
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye. There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy, along with the emerging field of X-ray microscopy.

The optical microscope, also referred to as a light microscope, is a type of microscope that commonly uses visible light and a system of lenses to generate magnified images of small objects. Optical microscopes are the oldest design of microscope and were possibly invented in their present compound form in the 17th century. Basic optical microscopes can be very simple, although many complex designs aim to improve resolution and sample contrast.
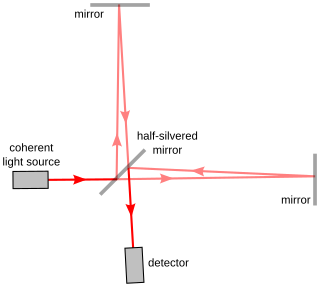
Interferometry is a technique in which waves are superimposed to cause the phenomenon of interference, which is used to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber optics, engineering metrology, optical metrology, oceanography, seismology, spectroscopy, quantum mechanics, nuclear and particle physics, plasma physics, remote sensing, biomolecular interactions, surface profiling, microfluidics, mechanical stress/strain measurement, velocimetry, optometry, and making holograms.

Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. These optically anisotropic materials are said to be birefringent. The birefringence is often quantified as the maximum difference between refractive indices exhibited by the material. Crystals with non-cubic crystal structures are often birefringent, as are plastics under mechanical stress.

An optical prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that refract light. At least one surface must be angled—elements with two parallel surfaces are not prisms. The traditional geometrical shape of an optical prism is that of a triangular prism with a triangular base and rectangular sides, and in colloquial use "prism" usually refers to this type. Some types of optical prism are not in fact in the shape of geometric prisms. Prisms can be made from any material that is transparent to the wavelengths for which they are designed. Typical materials include glass, plastic, and fluorite.
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties.
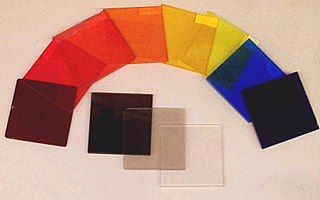
An optical filter is a device that selectively transmits light of different wavelengths, usually implemented as a glass plane or plastic device in the optical path, which are either dyed in the bulk or have interference coatings. The optical properties of filters are completely described by their frequency response, which specifies how the magnitude and phase of each frequency component of an incoming signal is modified by the filter.

A Wollaston prism is an optical device, invented by William Hyde Wollaston, that manipulates polarized light. It separates light into two separate linearly polarized outgoing beams with orthogonal polarization. The two beams will be polarized according to the optical axis of the two right angle prisms.
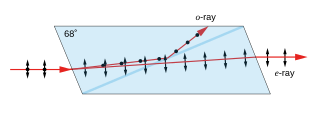
A Nicol prism is a type of polarizer, an optical device made from calcite crystal used to produce and analyse plane polarized light. It is made in such a way that it eliminates one of the rays by total internal reflection, i.e. the ordinary ray is eliminated and only the extraordinary ray is transmitted through the prism. It was the first type of polarizing prism, invented in 1828 by William Nicol (1770–1851) of Edinburgh. It consists of a rhombohedral crystal of Iceland spar that has been cut at an angle of 68° with respect to the crystal axis, cut again diagonally, and then rejoined as shown, using a layer of transparent Canada balsam as a glue.

Metallography is the study of the physical structure and components of metals, by using microscopy.

A polarizer or polariser is an optical filter that lets light waves of a specific polarization pass through while blocking light waves of other polarizations. It can filter a beam of light of undefined or mixed polarization into a beam of well-defined polarization, that is polarized light. The common types of polarizers are linear polarizers and circular polarizers. Polarizers are used in many optical techniques and instruments, and polarizing filters find applications in photography and LCD technology. Polarizers can also be made for other types of electromagnetic waves besides visible light, such as radio waves, microwaves, and X-rays.

A profilometer is a measuring instrument used to measure a surface's profile, in order to quantify its roughness. Critical dimensions as step, curvature, flatness are computed from the surface topography.

Optical mineralogy is the study of minerals and rocks by measuring their optical properties. Most commonly, rock and mineral samples are prepared as thin sections or grain mounts for study in the laboratory with a petrographic microscope. Optical mineralogy is used to identify the mineralogical composition of geological materials in order to help reveal their origin and evolution.
Georges (Jerzy) Nomarski was a Polish and naturalized-French physicist and optics theoretician. Creator of differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy, the method is widely used to study live biological specimens and unstained tissues and in many languages bears his name.
Differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy, also known as Nomarski interference contrast (NIC) or Nomarski microscopy, is an optical microscopy technique used to enhance the contrast in unstained, transparent samples. DIC works on the principle of interferometry to gain information about the optical path length of the sample, to see otherwise invisible features. A relatively complex optical system produces an image with the object appearing black to white on a grey background. This image is similar to that obtained by phase contrast microscopy but without the bright diffraction halo. The technique was developed by Polish physicist Georges Nomarski in 1952.

Phase-contrast microscopy is an optical microscopy technique that converts phase shifts in light passing through a transparent specimen to brightness changes in the image. Phase shifts themselves are invisible, but become visible when shown as brightness variations.

A petrographic microscope is a type of optical microscope used in petrology and optical mineralogy to identify rocks and minerals in thin sections. The microscope is used in optical mineralogy and petrography, a branch of petrology which focuses on detailed descriptions of rocks. The method is called "polarized light microscopy" (PLM).

A Rochon prism is a type of polariser. It is made from two prisms of a birefringent material such as calcite, which are cemented together.
A conoscopic interference pattern or interference figure is a pattern of birefringent colours crossed by dark bands, which can be produced using a geological petrographic microscope for the purposes of mineral identification and investigation of mineral optical and chemical properties. The figures are produced by optical interference when diverging light rays travel through an optically non-isotropic substance - that is, one in which the substance's refractive index varies in different directions within it. The figure can be thought of as a "map" of how the birefringence of a mineral would vary with viewing angle away from perpendicular to the slide, where the central colour is the birefringence seen looking straight down, and the colours further from the centre equivalent to viewing the mineral at ever increasing angles from perpendicular. The dark bands correspond to positions where optical extinction would be seen. In other words, the interference figure presents all possible birefringence colours for the mineral at once.
















