
MIDI is a technical standard that describes a communications protocol, digital interface, and electrical connectors that connect a wide variety of electronic musical instruments, computers, and related audio devices for playing, editing, and recording music.

A sound card is an internal expansion card that provides input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under the control of computer programs. The term sound card is also applied to external audio interfaces used for professional audio applications.
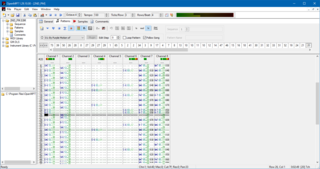
A music tracker is a type of music sequencer software for creating music. The music is represented as discrete musical notes positioned in several channels at chronological positions on a vertical timeline. A music tracker's user interface is traditionally number based. Notes, parameter changes, effects and other commands are entered with the keyboard into a grid of fixed time slots as codes consisting of letters, numbers and hexadecimal digits. Separate patterns have independent timelines; a complete song consists of a master list of repeated patterns.
Digital waveguide synthesis is the synthesis of audio using a digital waveguide. Digital waveguides are efficient computational models for physical media through which acoustic waves propagate. For this reason, digital waveguides constitute a major part of most modern physical modeling synthesizers.

The Roland D-50 is a synthesizer produced by Roland and released in April 1987. Its features include subtractive synthesis, on-board effects, a joystick for data manipulation, and an analogue synthesis-styled layout design. The external Roland PG-1000 (1987–1990) programmer could also be attached to the D-50 for more complex manipulation of its sounds. It was also produced in a rack-mount variant design, the D-550 (1987–1990), with almost 450 user-adjustable parameters.

The Korg Triton is a music workstation synthesizer, featuring digital sampling and sequencing, released in 1999. It uses Korg's HI Synthesis tone generator and was eventually available in several model variants with numerous upgrade options. The Triton became renowned as a benchmark of keyboard technology, and has been widely featured in music videos and live concerts. At the NAMM 2007, Korg announced the Korg M3 as its successor.

Yamaha XG is an extension to the General MIDI standard, created by Yamaha. It is similar in purpose to the Roland GS standard.

The Gravis UltraSound or GUS is a sound card for the IBM PC compatible system platform, made by Canada-based Advanced Gravis Computer Technology Ltd. It was very popular in the demoscene during the 1990s.

The Roland MT-32 Multi-Timbre Sound Module is a MIDI synthesizer module first released in 1987 by Roland Corporation. It was originally marketed to amateur musicians as a budget external synthesizer with an original list price of $695. However, it became more famous along with its compatible modules as an early de facto standard in computer music. Since it was made prior to the release of the General MIDI standard, it uses its own proprietary format for MIDI file playback.

A sound module is an electronic musical instrument without a human-playable interface such as a piano-style musical keyboard. Sound modules have to be operated using an externally connected device, which is often a MIDI controller, of which the most common type is the musical keyboard. Another common way of controlling a sound module is through a sequencer, which is computer hardware or software designed to record and playback control information for sound-generating hardware. Connections between sound modules, controllers, and sequencers are generally made with MIDI, which is a standardized interface designed for this purpose.

The Korg Trinity is a synthesizer music workstation released by Korg in 1995. It was also the first workstation to offer modular expansion for not only sounds, but also studio-grade feature such as ADAT, various sound engine processors, audio recording capability, and more. It was considered one of the most comprehensive music workstations, in term of features, at the time.

The discontinued Roland MC-909 Sampling Groovebox combines the features of a synthesizer, sequencer, and sampler, with extensive hands-on control of both the sound engine and the sequencing flow. It was intended primarily for live performance of pre-programmed patterns consisting of up to 16 tracks of MIDI data. It was released by Roland Corporation on October 8, 2002. This product was announced at the AES Fall Convention in 2002. It is the direct successor to the Roland MC-505 and is the predecessor to the Roland MC-808. Which eventually ended the "Groovebox by year 2010" line of products by Roland which began in the year 1996 with the Original Roland MC-303 groovebox. The Roland Groovebox began again resurgence in the year 2019 with a two new modern & redesign Roland MC-707 GROOVEBOX/Roland MC-101 GROOVEBOX. The Roland MC-909 was developed from the blueprint of Roland's own "Roland Fantom-S Workstation & Roland Fantom-X Workstation" and uses the same structure and operating system, with some differences regarding the Patterns section, not implemented in the Roland Fantom S/X6/X7/X8 Workstation.

The Korg Wavestation is a vector synthesis synthesizer first produced in the early 1990s and later re-released as a software synthesizer in 2004. Its primary innovation was Wave Sequencing, a method of multi-timbral sound generation in which different PCM waveform data are played successively, resulting in continuously evolving sounds. The Wavestation's "Advanced Vector Synthesis" sound architecture resembled early vector synths such as the Sequential Circuits Prophet VS.

Sound Blaster Live! is a PCI add-on sound card from Creative Technology Limited for PCs. Moving from ISA to PCI allowed the card to dispense with onboard memory, storing digital samples in the computer's main memory and then accessing them in real time over the bus. This allowed for a much wider selection of, and longer playing, samples. It also included higher quality sound output at all levels, quadrophonic output, and a new MIDI synthesizer with 64 sampled voices. The Live! was introduced in August 1998 and variations on the design remained Creative's primary sound card line into the early 2000's.

The Sound Blaster 16 is a series of sound cards by Creative Technology. They are add-on boards for PCs with an ISA or PCI slot.

The Roland JD-800 is a digital synthesizer that was manufactured between 1991 and 1996. It features many knobs and sliders for patch editing and performance control — features that some manufacturers, including Roland, had been omitting in the name of streamlining since the inception of the Yamaha DX7. The JD-800 thus became very popular with musicians who wished to take a hands-on approach to patch programming. The introduction in the manual states that Roland's intention with the JD-800 was to "return to the roots of synthesis".

The Roland U-20 is a PCM-sample synthesizer, released by Roland in 1989.It was the keyboard version of the U-220 rack module, which was in turn a similar follow-up product to Roland's U-110 rack module of 1988.

The Roland XP-50 is a music workstation that combines the synthesizer engine of Roland's JV-1080 sound module with the sequencing capabilities of their MRC-Pro sequencer and a 61-note keyboard. First released in 1995, the XP-50 and the Roland XP-10 were the first two Roland XP-series products, later joined by the XP-80 and XP-30.

Yamaha SY77 is a 16 voice multitimbral music workstation first produced by Yamaha Corporation in 1989. The SY77 is a synthesizer whose architecture combines AFM synthesis, AWM2 for ROM-borne sample-based synthesis, and the combination of these two methods christened Realtime Convolution and Modulation Synthesis (RCM). The same technology was also packaged in a rack-mounted module released simultaneously, the TG77.
The Roland JD-990 Super JD is a module version of Roland JD-800 synthesizer with expanded capabilities, which was released in 1993. JD-990 is a multitimbral synthesizer utilizing 'wave-table' sample-based synthesis technology. It is equipped with 6 MB of ROM containing sampled PCM waveforms, four sets of stereo outputs that are assignable to individual, internal, instruments, and standard MIDI in/out/through ports. JD-990 has a large LCD display and programming takes place through a keypad on the front panel of the unit. The unit can generate multi-timbral sounds reminiscent of the vintage analogue synthesizers but is also capable of generation of modern digital textures. There are several expansion boards available for JD-990 that can be installed in the provided expansion slot in the chassis of the unit.

















