nicol (1770–1851) of Edinburgh. It consists of a rhombohedral crystal of Iceland spar that has been cut at an angle of 68° with respect to the crystal axis, cut again diagonally, and then rejoined as shown, using a layer of transparent Canada balsam as a glue.

A polarizer or polariser is an optical filter that lets light waves of a specific polarization pass through while blocking light waves of other polarizations. It can filter a beam of light of undefined or mixed polarization into a beam of well-defined polarization, that is polarized light. The common types of polarizers are linear polarizers and circular polarizers. Polarizers are used in many optical techniques and instruments, and polarizing filters find applications in photography and LCD technology. Polarizers can also be made for other types of electromagnetic waves besides visible light, such as radio waves, microwaves, and X-rays.

A Glan–Thompson prism is a type of polarizing prism similar to the Nicol and Glan–Foucault prisms.

A Glan–Foucault prism is a type of prism which is used as a polarizer. It is similar in construction to a Glan–Thompson prism, except that two right-angled calcite prisms are spaced with an air gap instead of being cemented together. Total internal reflection of p-polarized light at the air gap means that only s-polarized light is transmitted straight through the prism.

A Glan–Taylor prism is a type of prism which is used as a polarizer or polarizing beam splitter. It is one of the most common types of modern polarizing prism. It was first described by Archard and Taylor in 1948.
Differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy, also known as Nomarski interference contrast (NIC) or Nomarski microscopy, is an optical microscopy technique used to enhance the contrast in unstained, transparent samples. DIC works on the principle of interferometry to gain information about the optical path length of the sample, to see otherwise invisible features. A relatively complex optical system produces an image with the object appearing black to white on a grey background. This image is similar to that obtained by phase contrast microscopy but without the bright diffraction halo. The technique was developed by Polish physicist Georges Nomarski in 1952.

A Nomarski prism is a modification of the Wollaston prism that is used in differential interference contrast microscopy. It is named after its inventor, Polish and naturalized-French physicist Georges Nomarski. Like the Wollaston prism, the Nomarski prism consists of two birefringent crystal wedges cemented together at the hypotenuse. One of the wedges is identical to a conventional Wollaston wedge and has the optical axis oriented parallel to the surface of the prism. The second wedge of the prism is modified by cutting the crystal so that the optical axis is oriented obliquely with respect to the flat surface of the prism. The Nomarski modification causes the light rays to come to a focal point outside the body of the prism, and allows greater flexibility so that when setting up the microscope the prism can be actively focused.

In optics, a dispersive prism is an optical prism, usually having the shape of a geometrical triangular prism, used as a spectroscopic component. Spectral dispersion is the best known property of optical prisms, although not the most frequent purpose of using optical prisms in practice. Triangular prisms are used to disperse light, that is, to separate light into its spectral components. Different wavelengths (colors) of light will be deflected by the prism at different angles, producing a spectrum on a detector. This is a result of the prism's material index of refraction varying with wavelength. By application of Snell's law, one can see that as the wavelength changes, and the refractive index changes, the deflection angle of a light beam will change, separating the colors of the light spatially. Generally, longer wavelengths (red) thereby undergo a smaller deviation than shorter wavelengths (blue) where the refractive index is larger.
The wedge prism is a prism with a shallow angle between its input and output surfaces. This angle is usually 3 degrees or less. Refraction at the surfaces causes the prism to deflect light by a fixed angle. When viewing a scene through such a prism, objects will appear to be offset by an amount that varies with their distance from the prism.

The Sénarmont prism is a type of polariser. It is made from two prisms of a birefringent material such as calcite, usually cemented together. The Sénarmont prism is named after Henri Hureau de Sénarmont. It is similar to the Rochon and Wollaston prisms.

Alexis-Marie de Rochon, known as Abbé Rochon, was born in Brest, France on 21 February 1741, and died in Paris on 5 April 1817. He was a French astronomer, physicist and traveller. He worked on lens design and crystal optics, inventing the Rochon prism polariser.
Beam expanders are optical devices that take a collimated beam of light and expand its size.
A Compound refractive lens (CRL) is a series of individual lenses arranged in a linear array in order to achieve focusing of X-rays in the energy range of 5-40 keV. They are an alternative to the KB mirror.














